Vitamin B6, or pyridoxine, is a water-soluble vitamin essential for amino acid metabolism, neurological function, and the synthesis of neurotransmitters. It is found in various foods such as whole grains, poultry, and legumes, with deficiencies leading to serious neurological and hematological symptoms. Supplementation may be necessary for certain populations, including the elderly and alcoholics, but excessive intake can cause adverse neurological effects.
![Vitamin B 6 is a water-soluble vitamin present in three major chemical
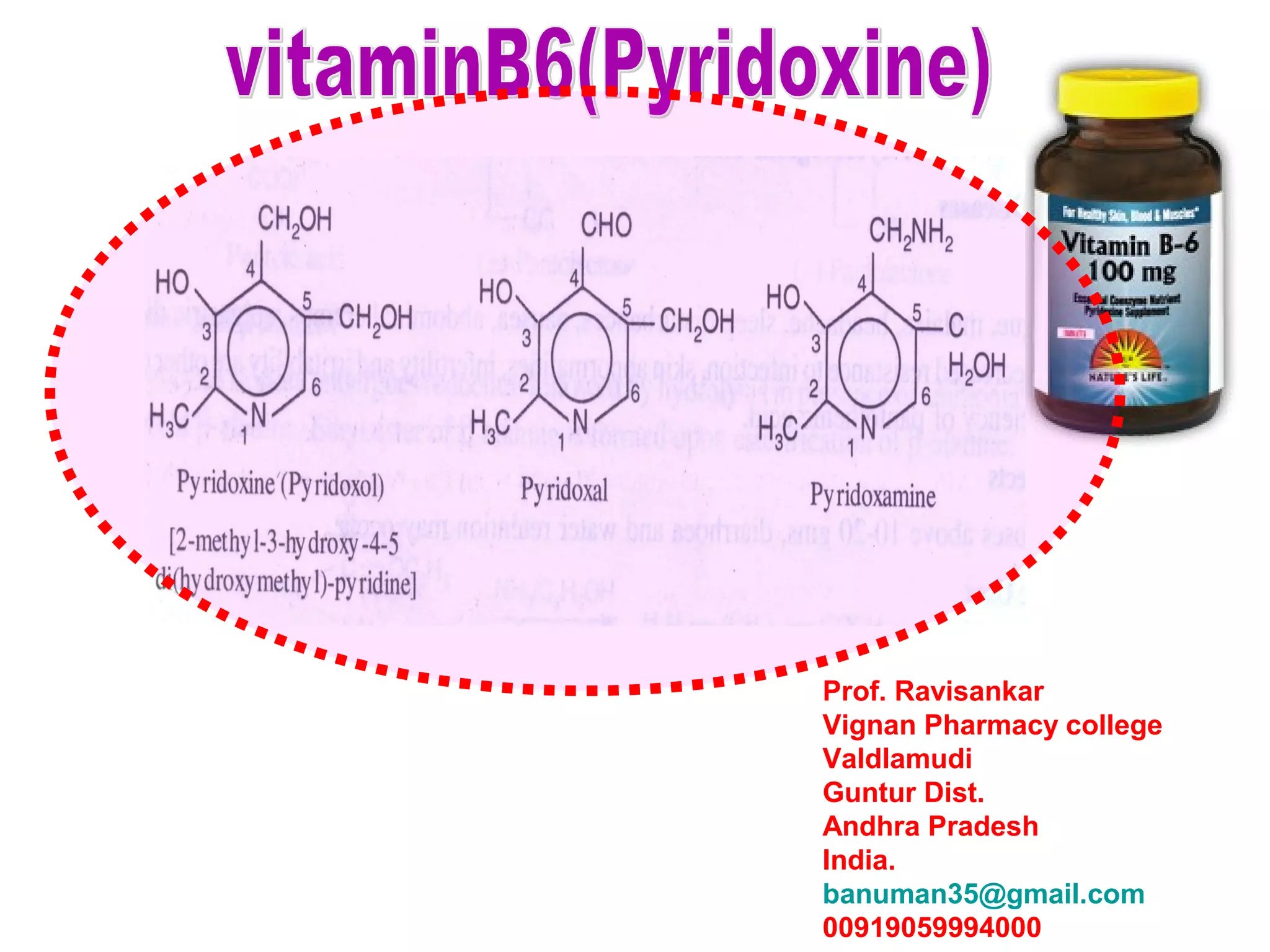
forms:
pyridoxine, pyridoxal,pyridoxamine
These three are interconvertible in their phosphorylated form.
It is also called Adermin,because it is used as an antidermatitic factor
(acrodynia factor )for rats.
The plant sources mainly contain pyridoxal,pyridoxamine and animal
sources contain Pyridoxine.
Active form is pyridoxal phosphate
It is essential coenzyme for trans amination and decarboxylation of
amino acids.
N
CH2OH
CH2OHHO
H3C
PYRIDOXINE
N
CHO
CH2OHHO
H3C N
CH2NH2
CH2OHHO
H3C
PYRIDOXAMINEPYRIXOXAL
Collectively, pyridoxine, pyridoxal and pyridoxamine are known as vitamin B6.
(Pyridoxol)
[2-methyl-3-hydroxy-4-5
di(hydroxymethyl)-Pyridine]
1
2
3 4 5
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vitaminb6pyridoxine-ravi-vig-130615121233-phpapp01/85/VITAMIN-B6-MEDICINAL-CHEMISTRY-BY-P-RAVISANKAR-SOURCES-STRUCTURES-OF-PYRIDOXINE-PYRIDOXAL-PYRIDOXAMINE-DEFICIENCY-OF-VITAMIN-B6-PYRIDOXINE-ANTAGONISTS-METABOLISM-PHYSIOGICAL-IMPORTANCE-SYNTHESIS-OF-PYRIDOXALAND-PYRIDOXAMINE-VITAMIN-B6-USES-2-320.jpg)











