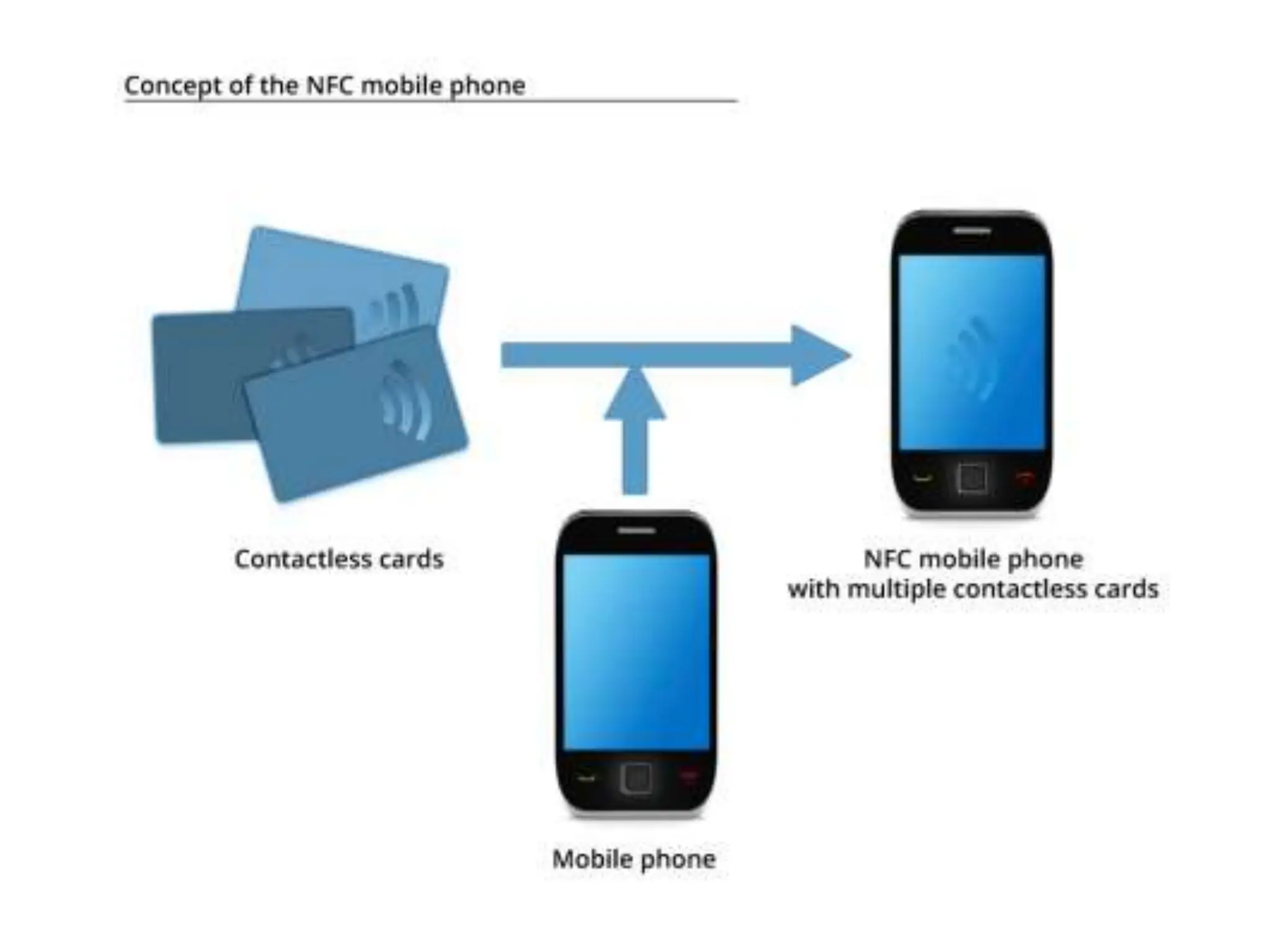
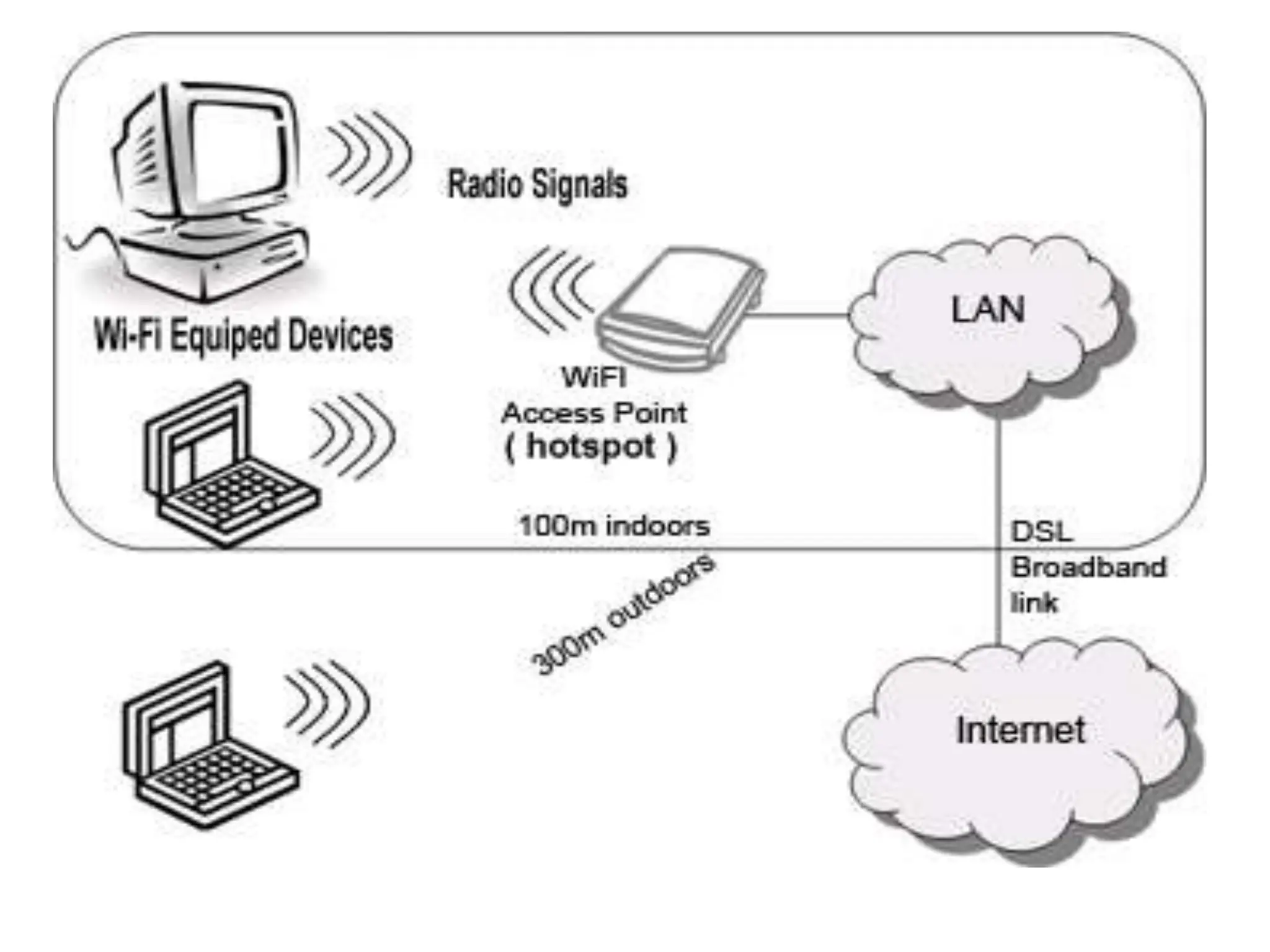
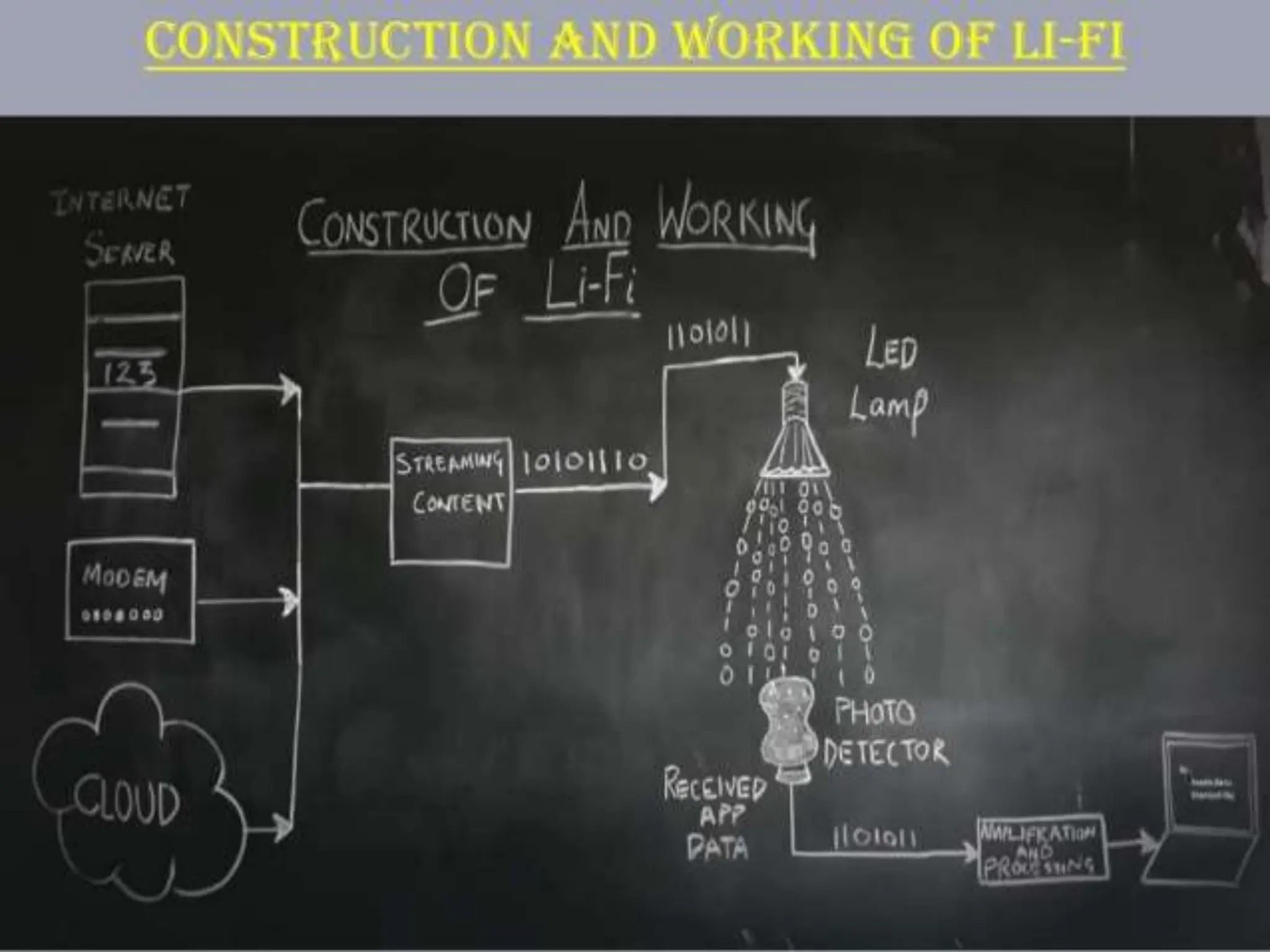
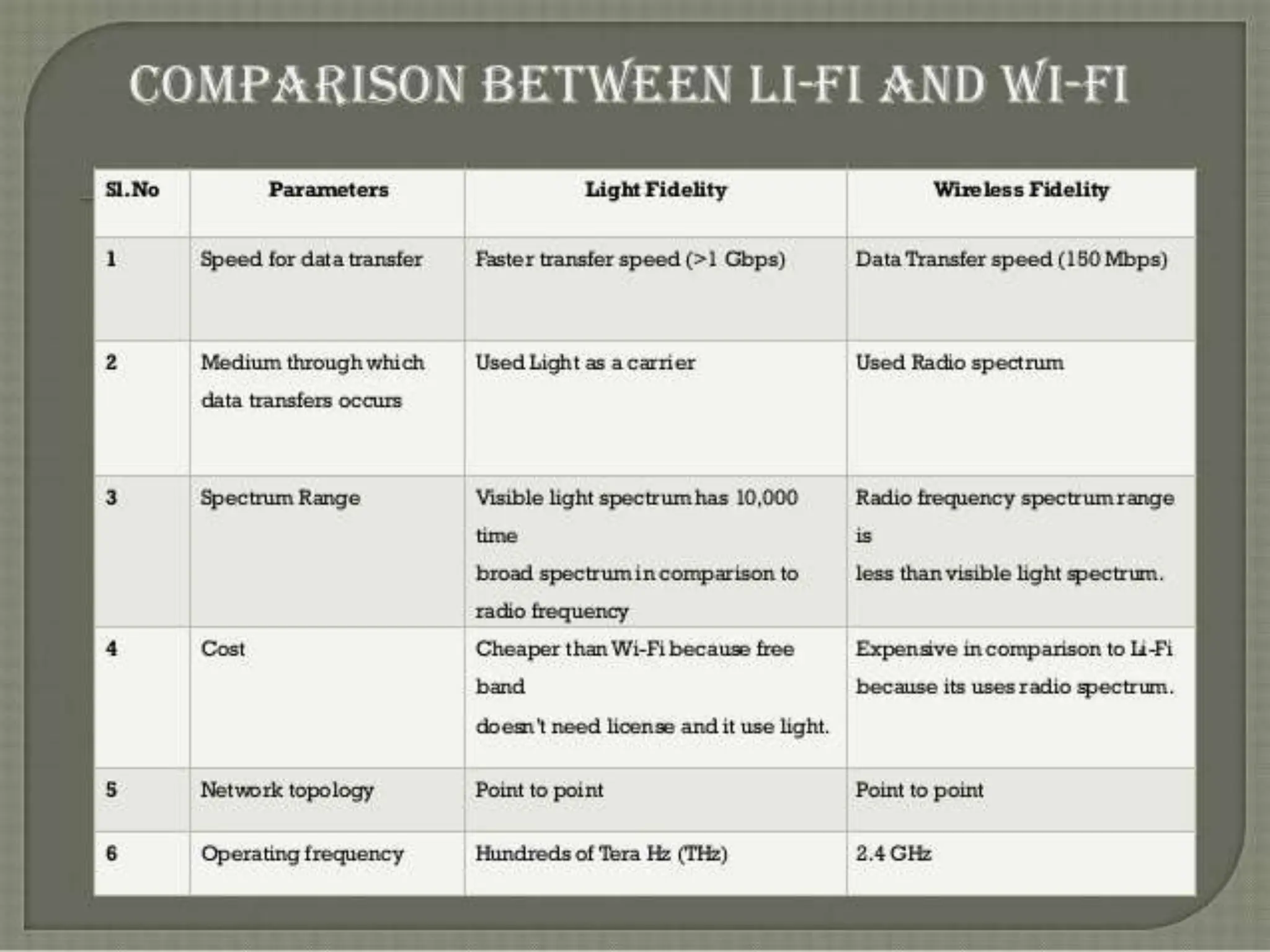
This document provides an overview of wireless communication technologies including Bluetooth, NFC, WiFi, and LiFi. It discusses what each technology is, how it works, common applications, advantages, and disadvantages. Bluetooth allows data transfer between devices using short-range radio links as an alternative to cables. NFC enables data exchange when devices are 10cm or closer by radio waves. WiFi allows internet access on mobile devices within the range of a wireless base station. LiFi is a new technology that transmits data through illumination by varying LED light intensity faster than the eye can detect.