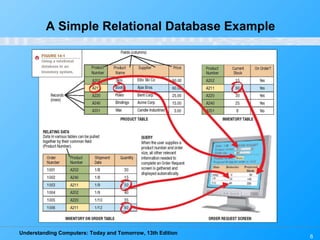
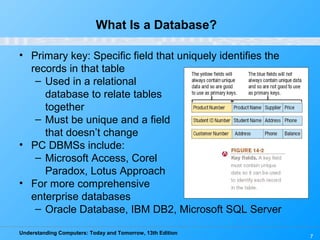
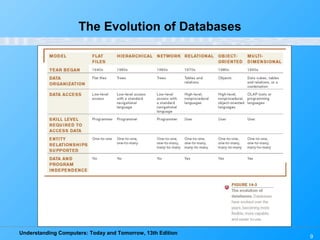
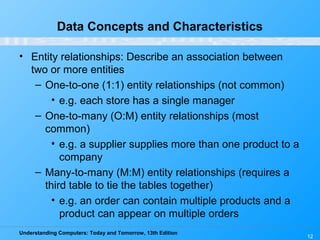
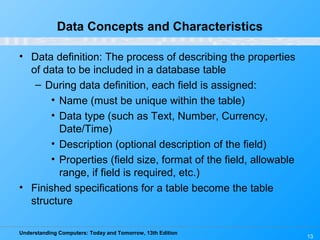
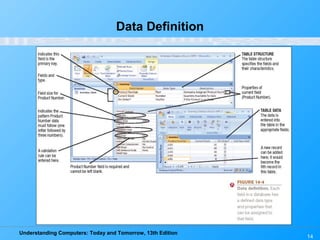
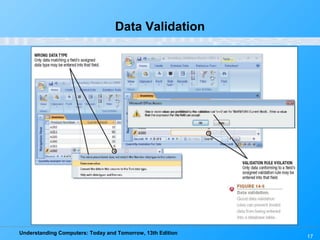
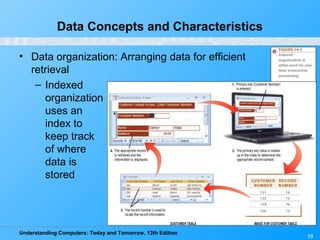
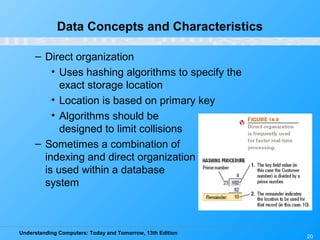
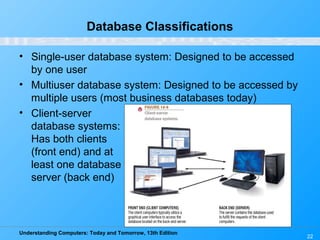
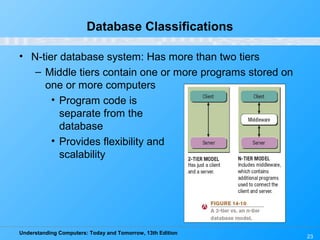
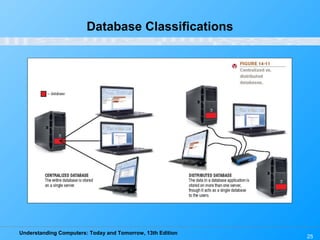
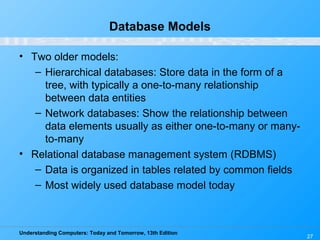
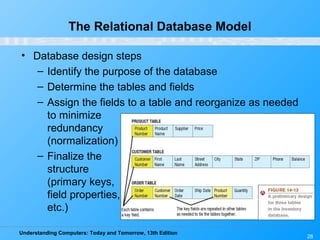
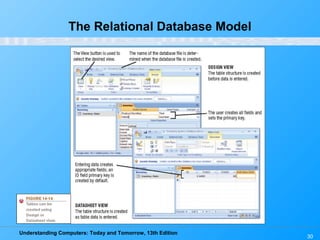
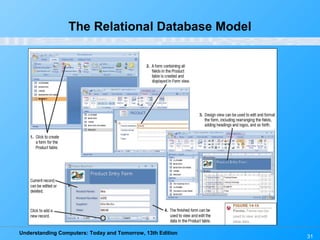
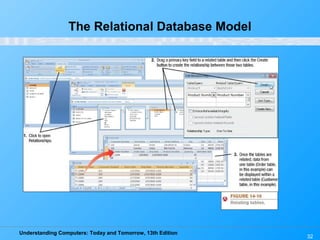
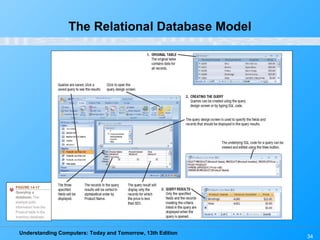
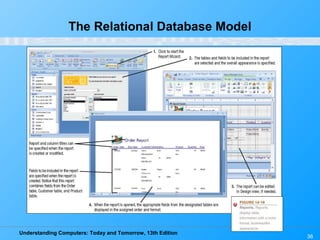
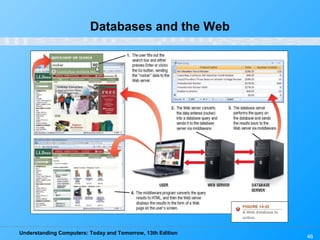
This chapter discusses databases and database management systems. It defines what a database is, including tables, fields, records and keys. It describes important database concepts like data integrity, security and privacy. It also covers different database classifications, models and how databases are commonly used on the web. The relational model is highlighted as the most widely used today for organizing data in tables related by common fields.