This document discusses wireless networking standards and vulnerabilities. It covers:
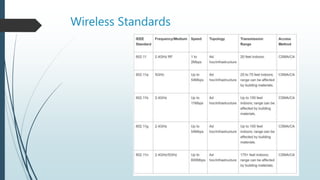
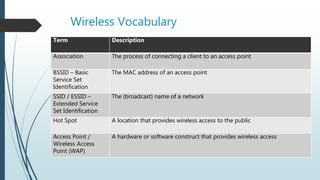
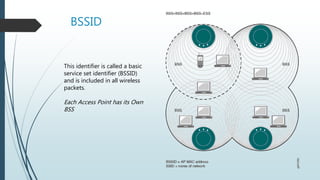
1. Wi-Fi standards including IEEE 802.11, common environments like multiple access points and hotspots, and wireless vocabulary.
2. Vulnerabilities in wireless encryption like WEP and ways to break it by intercepting initialization vectors.
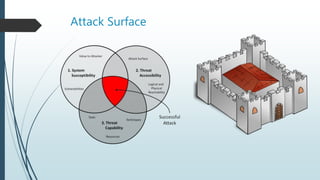
3. Attacks on wireless networks including exploiting weak encryption standards, attacking access points by brute forcing passwords, and compromising endpoints like user laptops broadcasting nearby networks.