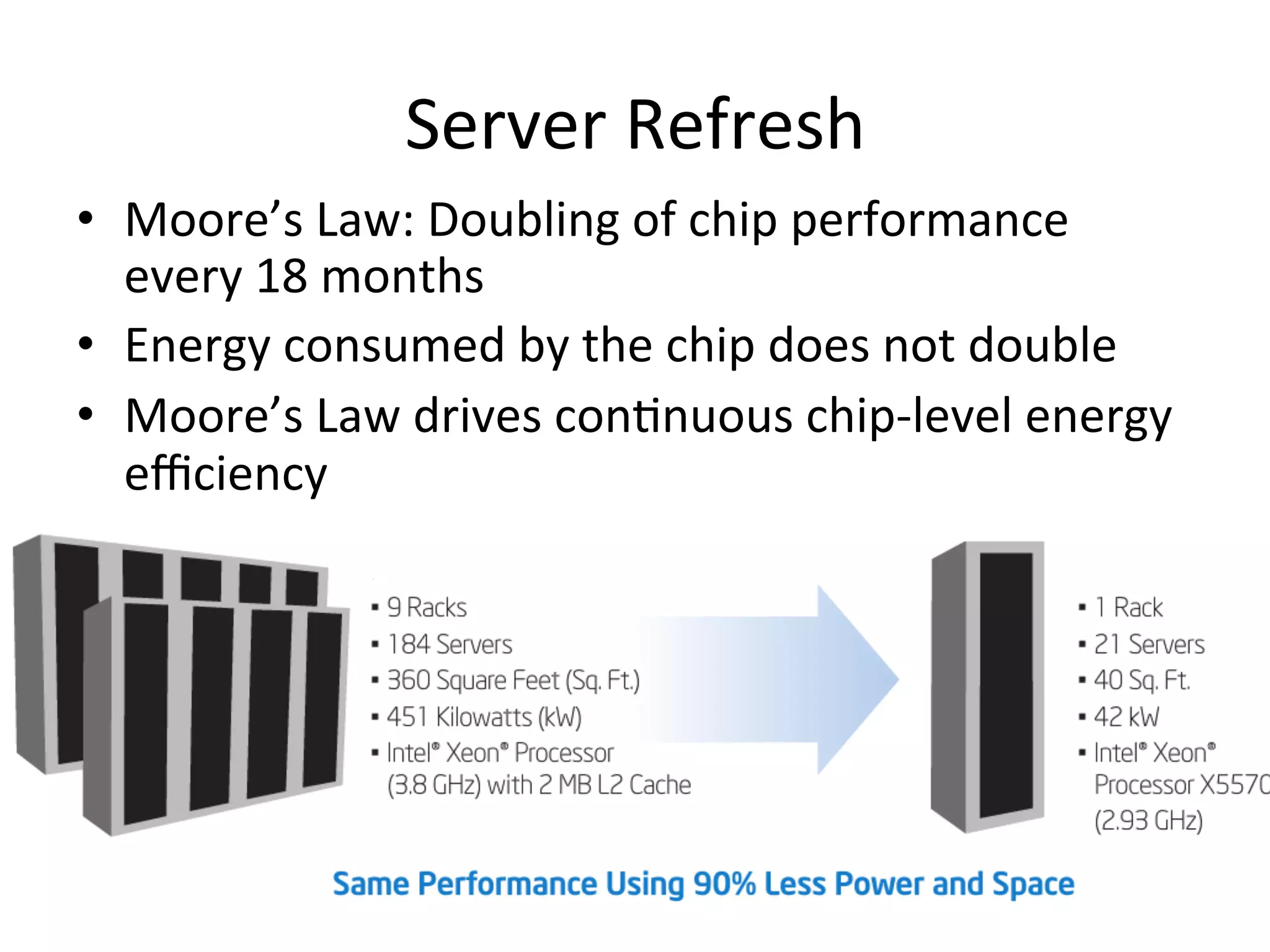
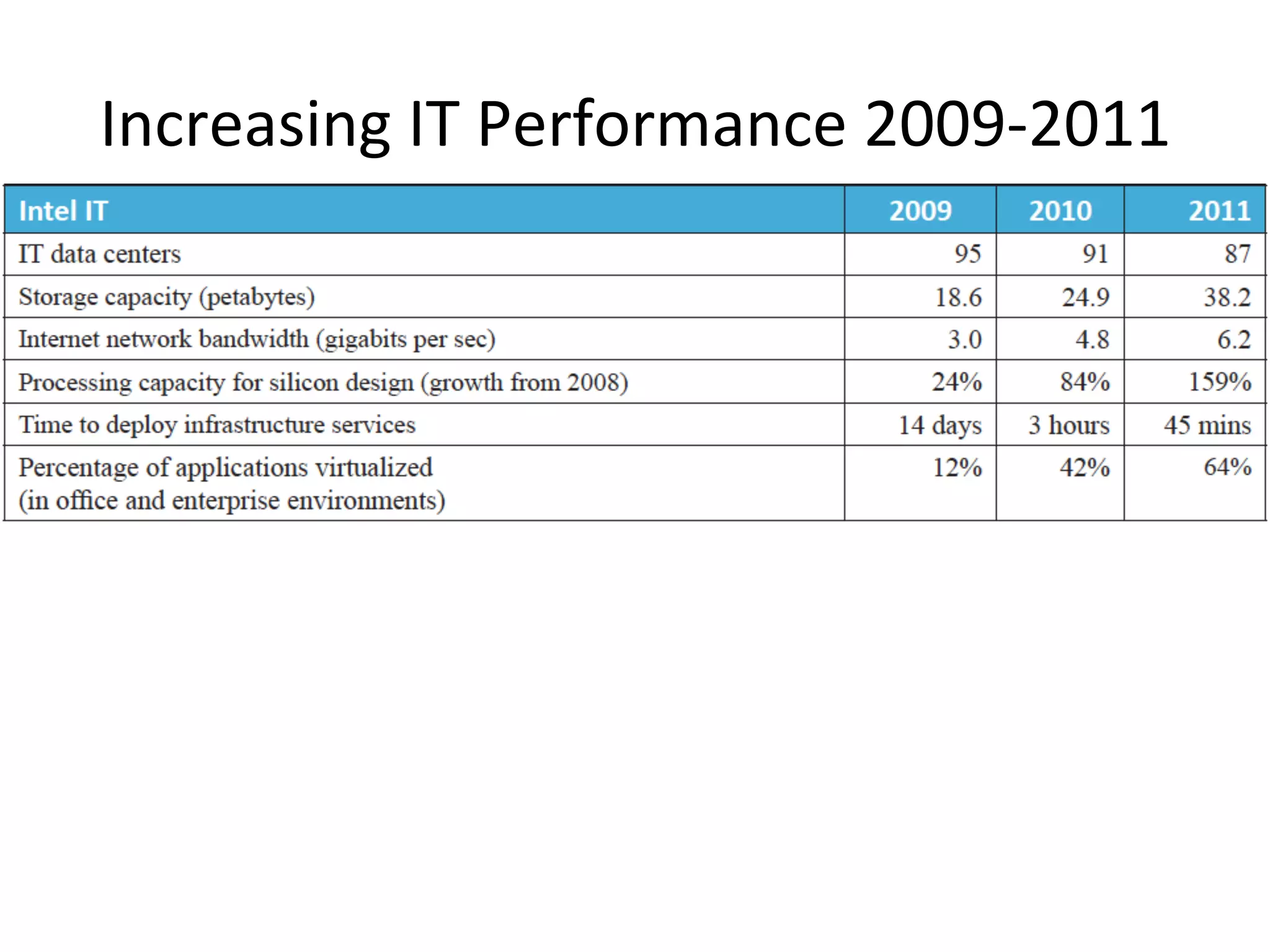
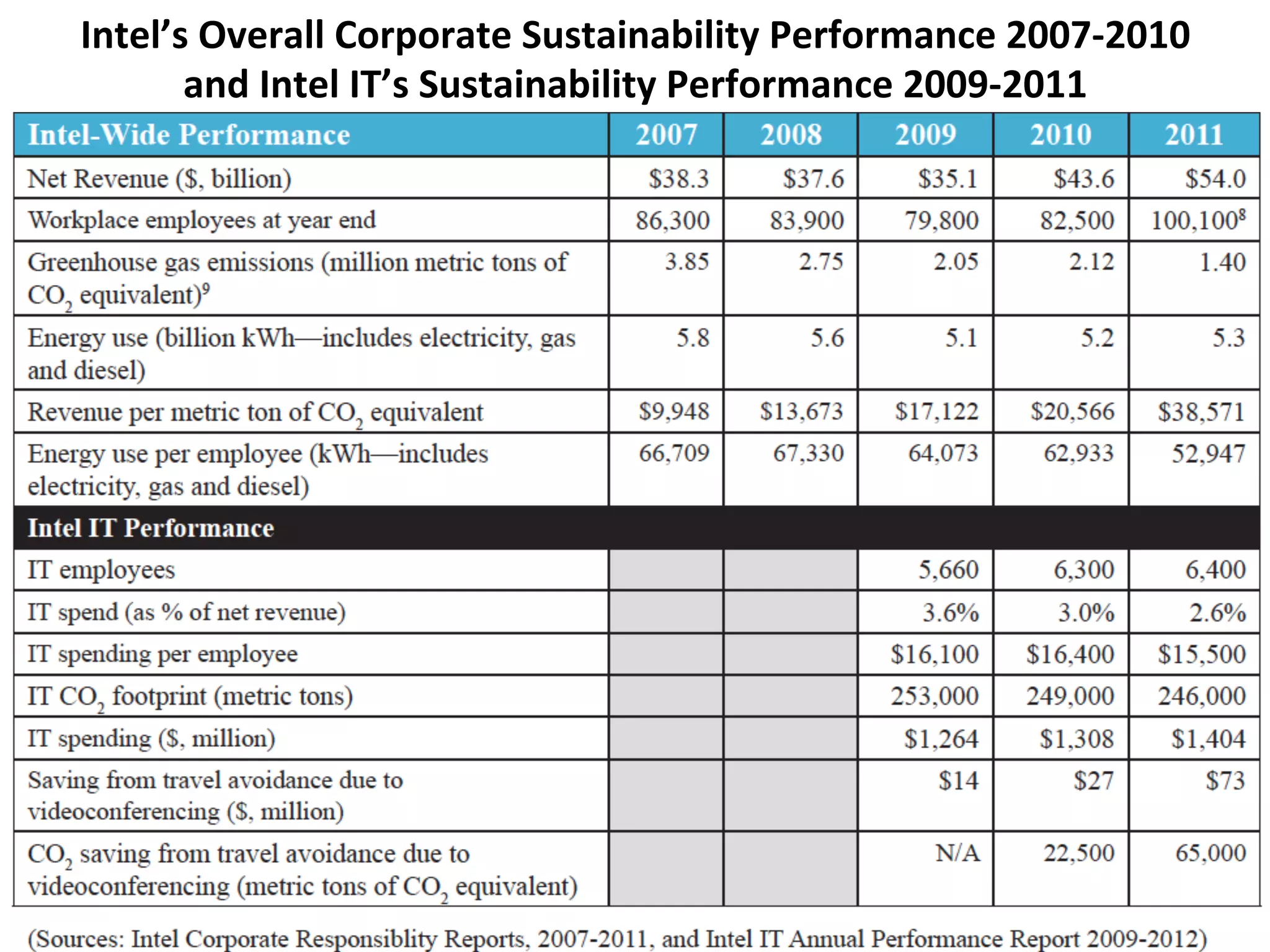
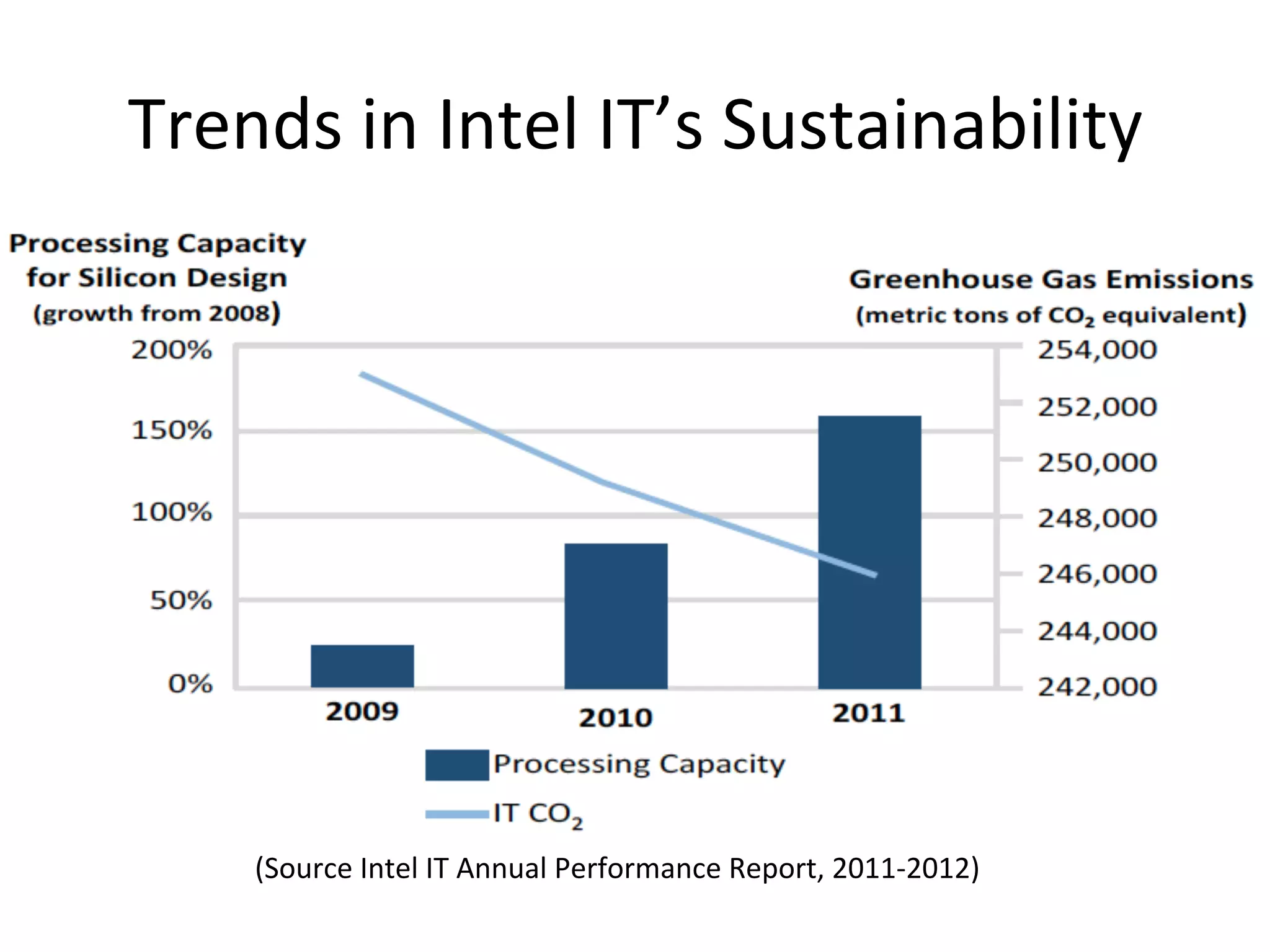
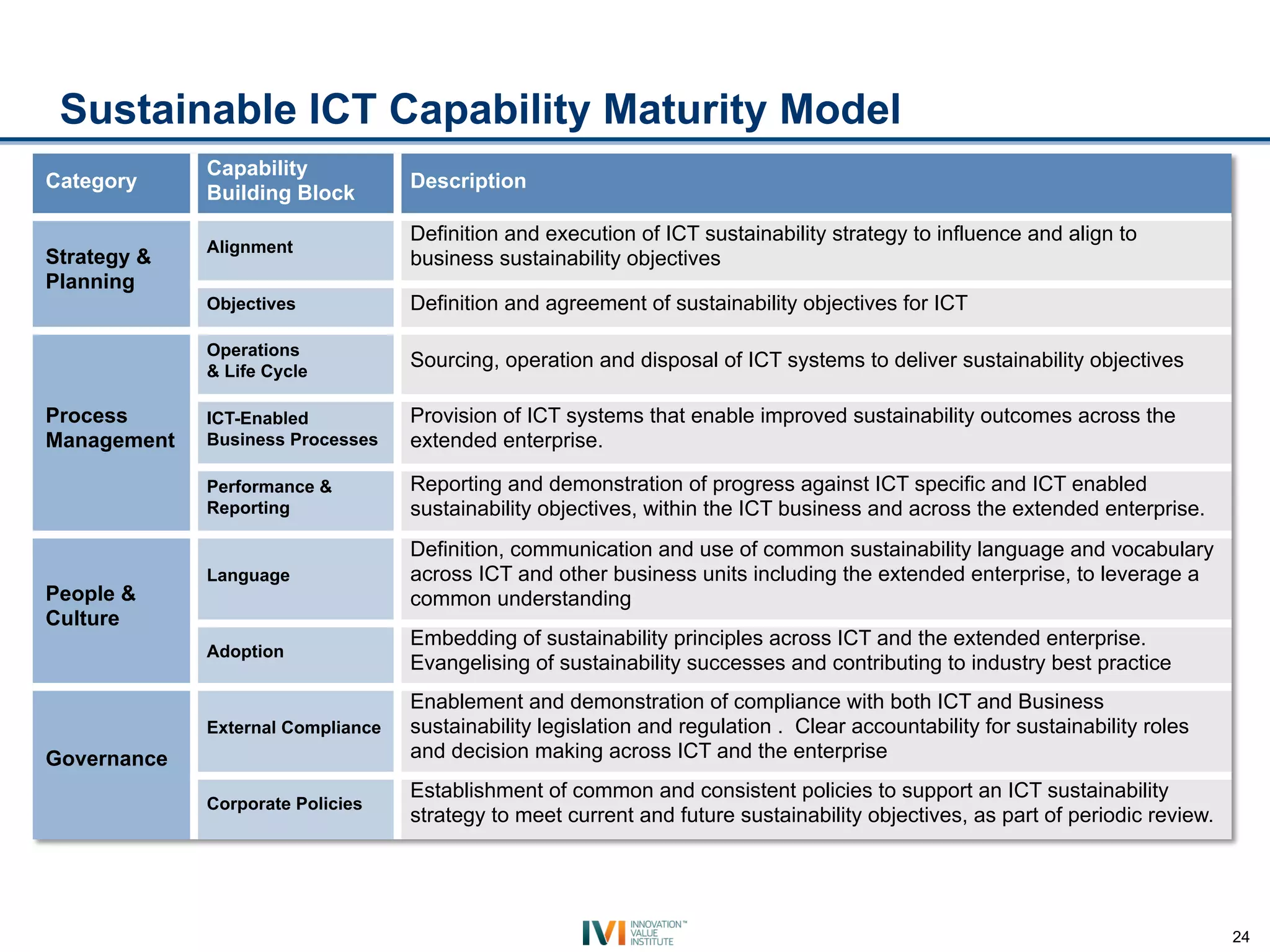
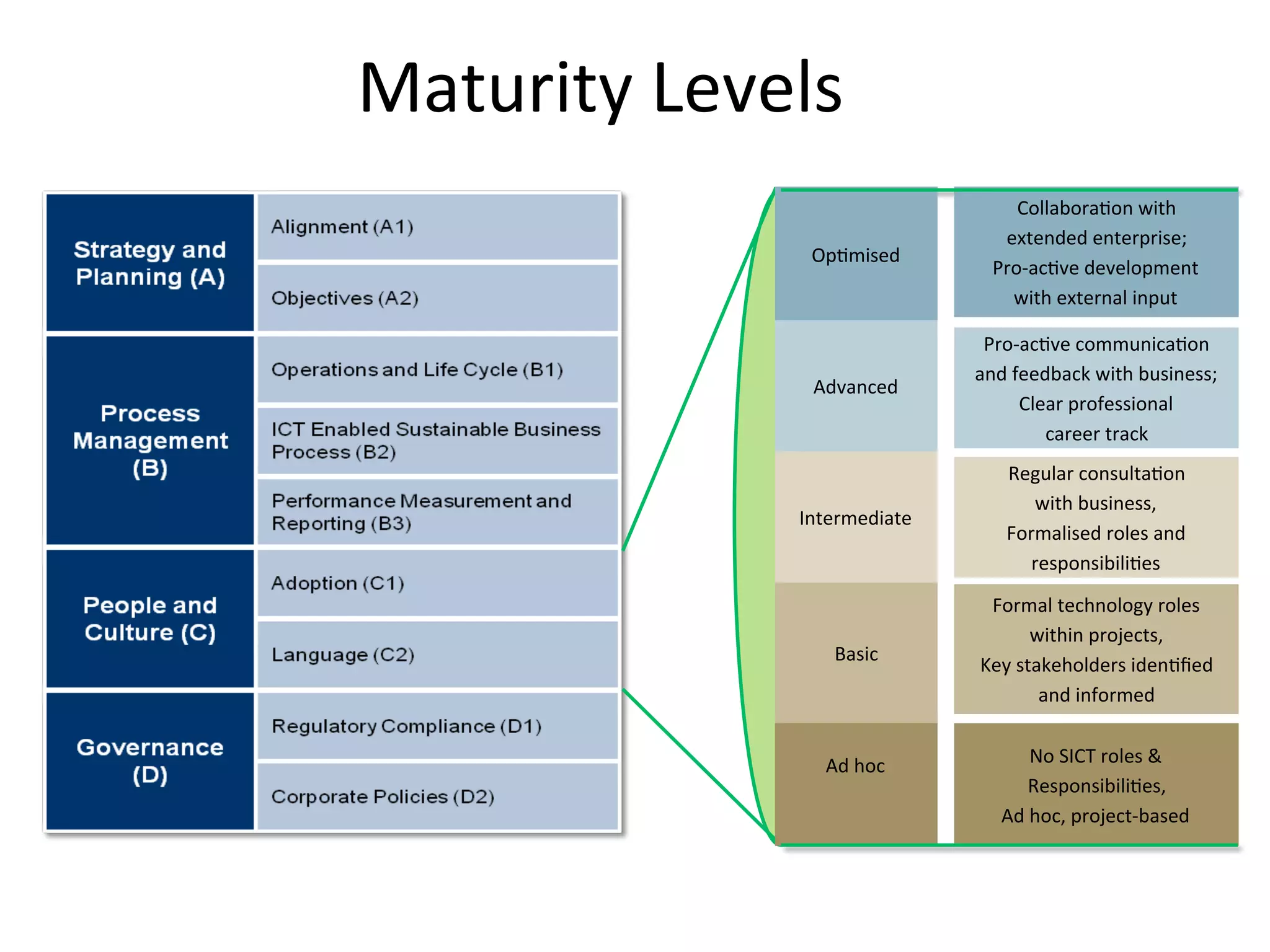
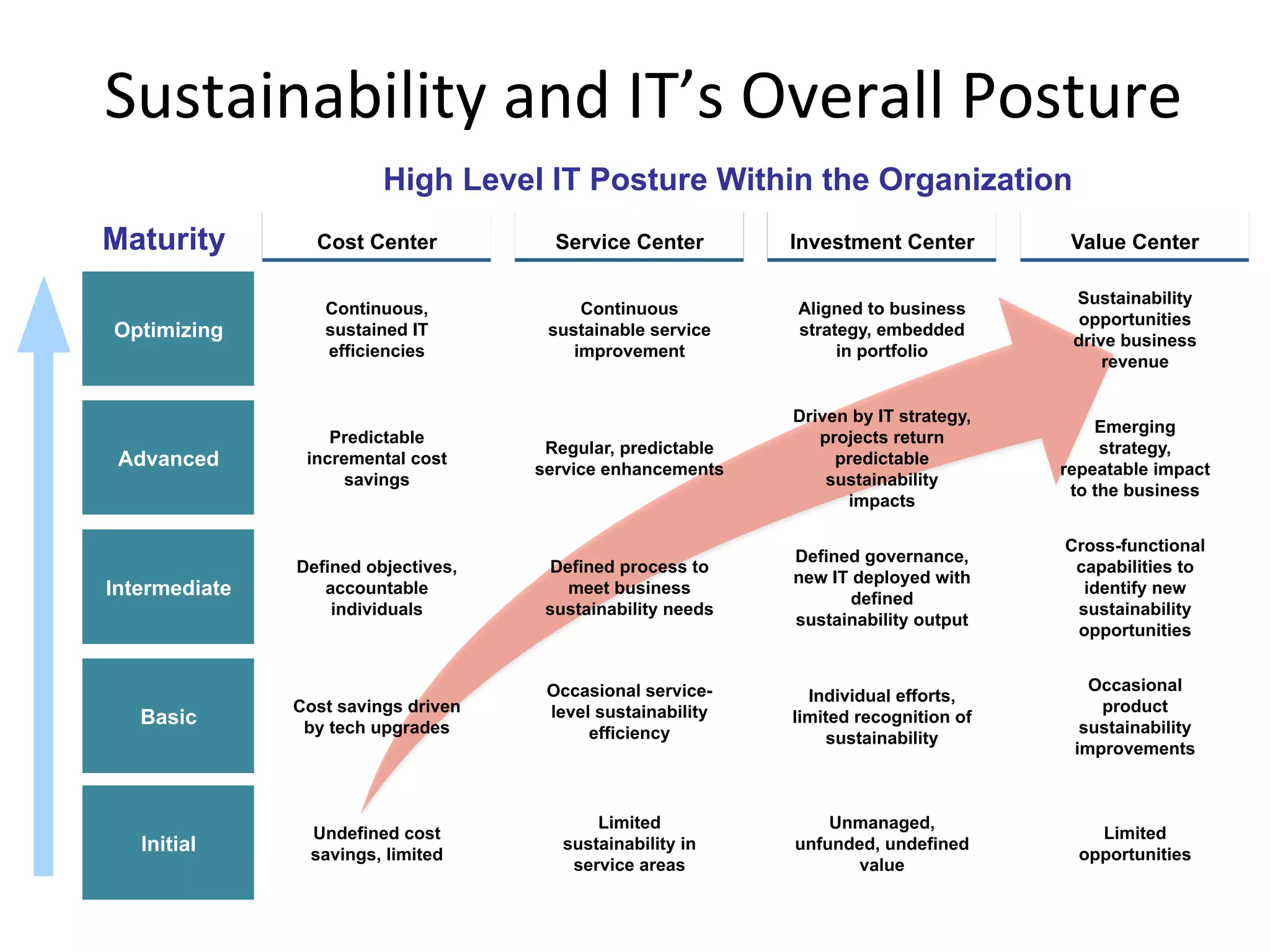
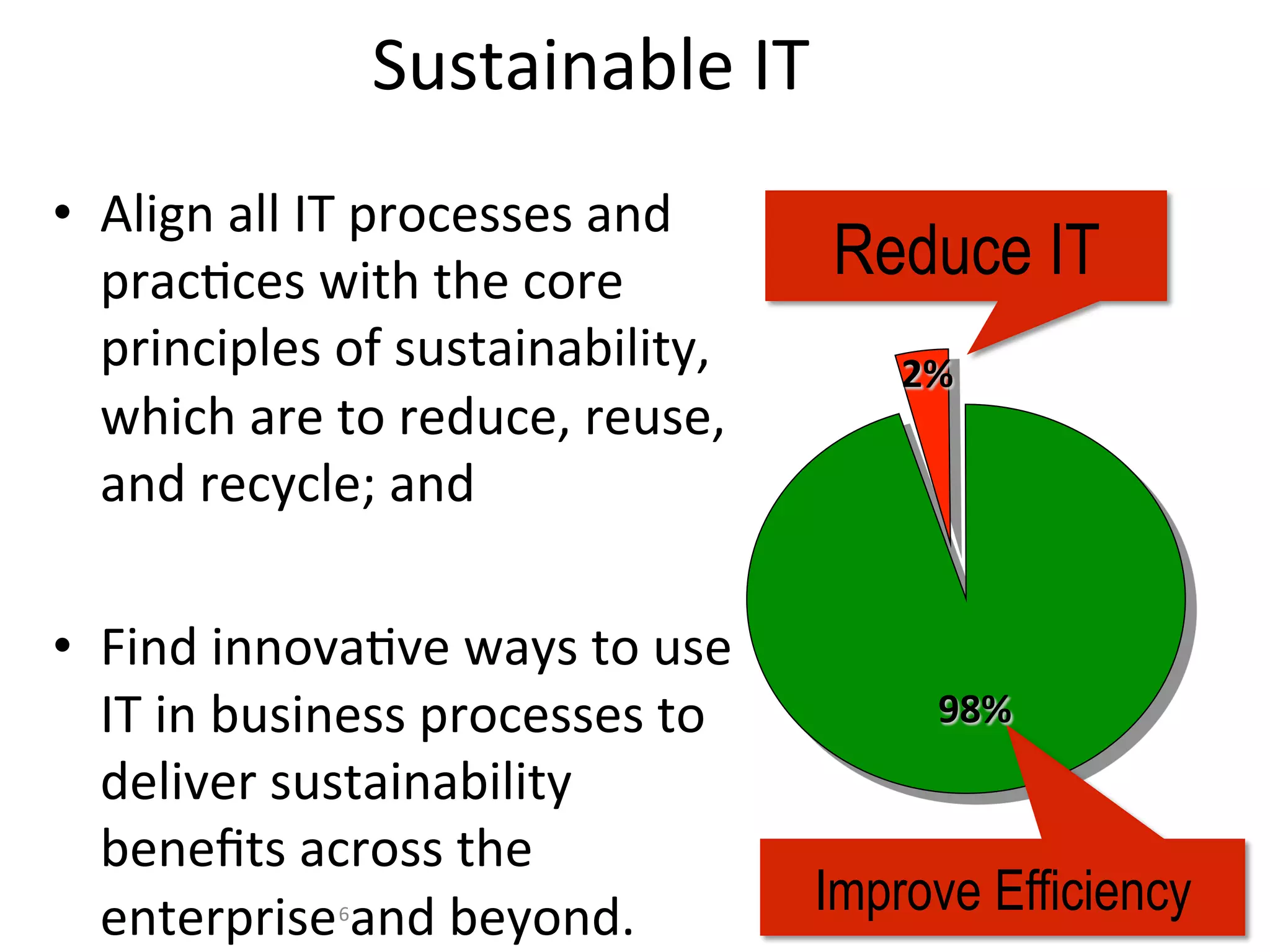
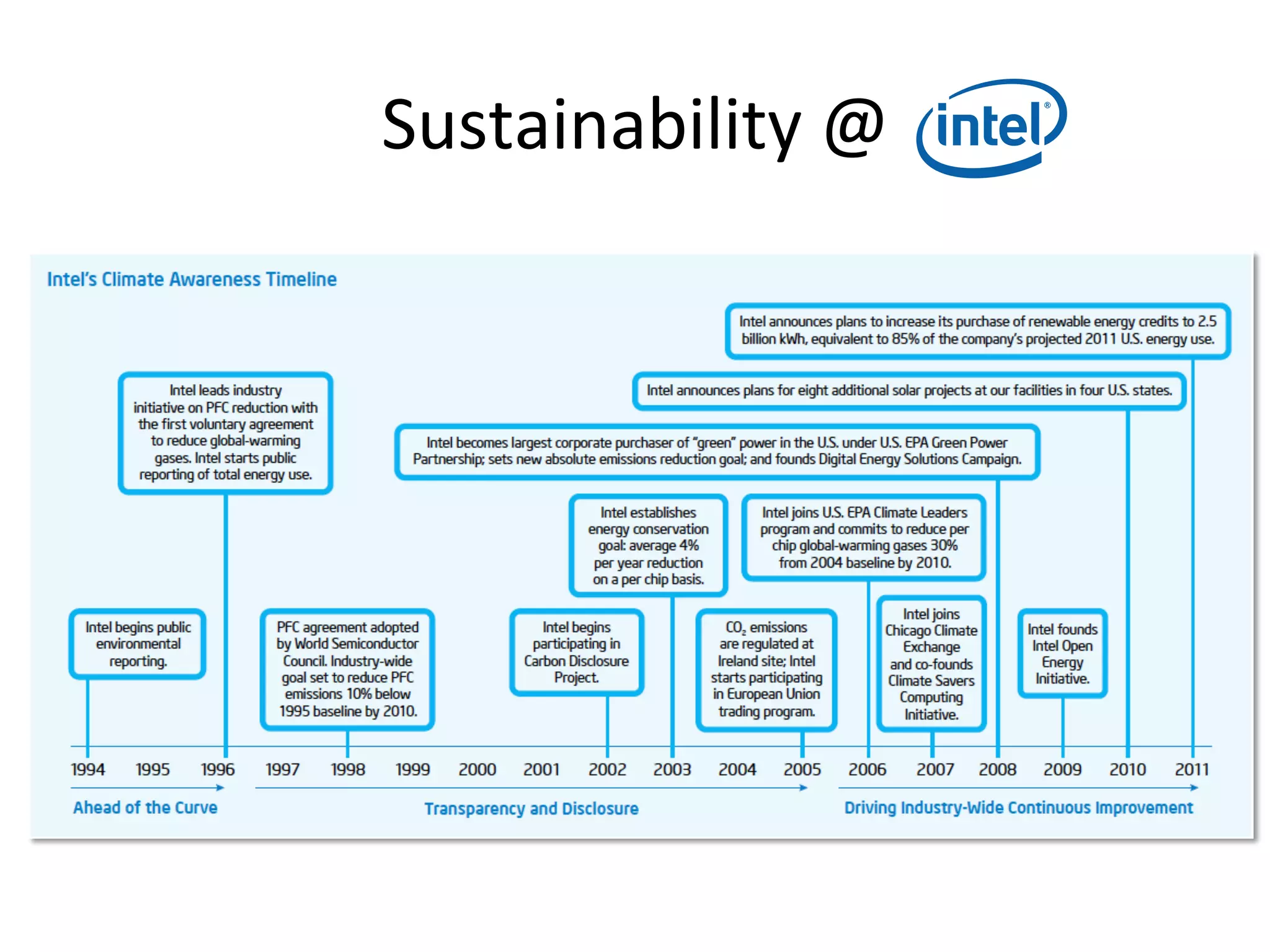
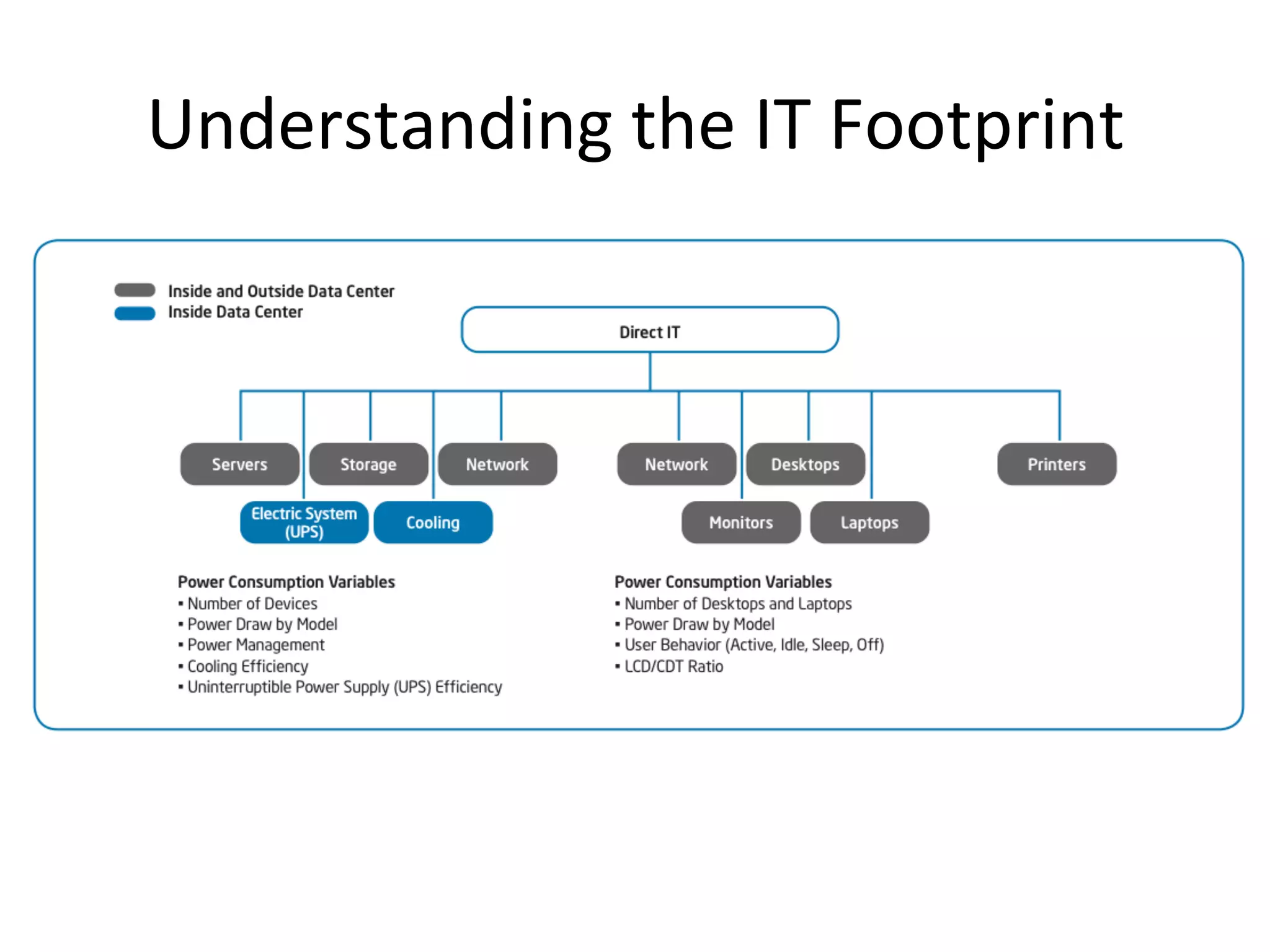
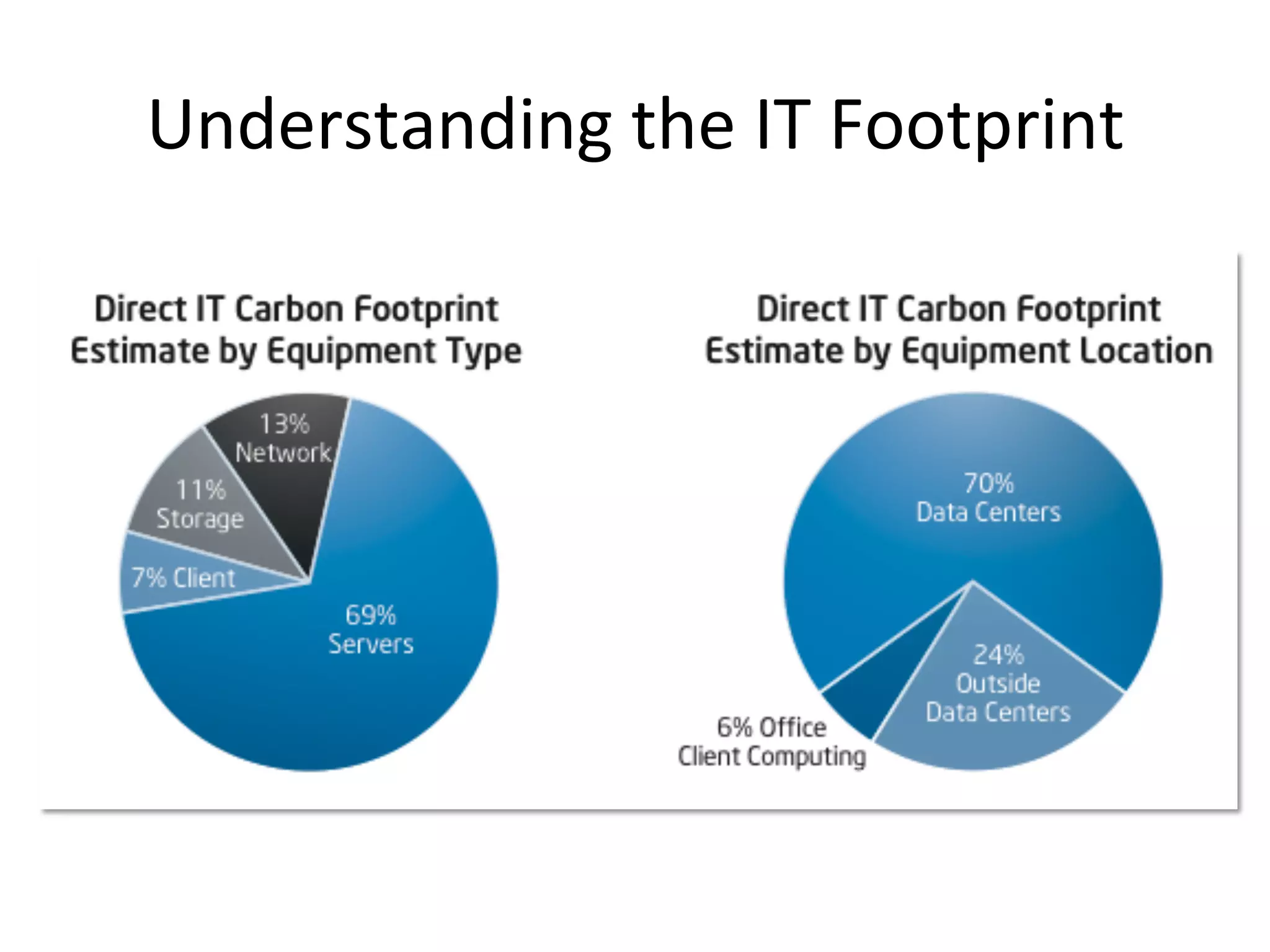
The document discusses Intel's initiatives to develop a sustainable IT capability, emphasizing the alignment of IT processes with sustainability principles to reduce carbon emissions and improve efficiency. Through various strategies and employee engagement, Intel achieved significant cost savings and reductions in CO2 emissions while enhancing its overall corporate sustainability. Additionally, it outlines a maturity model for assessing the development of ICT-enabled sustainability practices within organizations.




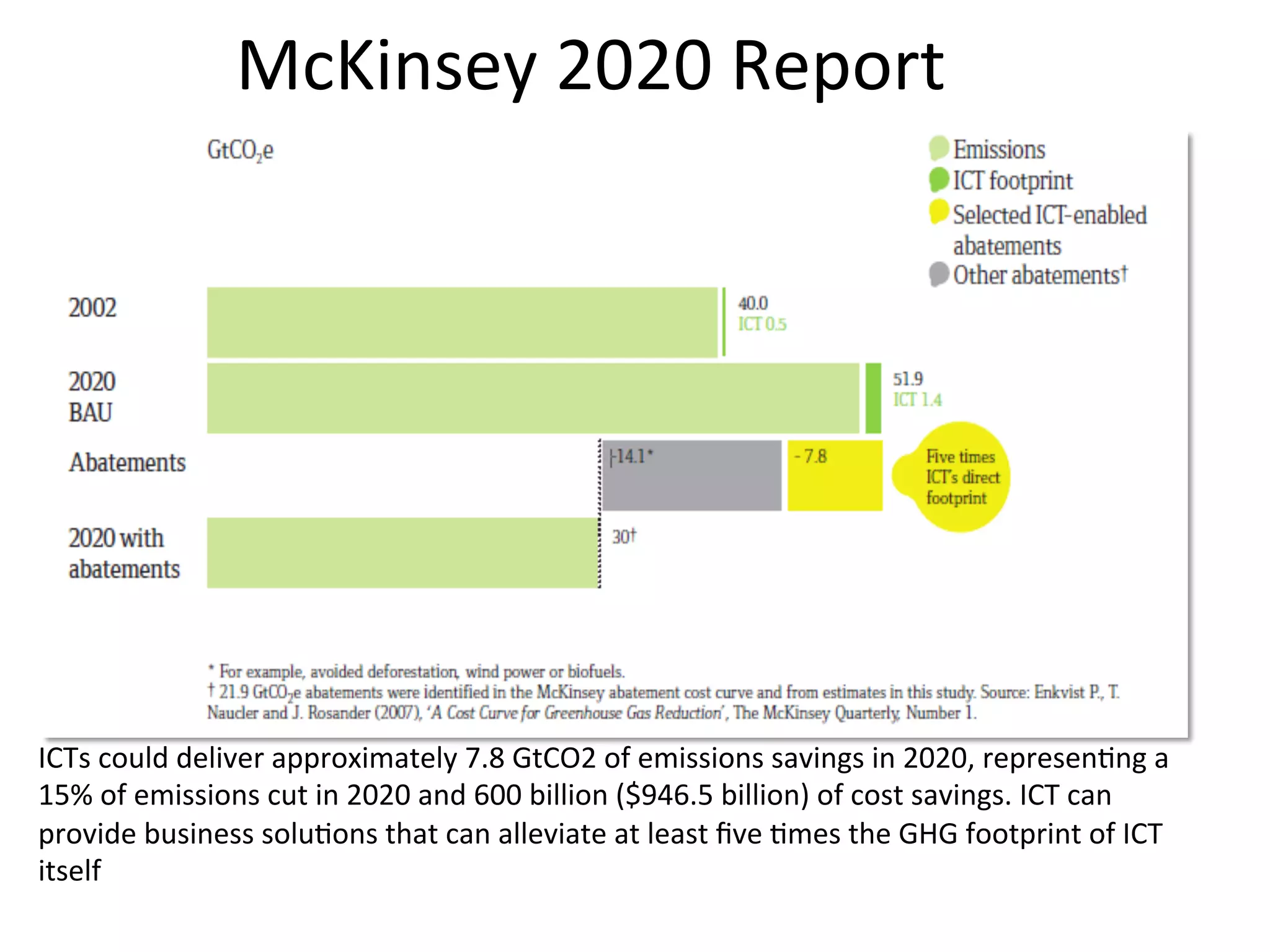







![Data
Centres:
An
Inefficient
Truth
*
Source:
EPA
Report
to
Congress
on
Server
and
Data
Center
Energy
Efficiency,
August
2007
32%
Processor
Drives5%
Peripheral Slots 20%
PSU 15%45%
IT
Load
55%
Power,
Cooling
&
LighGng
Data
Center
Server
Processor
100
Wa]s
Supplied
14
Wa]s
supplied
to
CPU
11.2
Wa]s
used
for
computaGon
45
Wa]s
supplied
to
IT
equipment
Up
to
88.8%
of
the
power
consumed
by
a
data
centre
is
used
before
computa8on
17
80%
UGlised
20%
Idle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/misqeintel2013print-130715101434-phpapp01/75/Developing-an-Sustainable-IT-Capability-Lessons-From-Intel-s-Journey-17-2048.jpg)