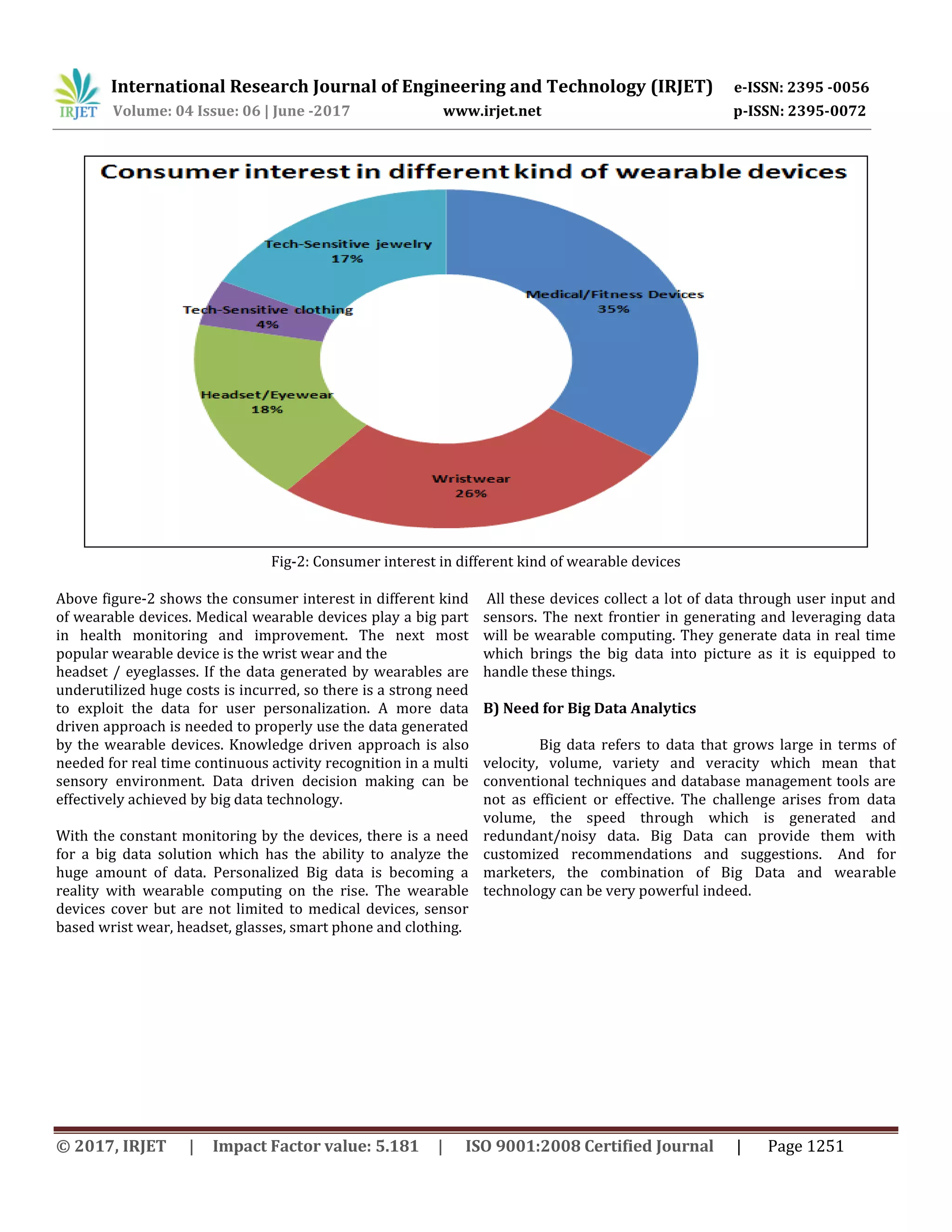
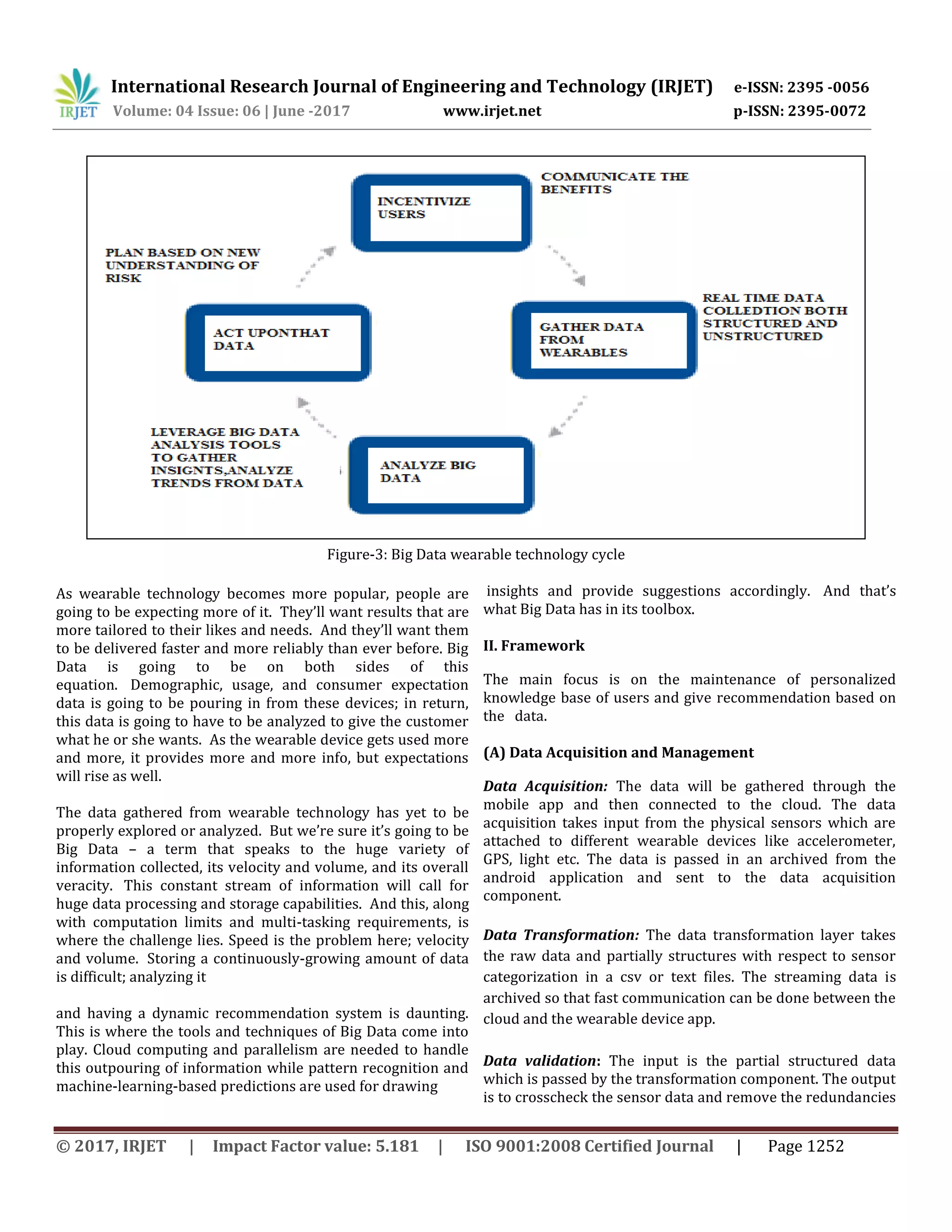
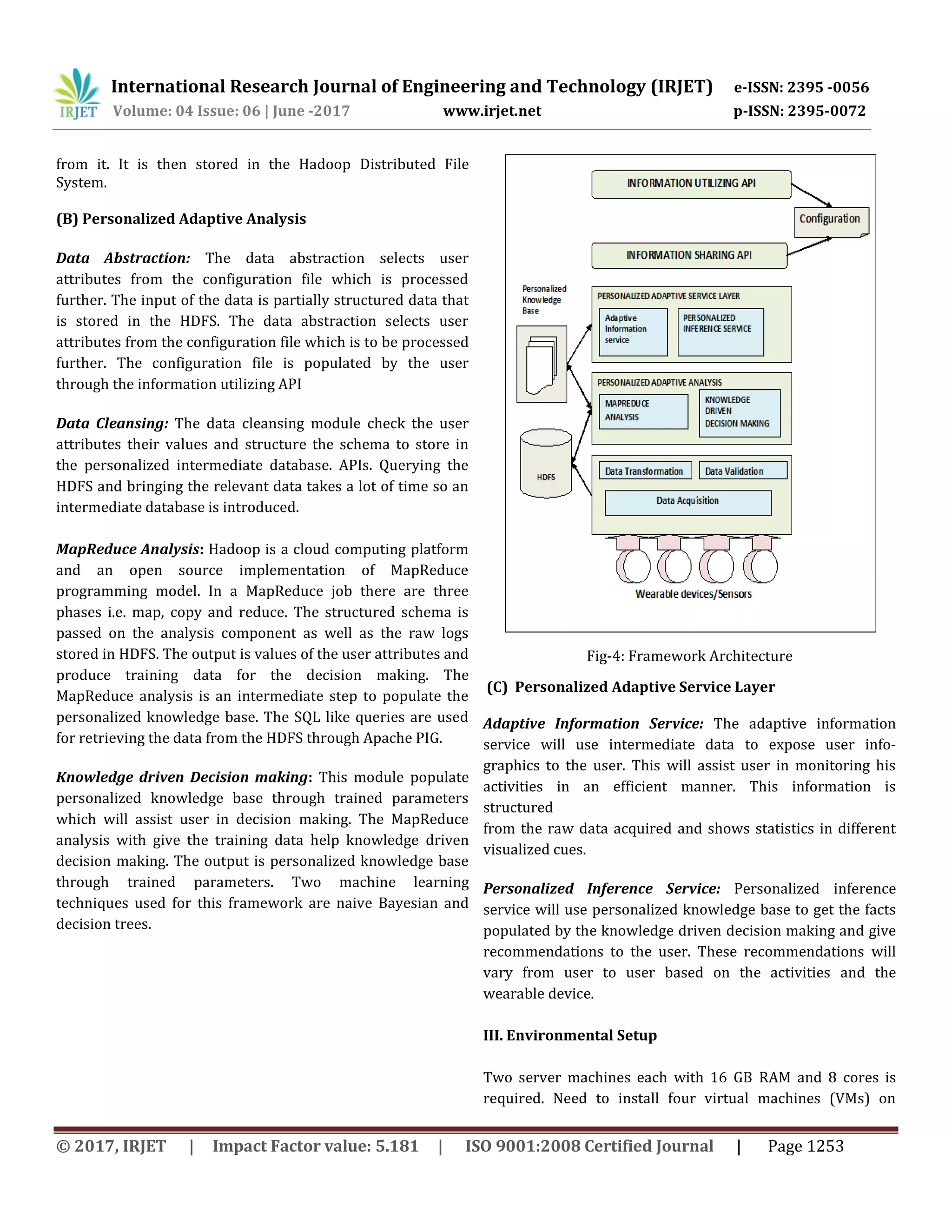
This document discusses using big data analytics on data from wearable devices to improve personalized recommendations and quality of life. It proposes a framework that uses Hadoop and MapReduce to analyze large amounts of data from various wearables. The framework includes data acquisition, processing, and storing in HDFS. It then performs analytics to populate a personalized knowledge base and provide adaptive recommendations. This framework aims to better leverage and analyze the large and growing volumes of data from wearables.