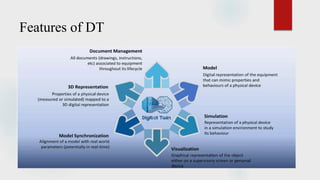
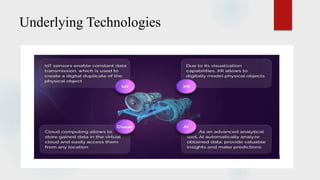
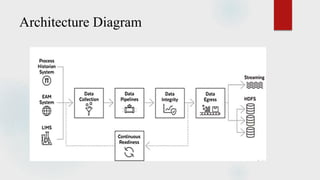
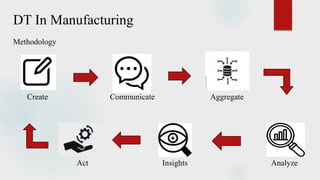
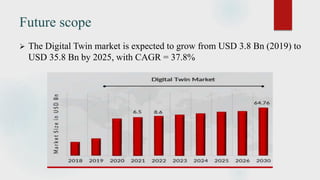
The document presents a technical seminar on digital twin technology, detailing its introduction, historical background, key characteristics, underlying technologies, architecture, applications, and advantages and limitations. Digital twins are virtual representations that enhance decision-making across a product's lifecycle, leveraging real-time data for predictive capabilities. The seminar emphasizes the growing importance and future market potential of digital twin technology, predicting substantial growth from $3.8 billion in 2019 to $35.8 billion by 2025.