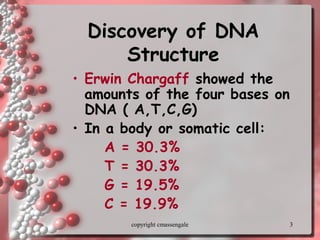
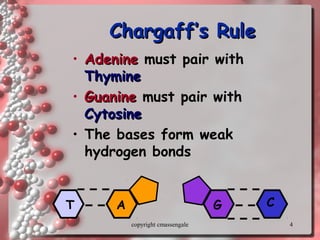
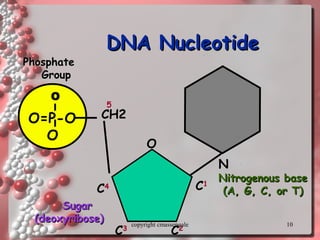
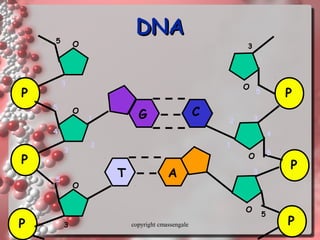
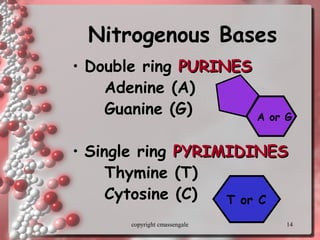
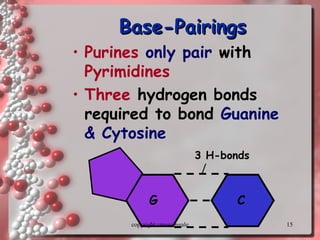
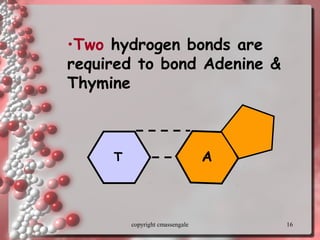
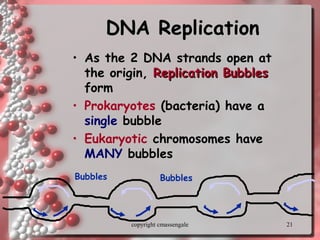
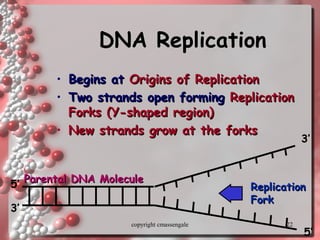
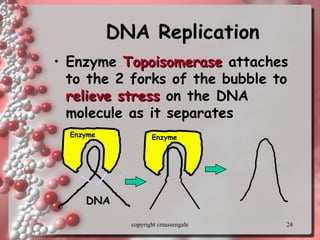
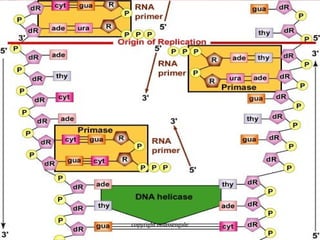
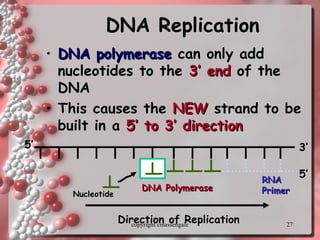
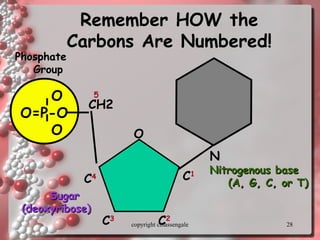
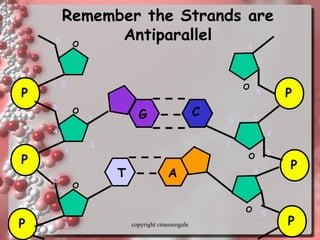
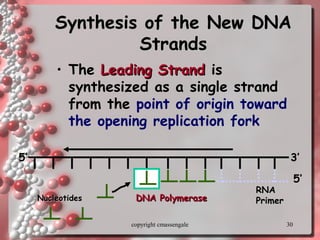
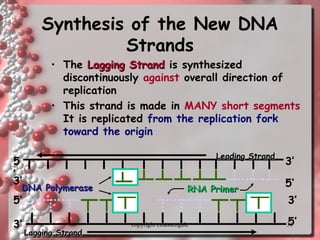
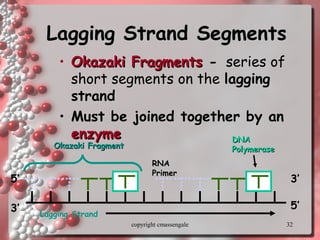
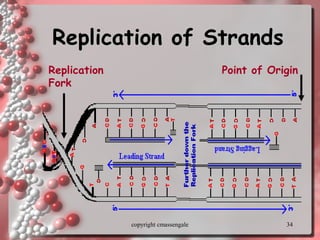
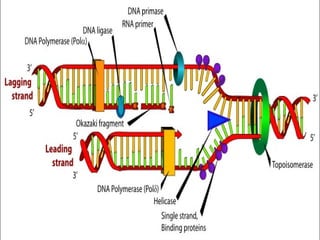
The document describes DNA replication. It explains that DNA must be copied before cells divide so that new cells have identical DNA. Replication begins at origins of replication and forms replication bubbles or forks. Enzymes such as helicase unwind the DNA strands, primase adds RNA primers, and DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the 3' ends of the strands. The leading strand is synthesized continuously while the lagging strand is synthesized in short segments called Okazaki fragments that are later joined by ligase. The process results in two new DNA molecules each with one original and one new strand, supporting the semiconservative model of replication.