Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


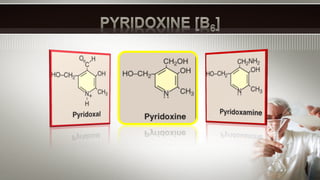
![PYRIDOXINE [B6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b6-150331160811-conversion-gate01/85/vitamin-B6-5-320.jpg)
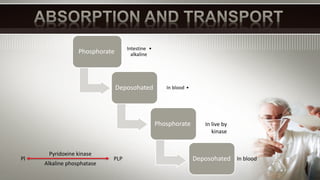


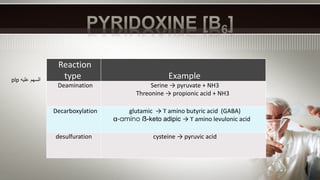
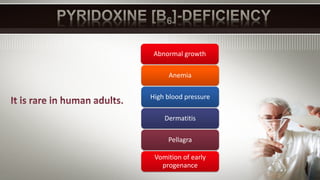




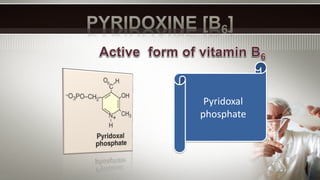
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, is important for many metabolic processes in the body. It acts as a coenzyme in reactions involving transamination, deamination, and decarboxylation. A lack of vitamin B6 can lead to abnormal growth, anemia, high blood pressure, dermatitis, and pellagra. Risk factors for vitamin B6 deficiency include a low vitamin intake, pregnancy, alcohol or smoking, older age, antibiotic use, and diabetes.




![PYRIDOXINE [B6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b6-150331160811-conversion-gate01/85/vitamin-B6-5-320.jpg)












