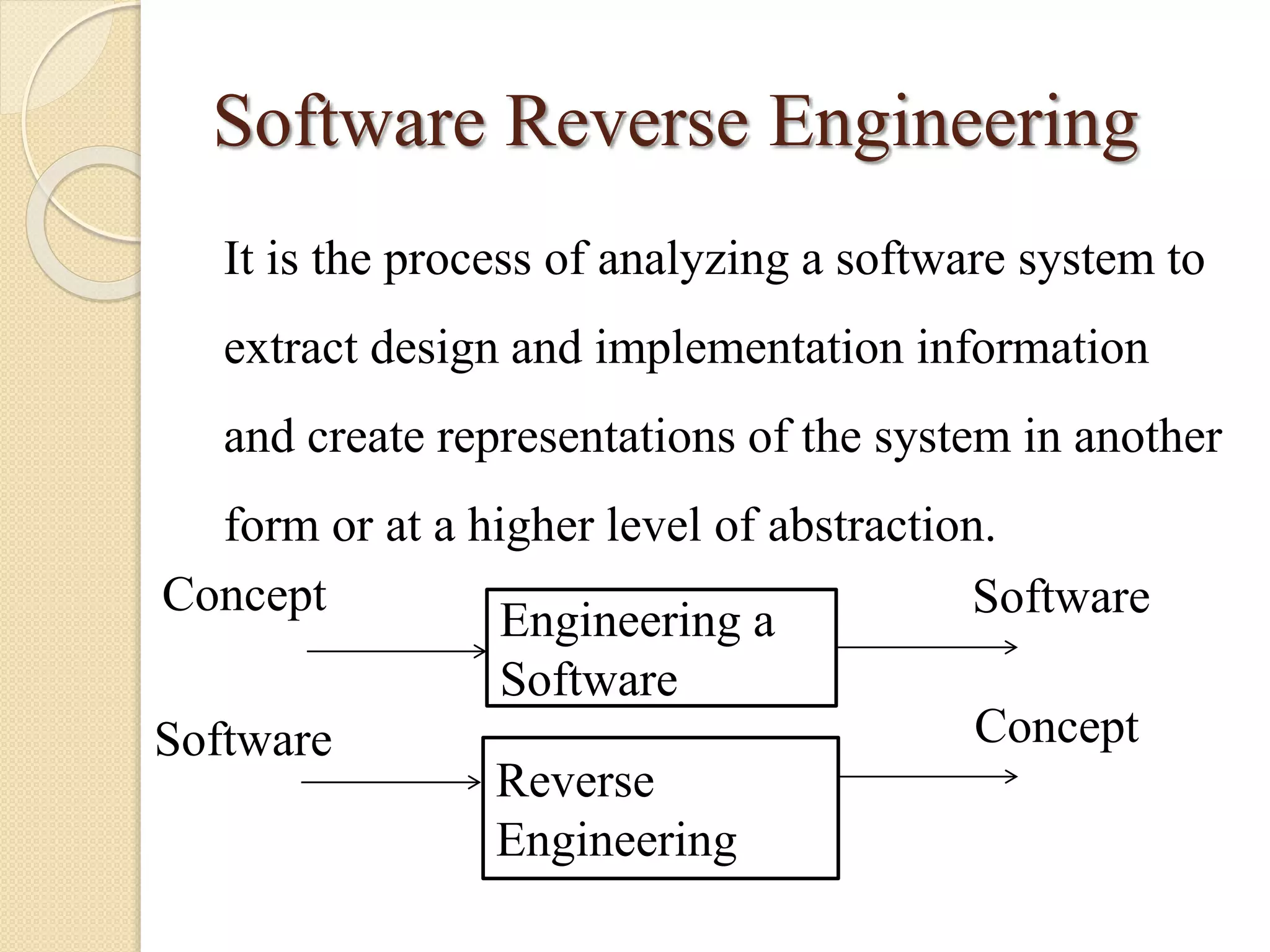
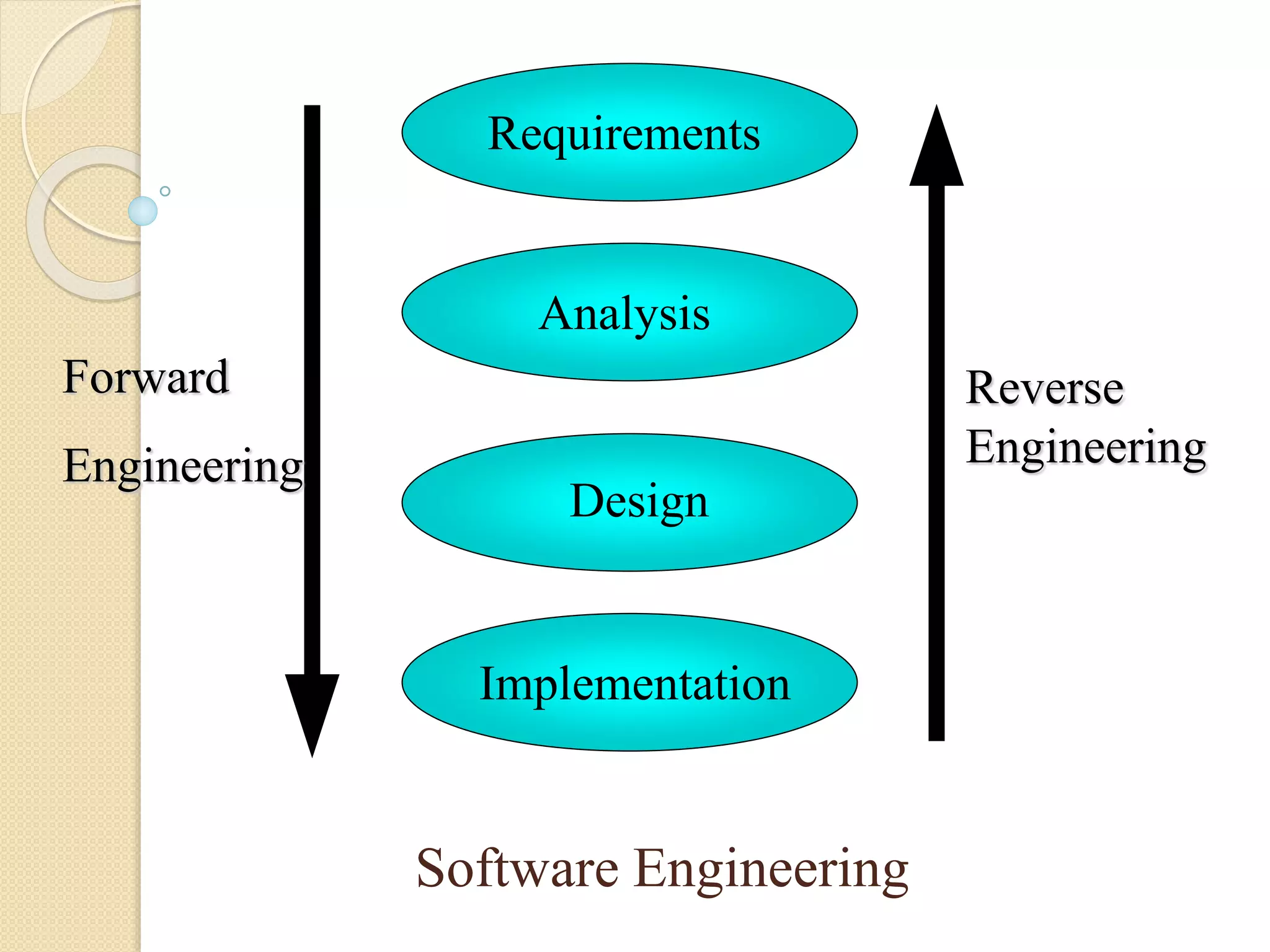
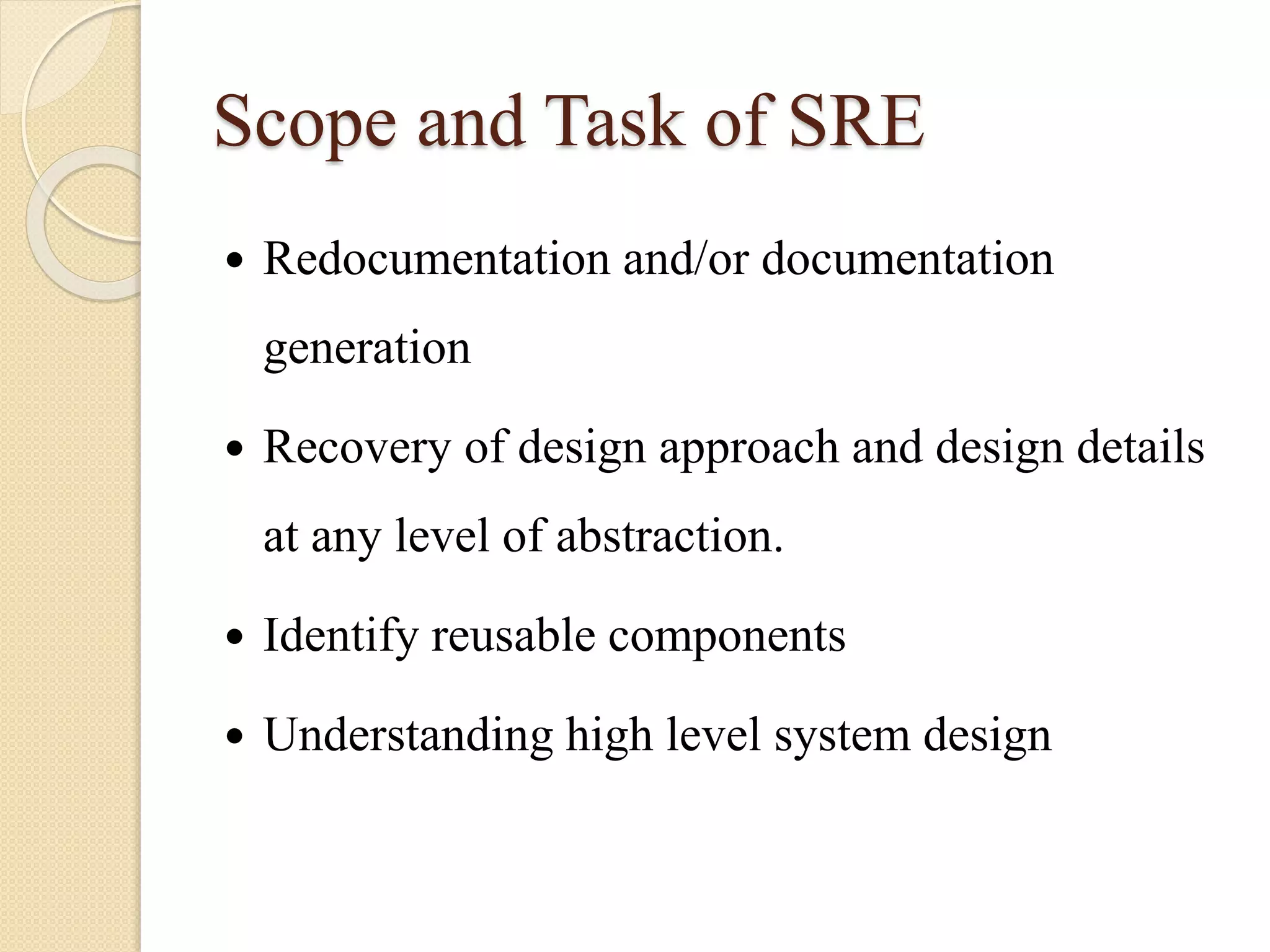
This document discusses software reverse engineering. It defines reverse engineering as extracting knowledge or design information from a man-made system to recreate it at a higher level of abstraction. For software, reverse engineering analyzes a system to understand its design and implementation. It is used to recover lost information, assist with maintenance, enable reuse, and discover flaws. Reverse engineering tools include disassemblers, debuggers, and decompilers. The process involves system and code level analysis to document designs, components, and algorithms from binary code. While it faces limitations like legality issues and missing information, reverse engineering provides important benefits for software development and security analysis.