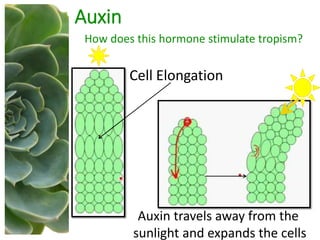
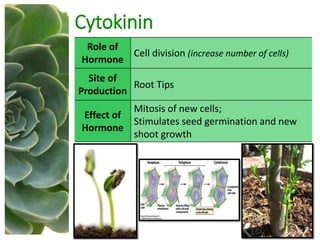
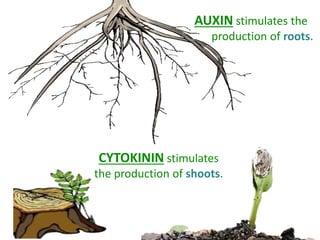
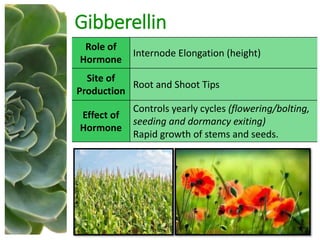
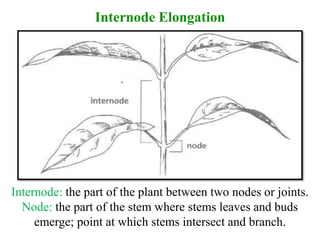
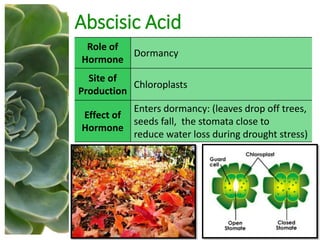
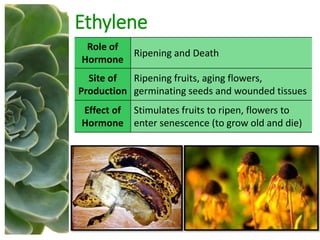
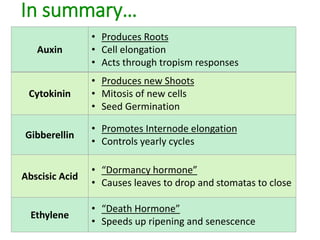
The document outlines the five main types of plant hormones—auxin, cytokinin, gibberellin, abscisic acid, and ethylene—each playing distinct roles in plant growth and development. Auxin promotes cell elongation and root formation; cytokinin stimulates cell division and shoot growth; gibberellin controls height and seasonal cycles; abscisic acid induces dormancy; and ethylene facilitates ripening and aging. The interactions among these hormones influence various growth responses such as tropism and seasonal changes.