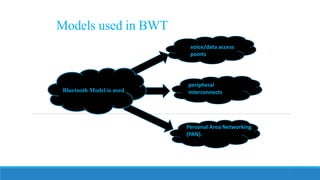
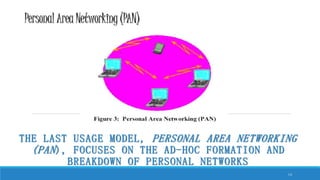
This document discusses Bluetooth technology. It provides an overview of Bluetooth including its history, how it works using short-range radio waves, common uses in connecting devices like phones, laptops and printers, and establishing personal area networks. The document also outlines Bluetooth security measures, advantages like wireless connectivity and low energy use, disadvantages such as low data transfer rates, and the future of Bluetooth depending on successful integration into consumer products.