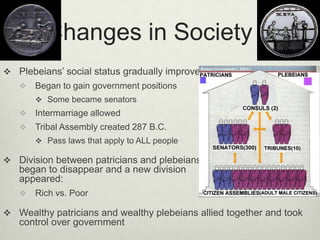
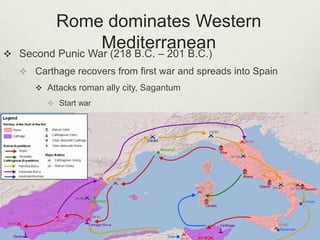
The document provides an overview of the early history and foundations of ancient Rome. It describes how the early Latins settled in northern Italy and eventually moved south, and how the Etruscans and Greeks also colonized parts of Italy. It then discusses the founding of Rome around 753 BC by Romulus and Remus, and the early society structured around patrician and plebeian classes. The early government was a monarchy that later transitioned to a republic with consuls, a senate, and assemblies. Over time the plebeians gained more rights and representation, and Rome expanded its power throughout Italy and engaged in three Punic Wars against Carthage to gain control of the Mediterranean.