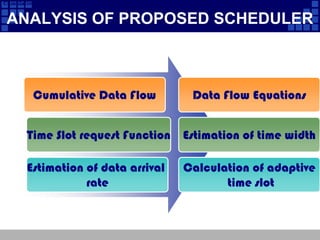
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on proposing an adaptive bandwidth request scheduler for real-time polling service (rtPS) in WiMax networks. The proposed scheduler aims to estimate data arrival rates and calculate adaptive time slot allocations to address problems in the standard rtPS scheduler, such as requests made before grants are received. Analysis shows the adaptive scheduler reduces average queue lengths and delays compared to conventional scheduling. In conclusion, the adaptive approach requires smaller buffers and decreases delays significantly for rtPS traffic.