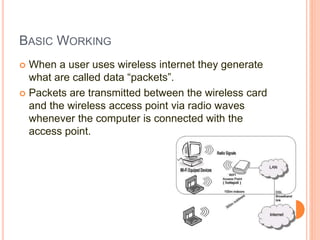
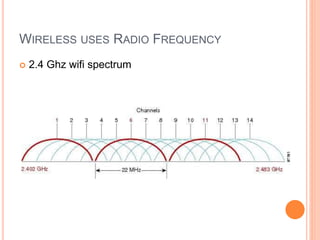
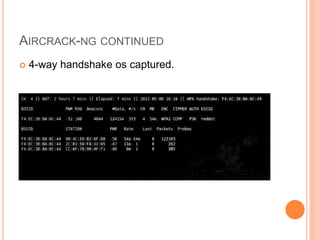
This document discusses WPA exploitation in wireless networks. It begins by explaining basic wireless networking concepts like WiFi, MAC addresses, and SSIDs. It then describes how wireless networks are vulnerable due to weak encryption methods like WEP. The document outlines stronger encryption methods like WPA and WPA2, but notes they can still be cracked with tools if a weak password is used. It proceeds to explain how tools like Aircrack-ng, Reaver, and John the Ripper can be used to crack wireless network encryption keys through techniques like packet sniffing, dictionary attacks, and exploiting WPS pins. In the end, it emphasizes the importance of using long, complex passwords to keep wireless networks secure.















![WORD FIELD
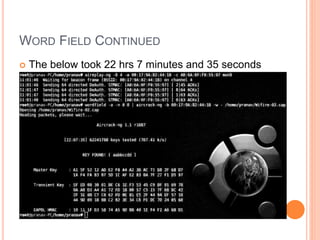
Word Field is a brute force attack.
Command line used wordfield [OPTION...]
MINLENGTH [MAXLENGTH]
Wordfield -a -n 8 8" will output all possible
alphanumeric strings which are 8 characters long.
wordfield -a -n 8 8 | aircrack-ng –b
00:17:9A:82:44:1B -w - /home/pranav/Wifire-
02.cap
This attack is really effective on weak keys.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wifi-140617224344-phpapp01/85/Exploiting-WiFi-Security-23-320.jpg)