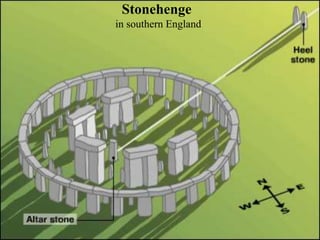
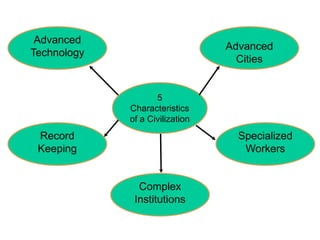
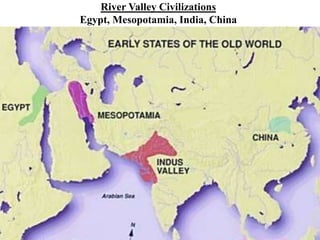
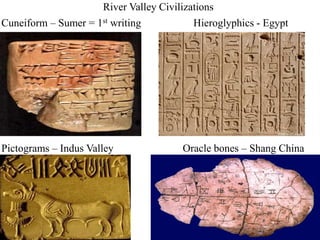
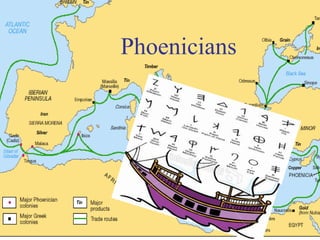
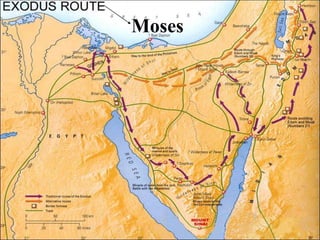
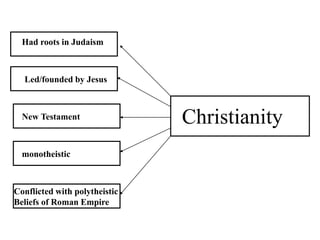
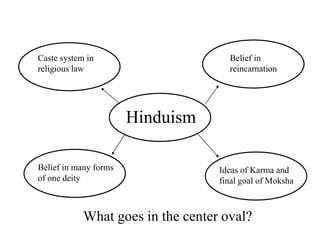
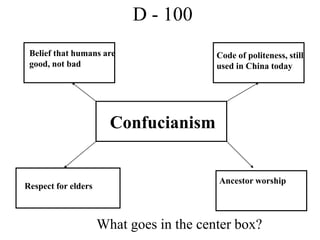
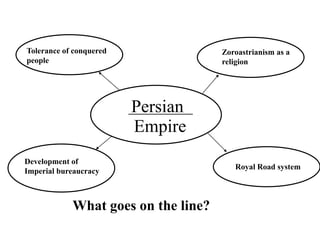
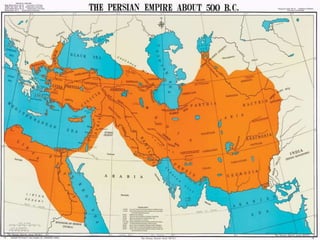
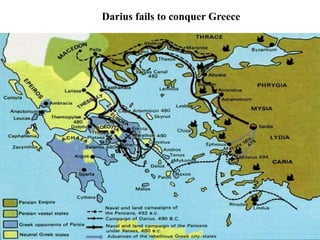
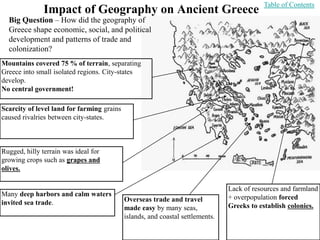
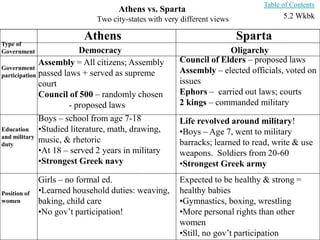
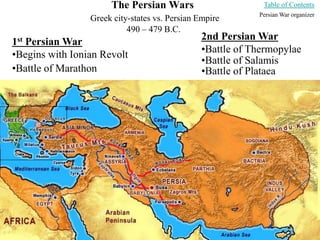
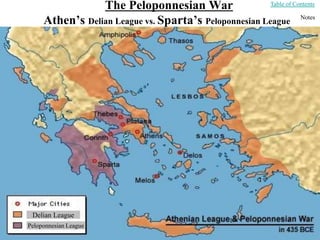
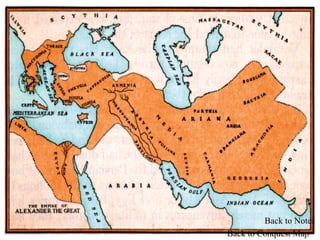
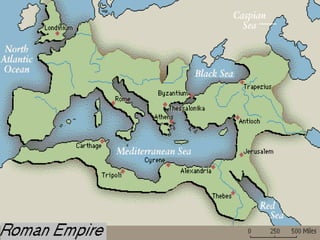
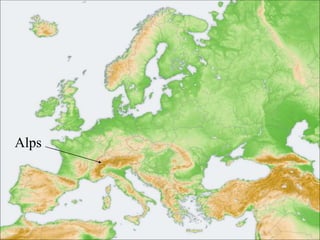
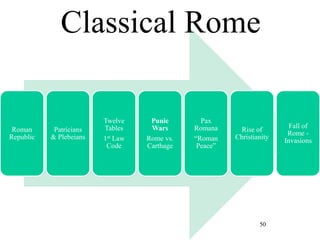
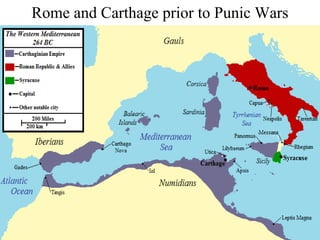
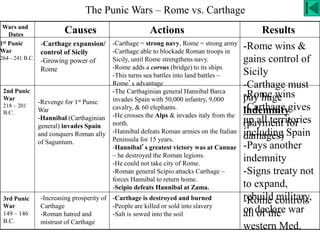
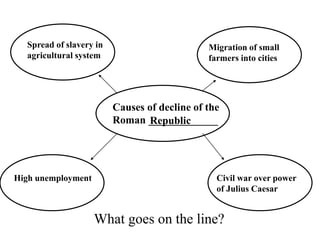
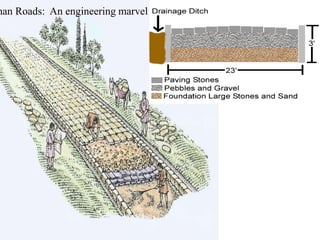
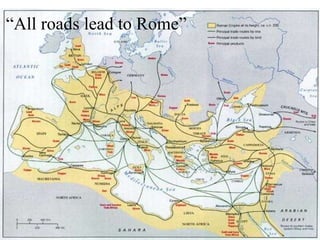
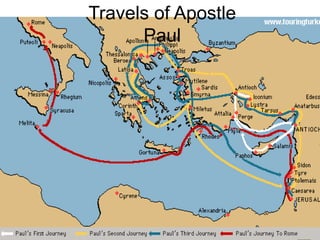
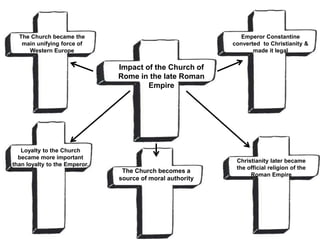
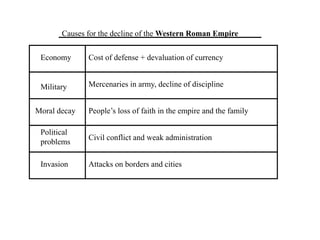
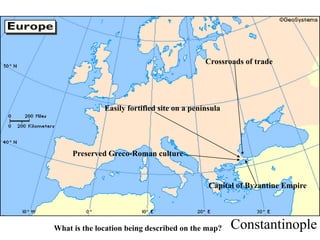
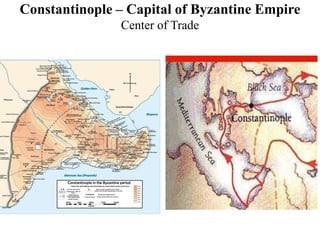
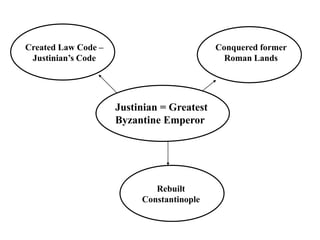
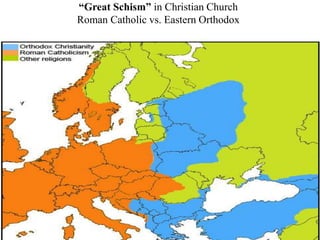
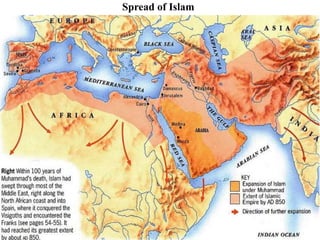
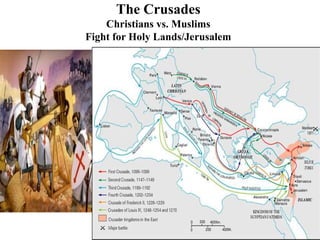
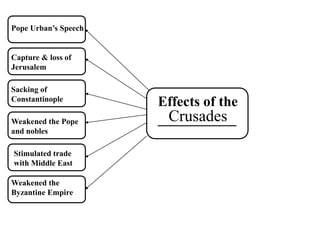
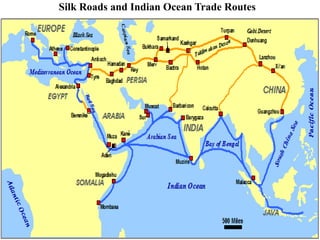
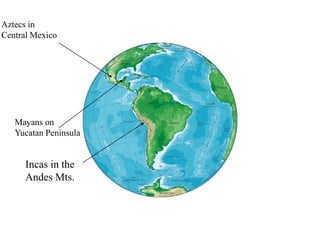
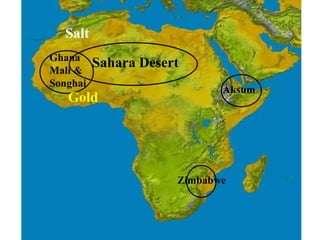
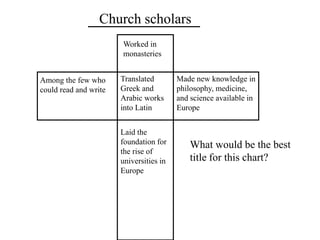
This document provides information about various topics related to early human civilizations and world history. It discusses the Neolithic period in England and the construction of Stonehenge. It also covers the key characteristics of early civilizations, the development of writing systems in Mesopotamia and Egypt, and influential early religions like Judaism, Christianity, Hinduism, Buddhism, Confucianism, and Islam. The document then discusses the classical civilizations of Persia and the major figures of Cyrus the Great and Darius I. It also summarizes the Punic Wars between Rome and Carthage and provides details about the decline of the Roman Republic and rise of Christianity.