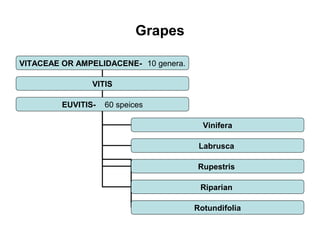
Wine is defined as the fermented juice of freshly gathered grapes. It can only be made from grapes, not other fruits. Wine must be fermented in the district where the grapes originated following local traditions. There are over 5000 grape varieties but only around 50 are commonly used for wine production. The document then describes the history of winemaking, types of wines, important grape varieties like Vitis Vinifera, and the wine production processes of viticulture, vinification, aging, and bottling.