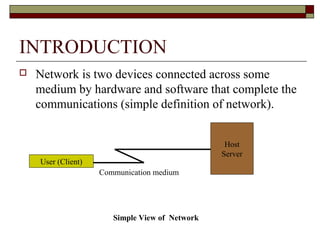
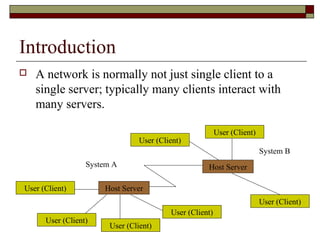
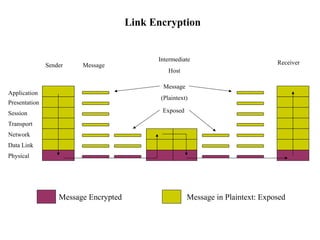
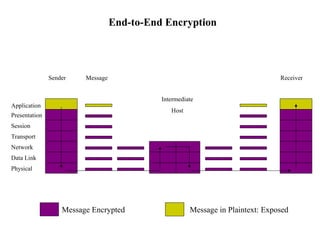
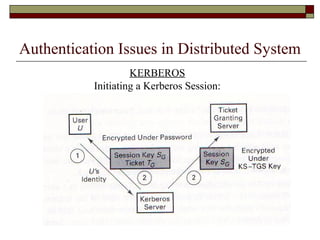
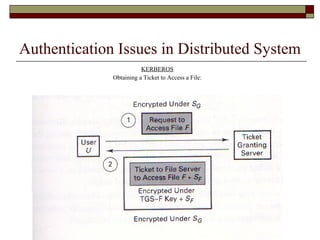
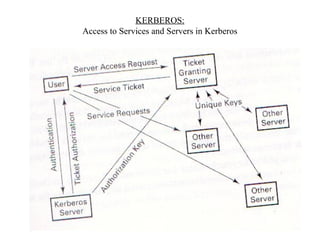
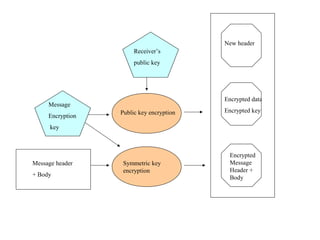
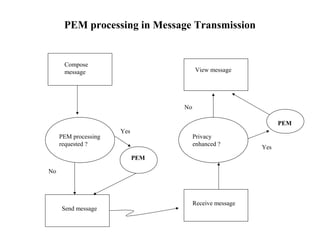
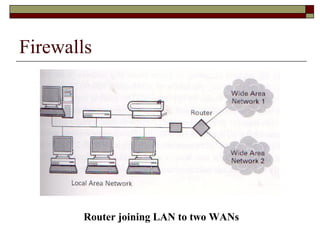
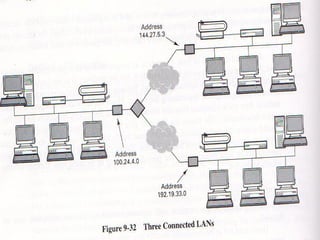
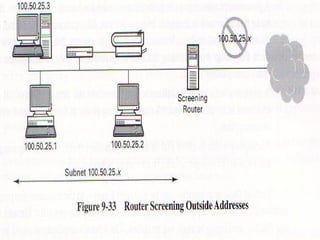
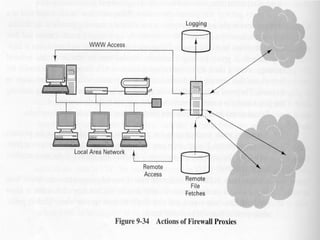
The document discusses security issues in networks and distributed systems. It describes possible network security threats like wiretapping, impersonation, message integrity violations, hacking, and denial of service attacks. It also discusses network security controls like encryption and authentication methods. Specifically, it covers Kerberos, PEM, and PGP for authentication and encryption. It describes different types of firewalls - screening routers, proxy gateways, and guards - and their functions in securing networks. However, it notes that firewalls are not complete solutions and have their own security issues.