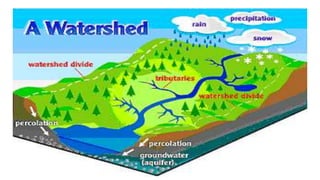
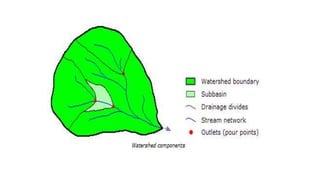
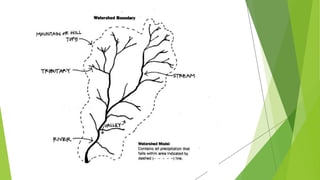
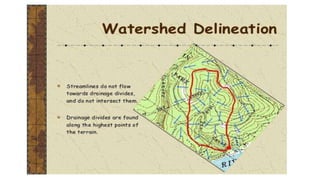
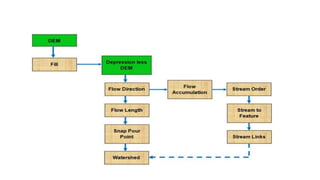
The document covers watershed analysis and planning using GIS, detailing the definition, components, and methodologies for watershed delineation. It emphasizes the role of GIS in enhancing watershed modeling techniques and the benefits of effective watershed management for resource conservation and agricultural productivity. The analysis involves various steps, such as DEM acquisition, flow direction assessment, and the establishment of stream networks, along with factors influencing the accuracy of these analyses.
















![8. Point-Based Watersheds;
Delineation of individual watershed
-s based on point of intersection [ pour point ] foll
-ows the same steps as for delineation of Area-
wide watersheds .
Point based watersheds delineation
Is based on the point of interest . This point of
interest may be stream gauge stations or dams.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/watersheddelinationgroup2ndvishal-240706061957-d9846df4/85/watershed-analysis-and-delineation-through-GIS-22-320.jpg)



