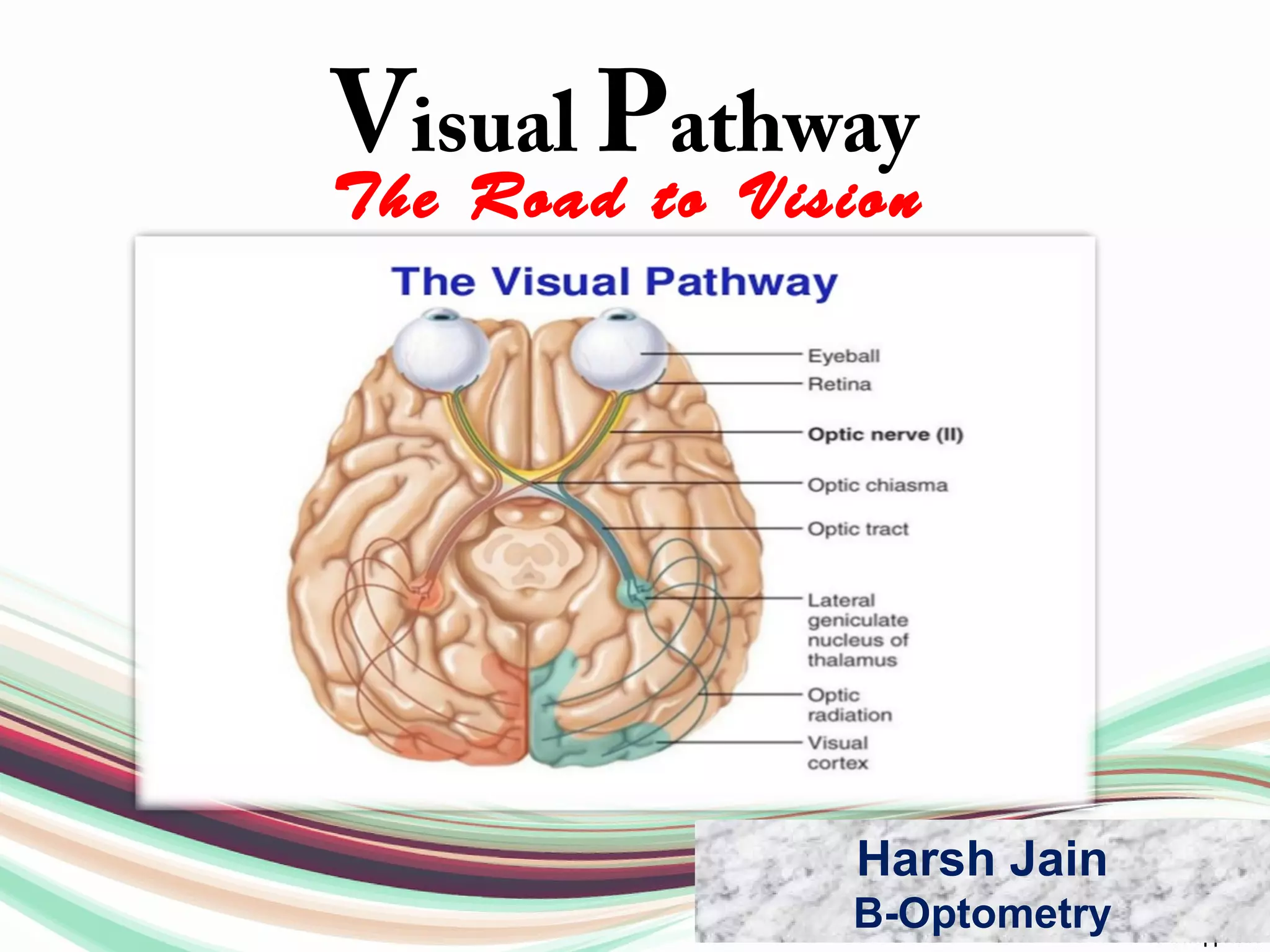
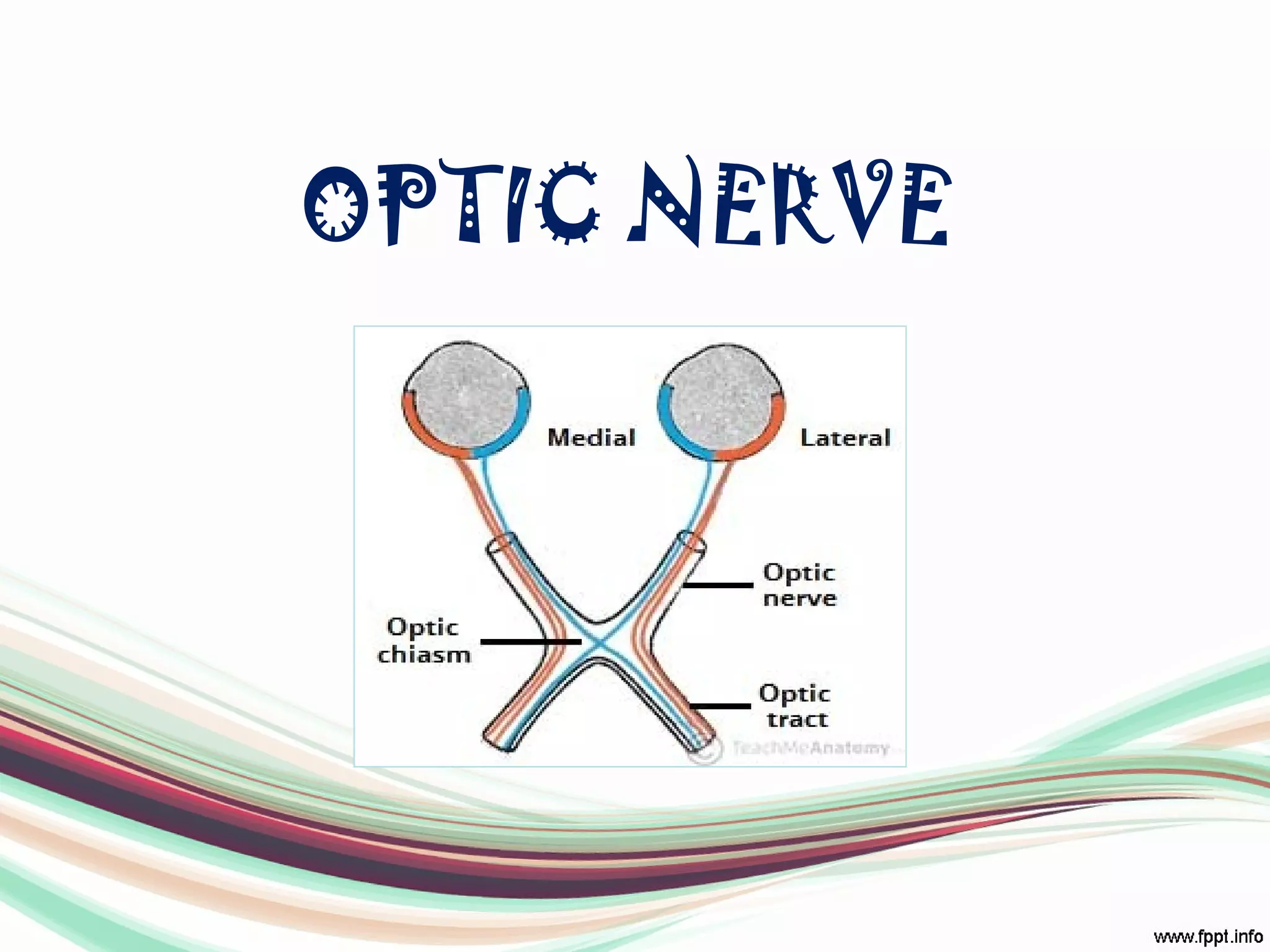
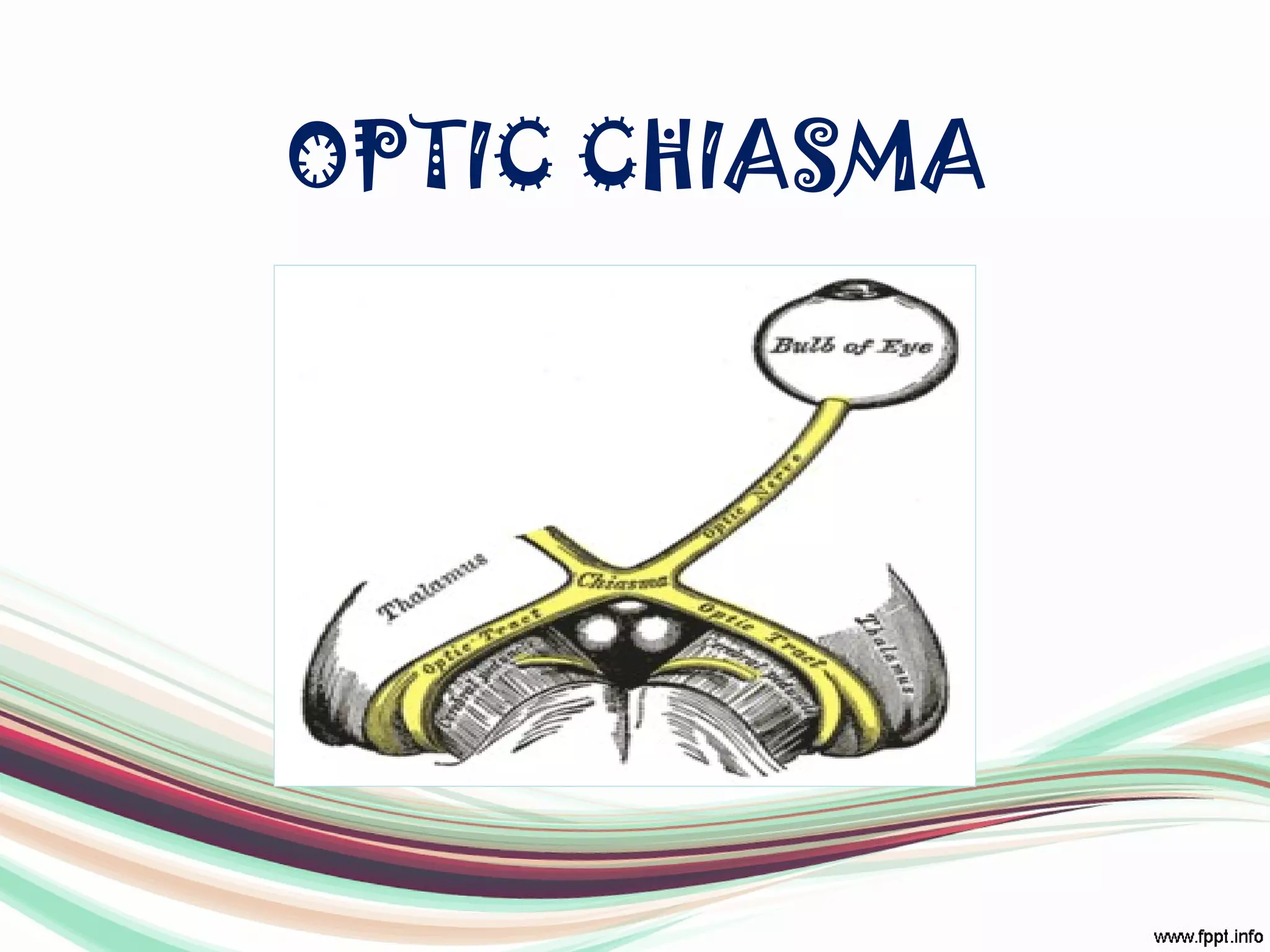
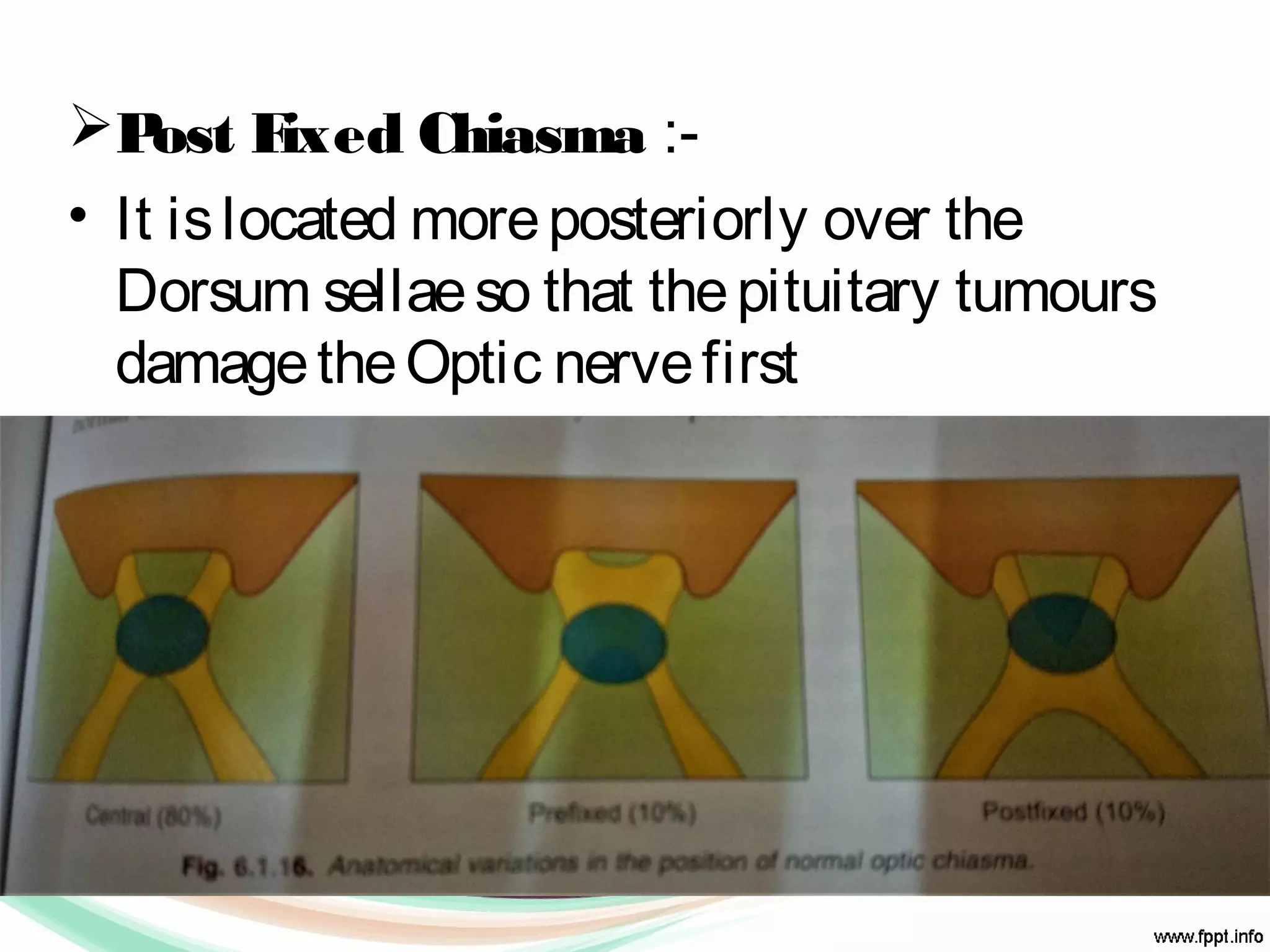
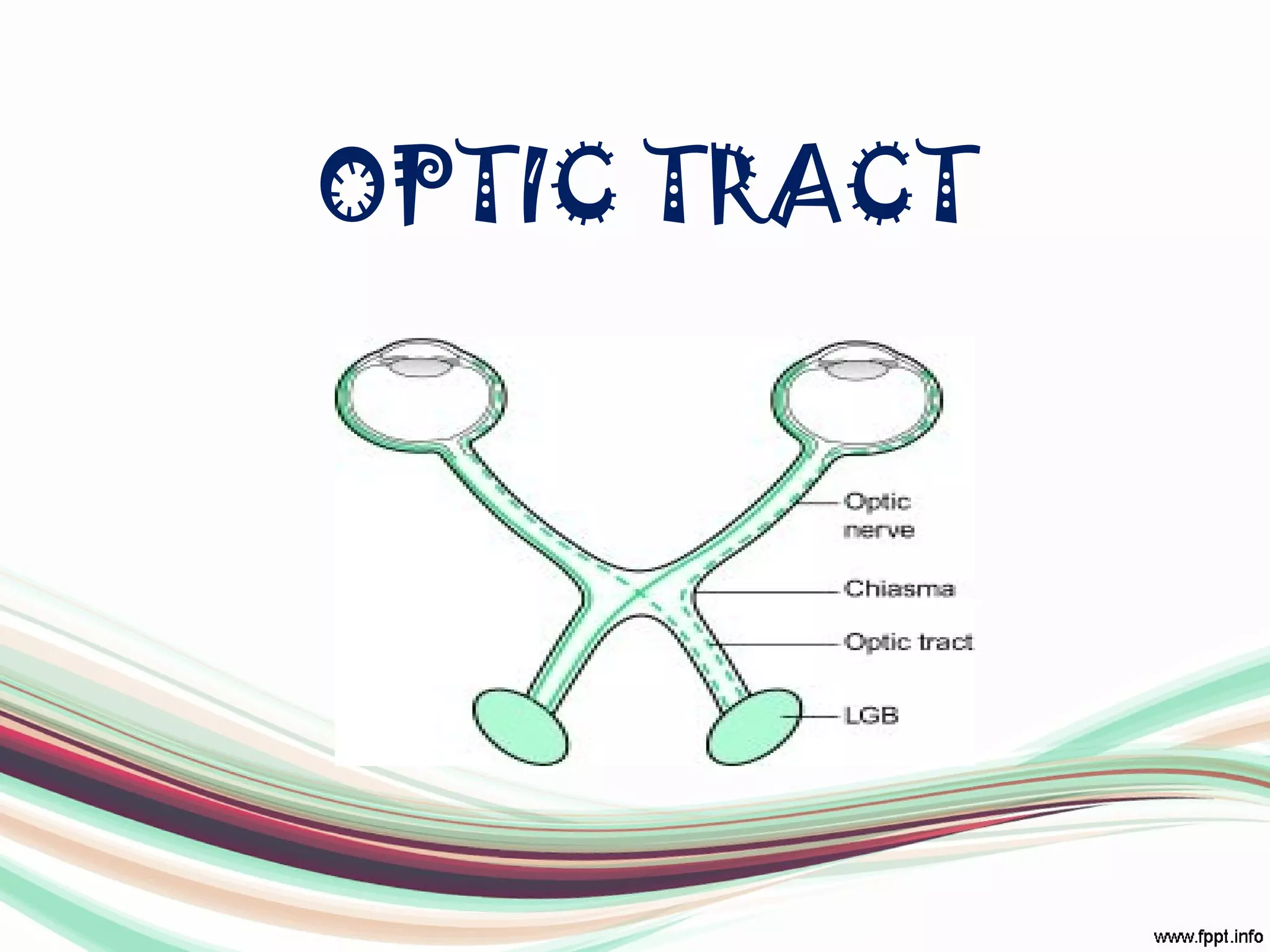
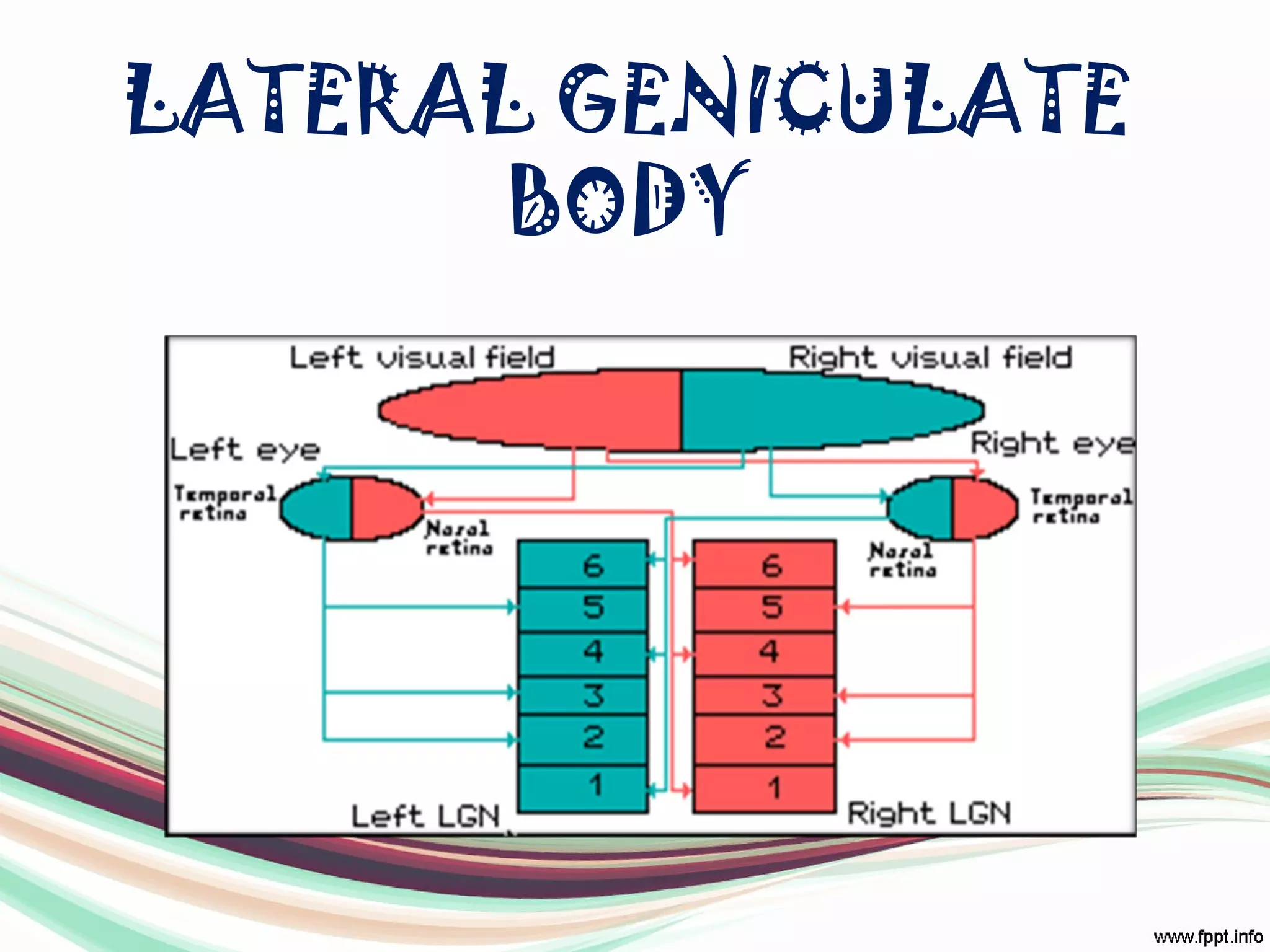
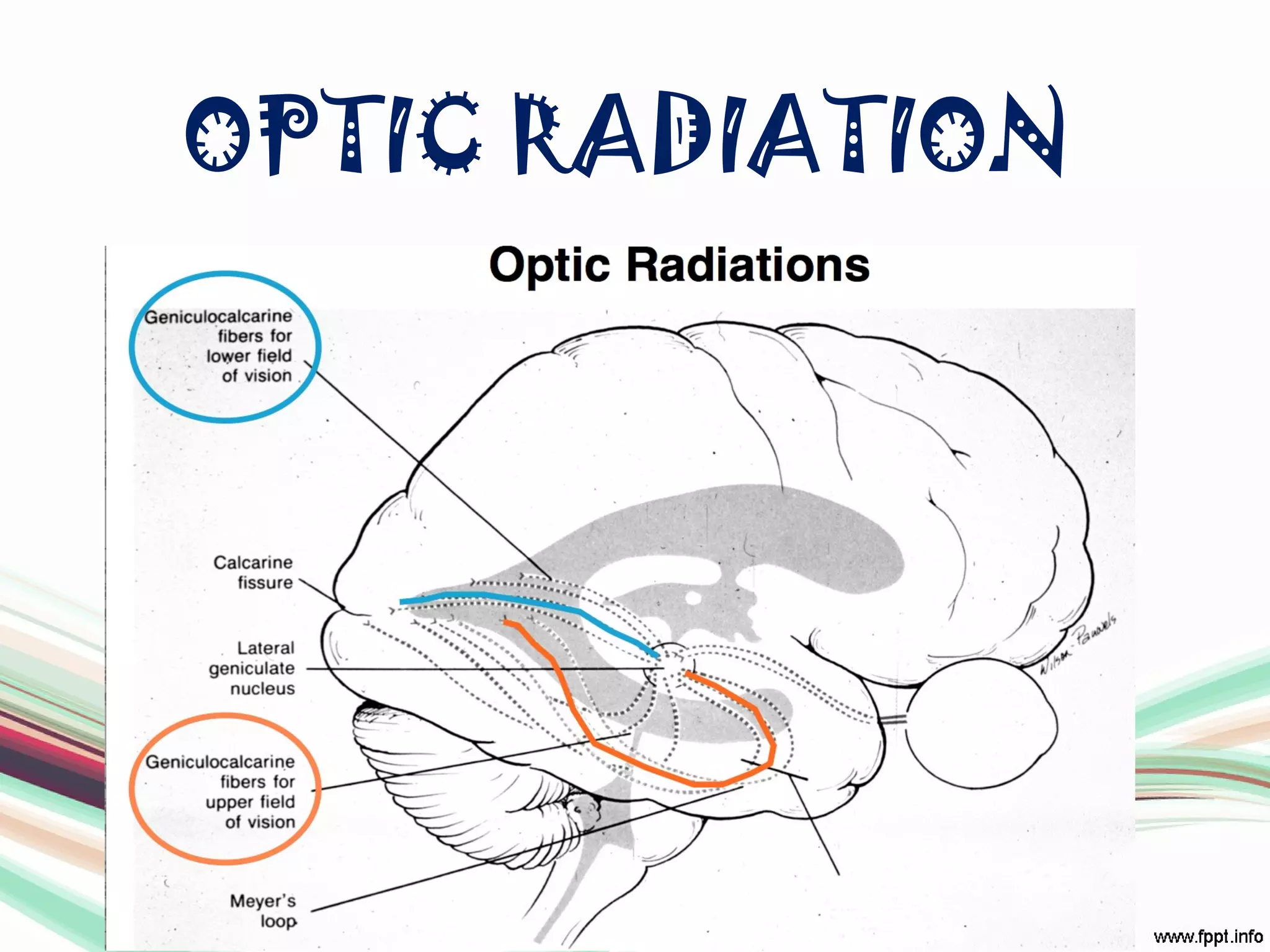
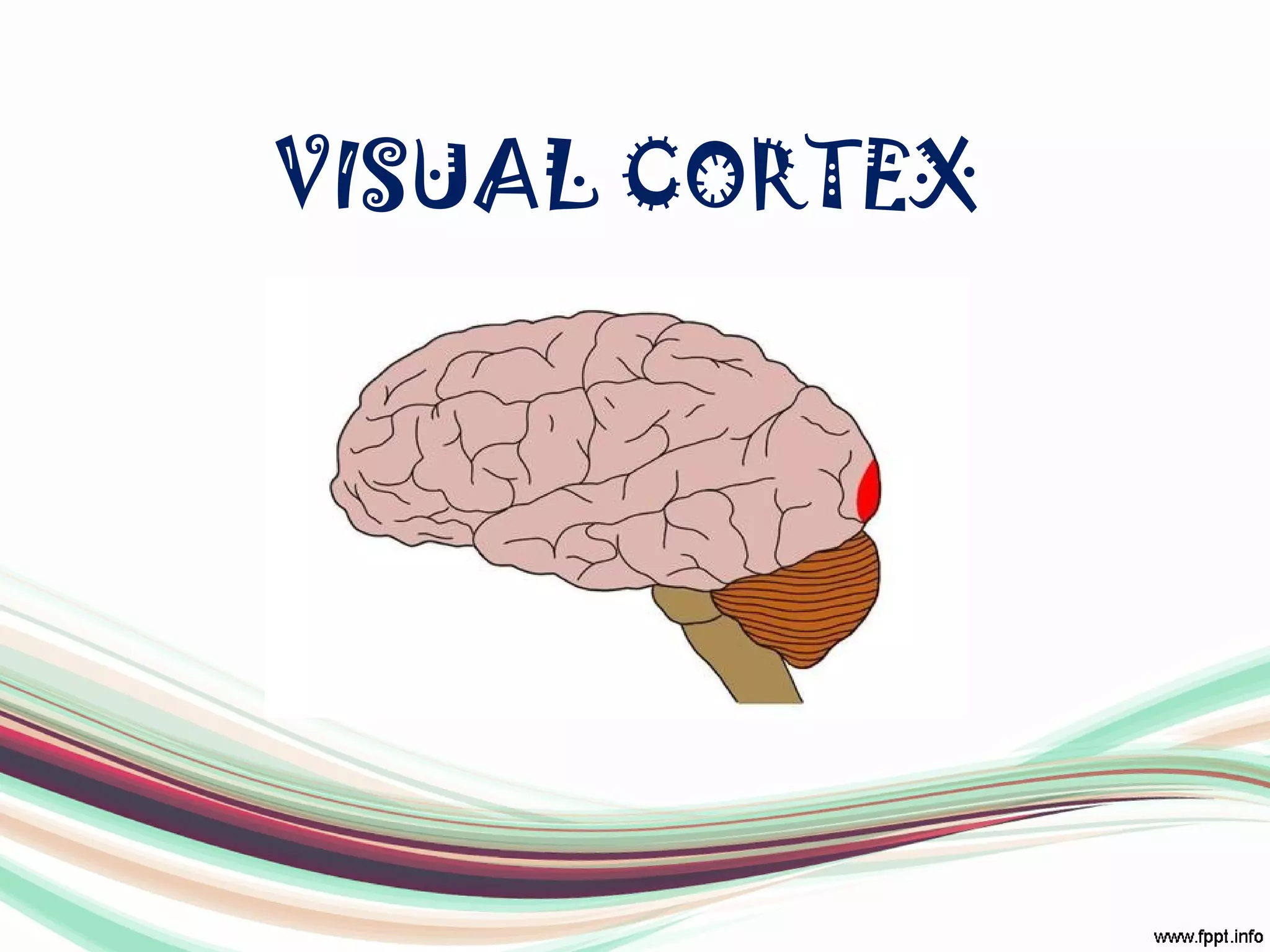
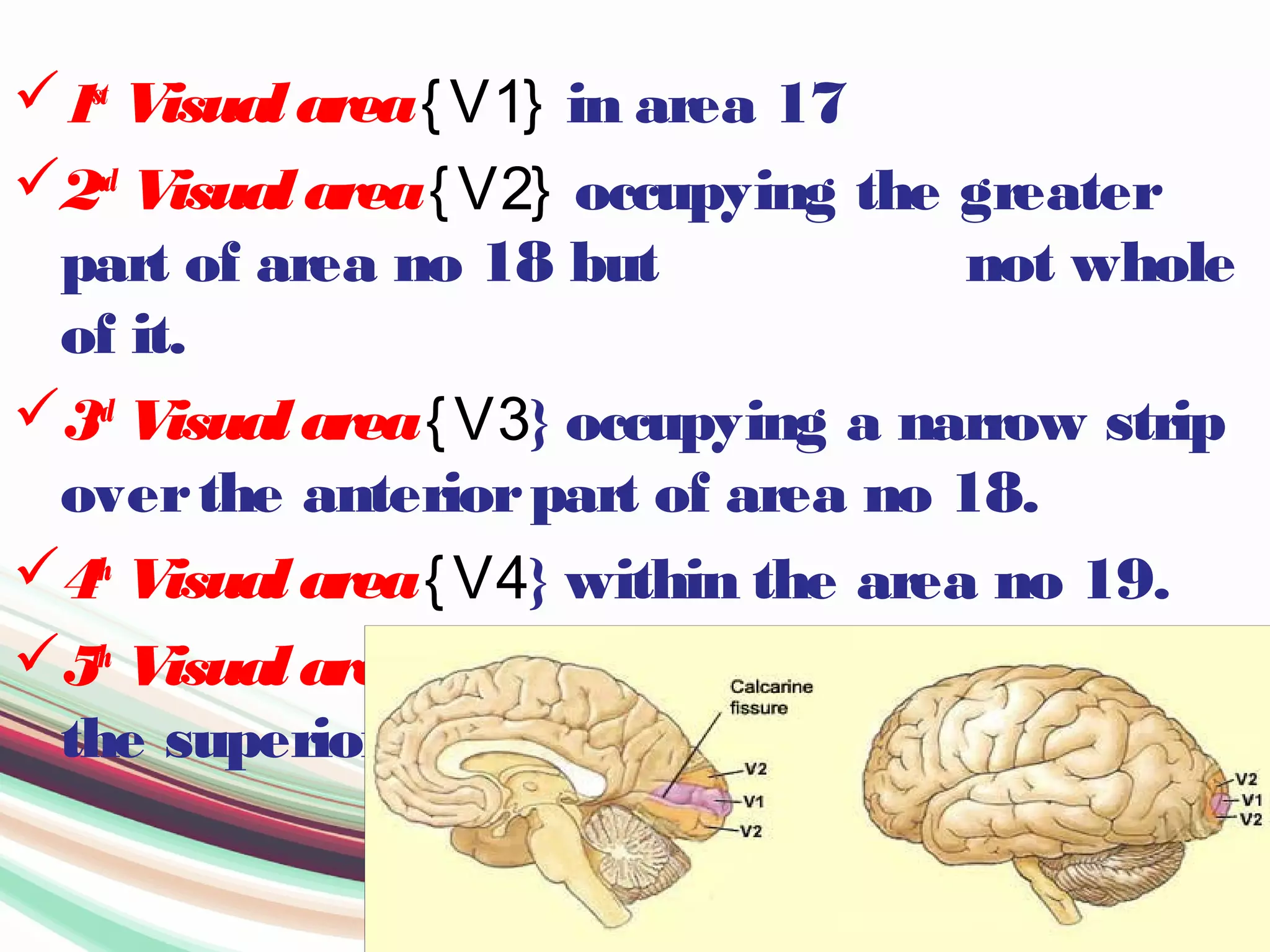
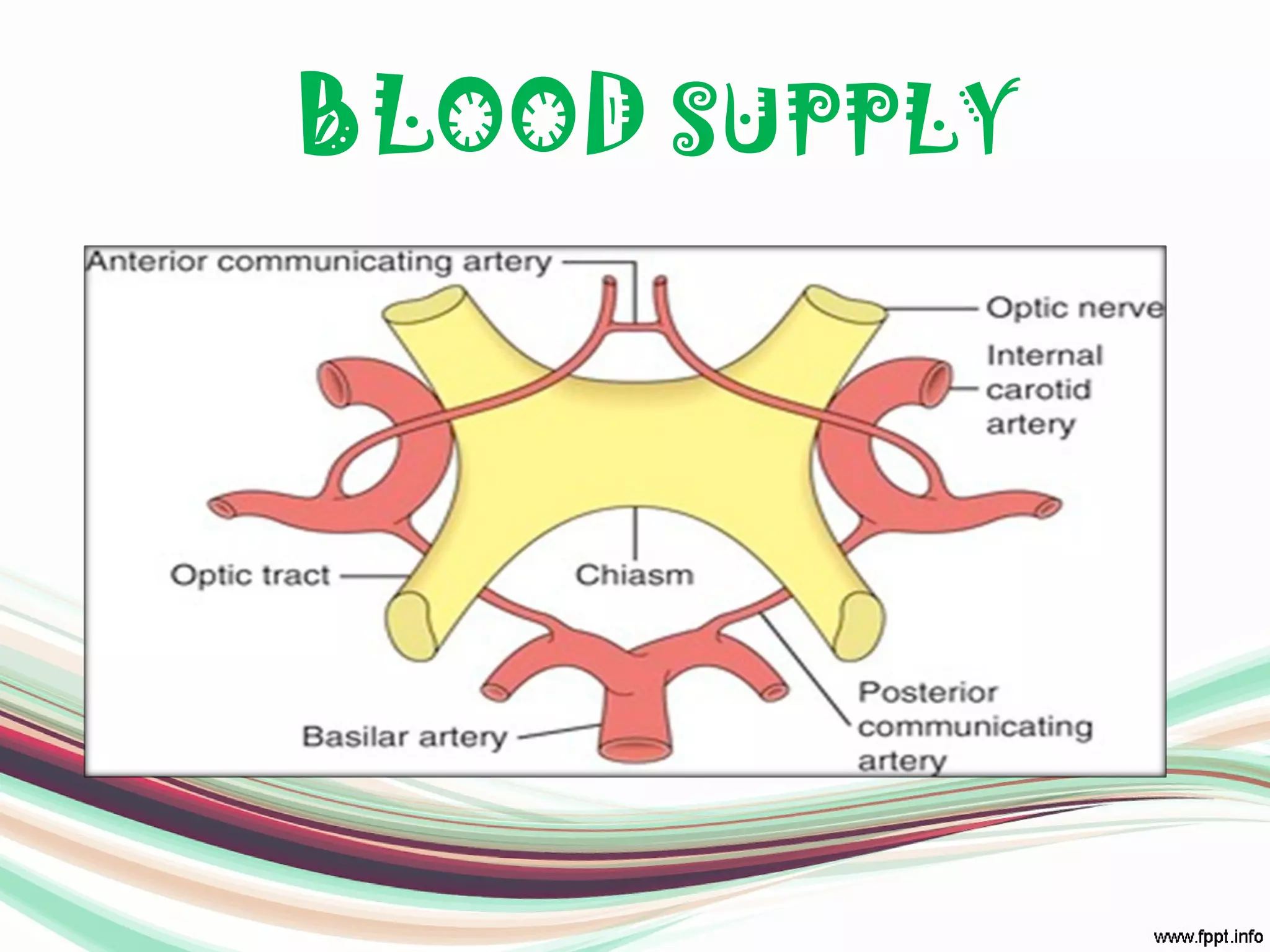
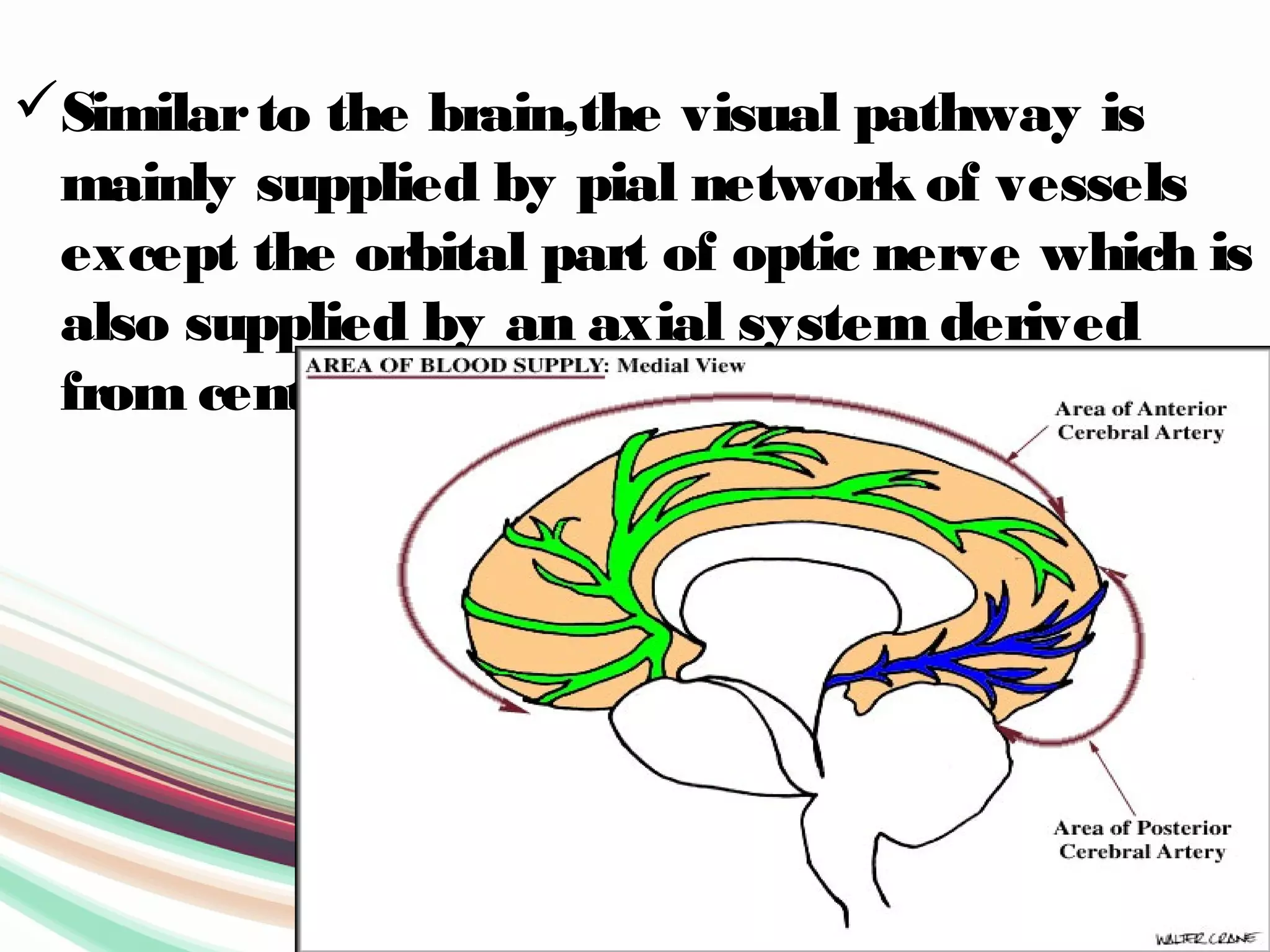
The visual pathway consists of structures that relay visual information from the eyeballs to the visual cortex, including the optic nerve, optic chiasma, optic tract, lateral geniculate body, optic radiations, and the visual cortex. Each component plays a specific role in the transmission and processing of visual stimuli, with the optic chiasma facilitating the crossing of nerve fibers from the nasal retina. The pathway is supplied by arteries connected at the base of the brain, ensuring proper blood flow to support visual processing.