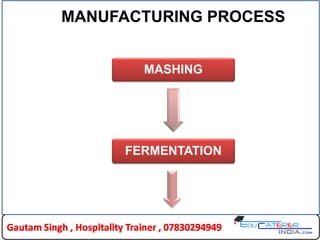
The document provides a comprehensive overview of gin, detailing its definition, history, manufacturing process, types, and popular brands. Gin is a white spirit flavored primarily with juniper berries and various botanicals, with its origins dating back to the late 1580s in Holland. It also describes different varieties of gin, such as American dry, Old Tom, and London dry, along with notable brands like Beefeater and Bombay Sapphire.