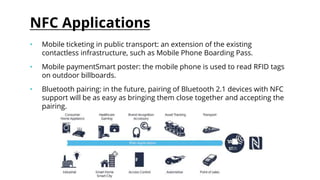
This document provides an overview of Near Field Communication (NFC) technology. It discusses what NFC is, how it evolved and works, its communication modes, uses and applications. Key points made include that NFC allows short-range wireless data exchange between devices within 4 cm, operates at 13.56 MHz, and can be used for mobile payments, ticketing, and Bluetooth pairing. The document also compares NFC to Bluetooth and addresses security issues and the future scope of NFC technology.