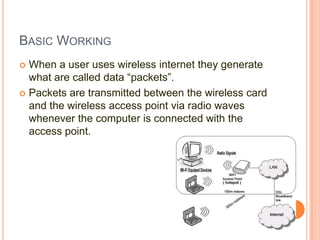
This document provides an overview of wireless hacking and WiFi security. It discusses basic WiFi terms like SSID, BSSID, and MAC addresses. It explains how wireless networks work by transmitting data packets between devices and access points. Common wireless encryption standards like WEP, WPA, and WPA2 are described as well as how they can be cracked. Tools for wireless hacking in Backtrack like Airodump-ng, Aireplay-ng, and Aircrack-ng are introduced along with how they can be used to crack encryption keys through techniques like dictionary attacks and capturing handshakes. The document concludes by stating it is time to start hacking wireless networks.