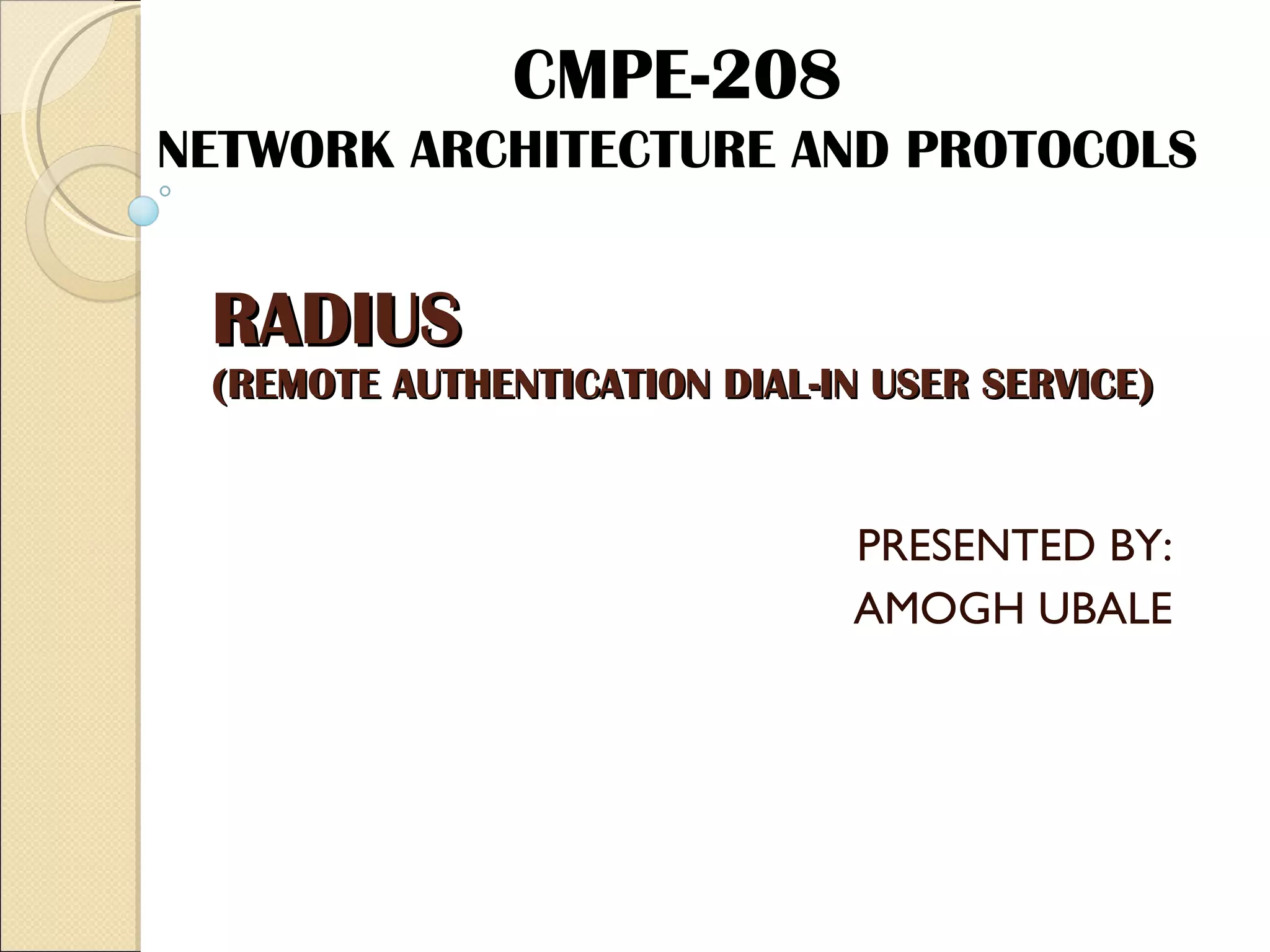
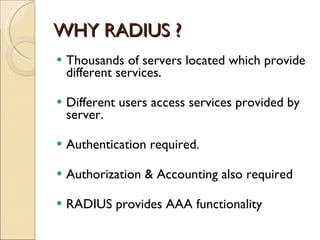
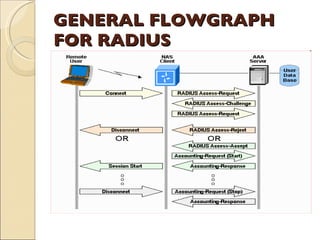
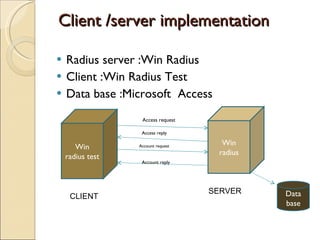
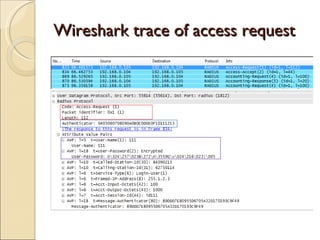
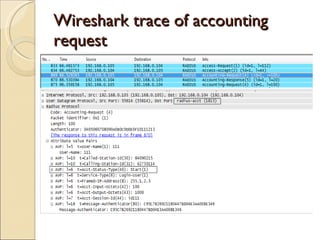
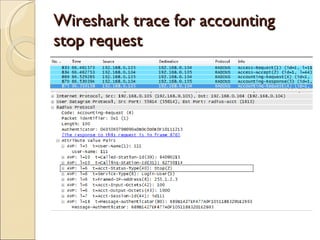
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service) is a protocol that provides authentication, authorization and accounting functionality. It is commonly used for remote access to networks using modems or VPNs. The RADIUS protocol uses UDP and runs on ports 1812 and 1813. It operates on a client-server model where the client is typically a network access server and the server handles authentication requests from clients. RADIUS provides basic security through MD5 hashing of packets and a shared secret between clients and servers. However, it is vulnerable to sniffing and spoofing attacks.















![REFERENCES 1] http://www.faqs.org/rfcs/rfc2865.html 2] BOOK: AAA network security and mobile access radius, diameter, EAP and IP mobility by Madjid Nakhjri and Mahsa Nakhjri 3] BOOK:RADIUS by Johanathan Hassell 4] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RADIUS 5] http://www.itconsult2000.com/en/product/WinRadius.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalppt-124890966094-phpapp02/85/RADIUS-23-320.jpg)
