Embed presentation
Downloaded 148 times


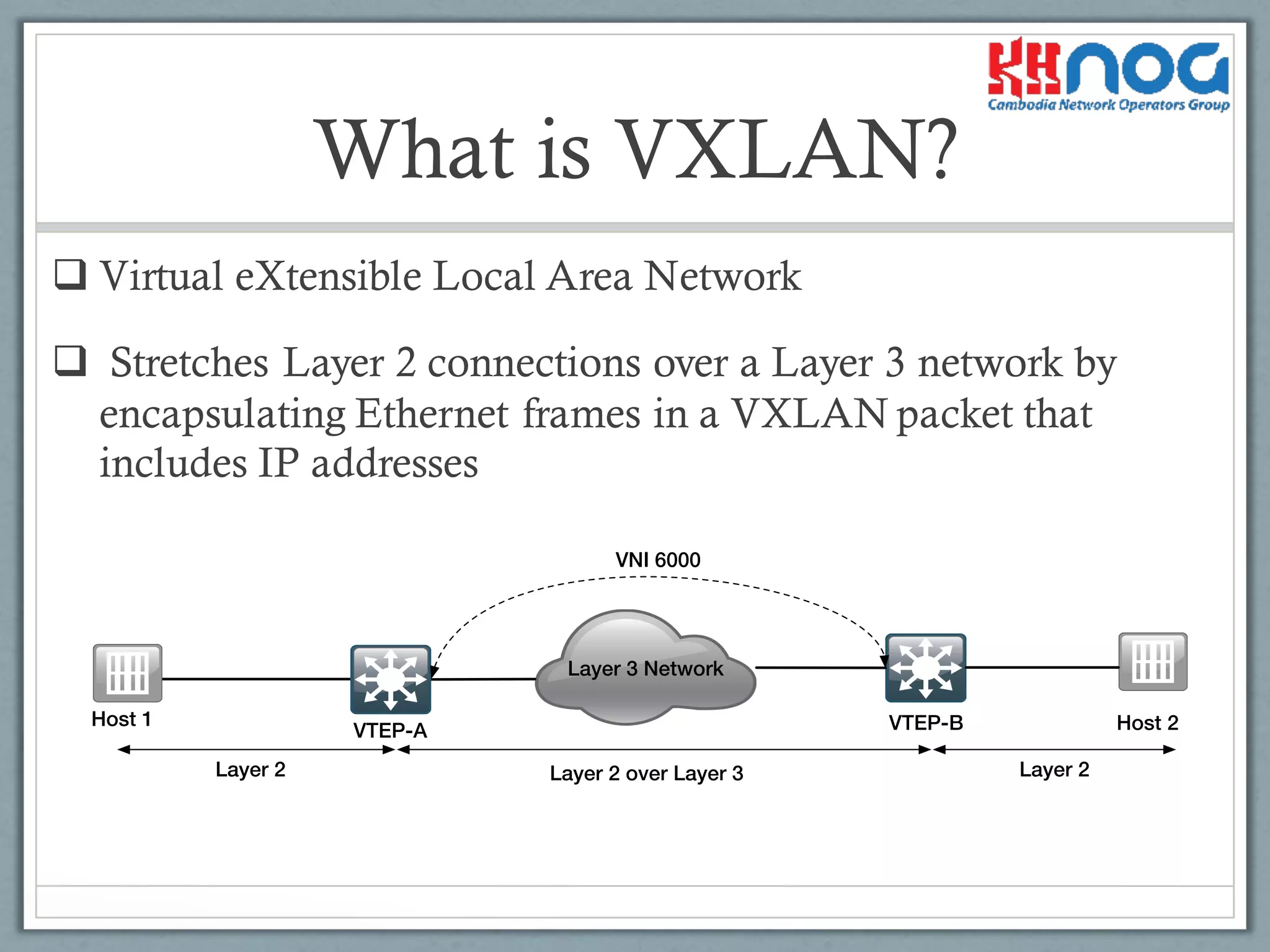
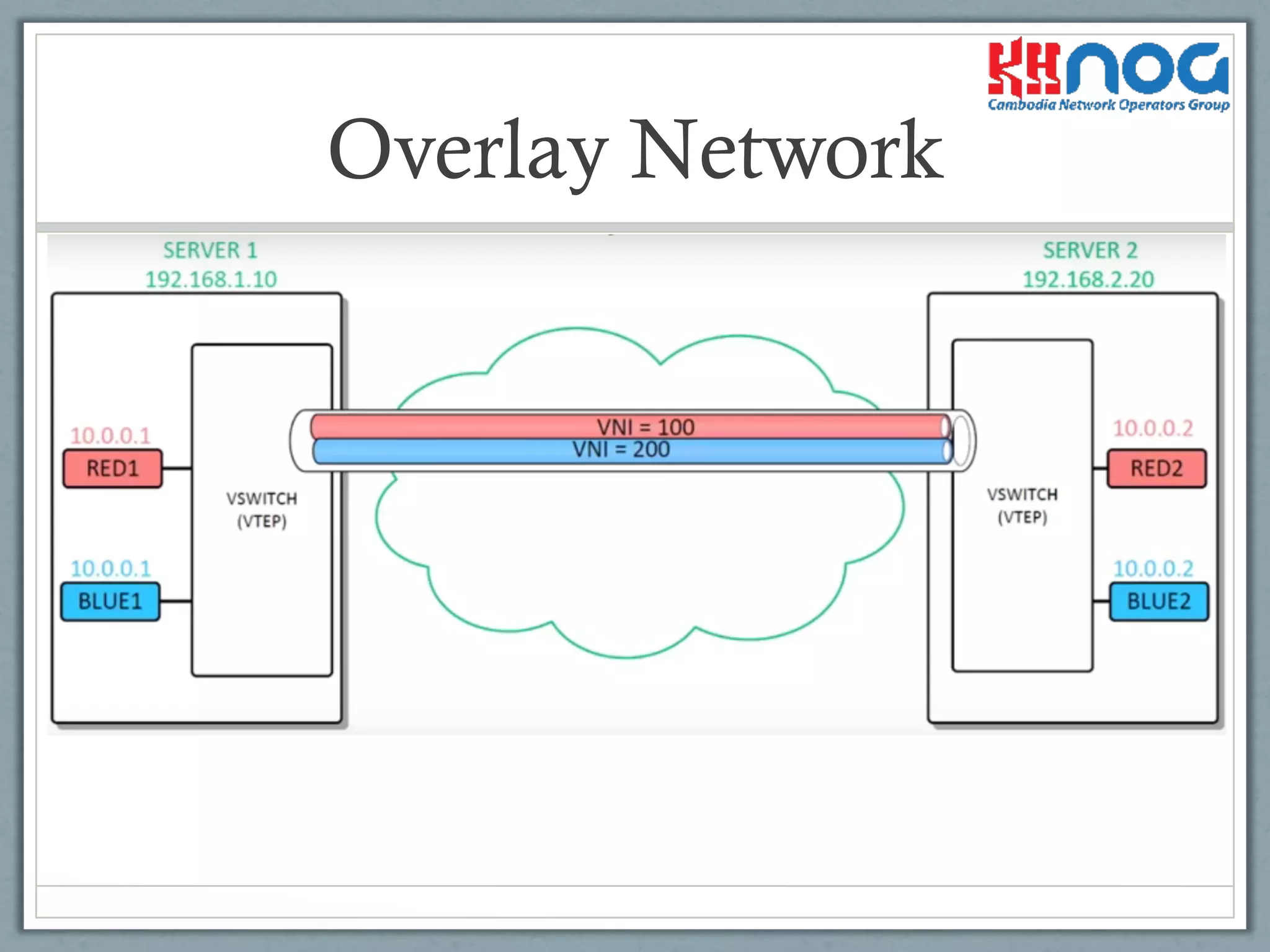



VXLAN allows layer 2 segments to span layer 3 networks by encapsulating Ethernet frames within UDP packets. This allows virtual machines and servers to communicate securely across physical networks as if they were on the same local area network. VXLAN uses VXLAN Tunnel End Points and a VXLAN Network Identifier to encapsulate packets and identify virtual network segments. Up to 16 million virtual networks can be created, enabling data center tenants and workloads to be isolated from each other while residing on the same physical network.
Overview of VXLAN, presented by Math Tea from eintellego Networks on March 30, 2016.
Slide outlines the topics discussed: Introduction, Benefits, and Reference for VXLAN.
VXLAN is a Virtual eXtensible LAN enabling Layer 2 over Layer 3 by encapsulating Ethernet frames.
VXLAN supports 16 million+ segments, facilitates VM migration across networks, and enhances performance.
VNI (24 bits) allows the creation of over 16 million VXLAN segments for multi-tenant data centers.
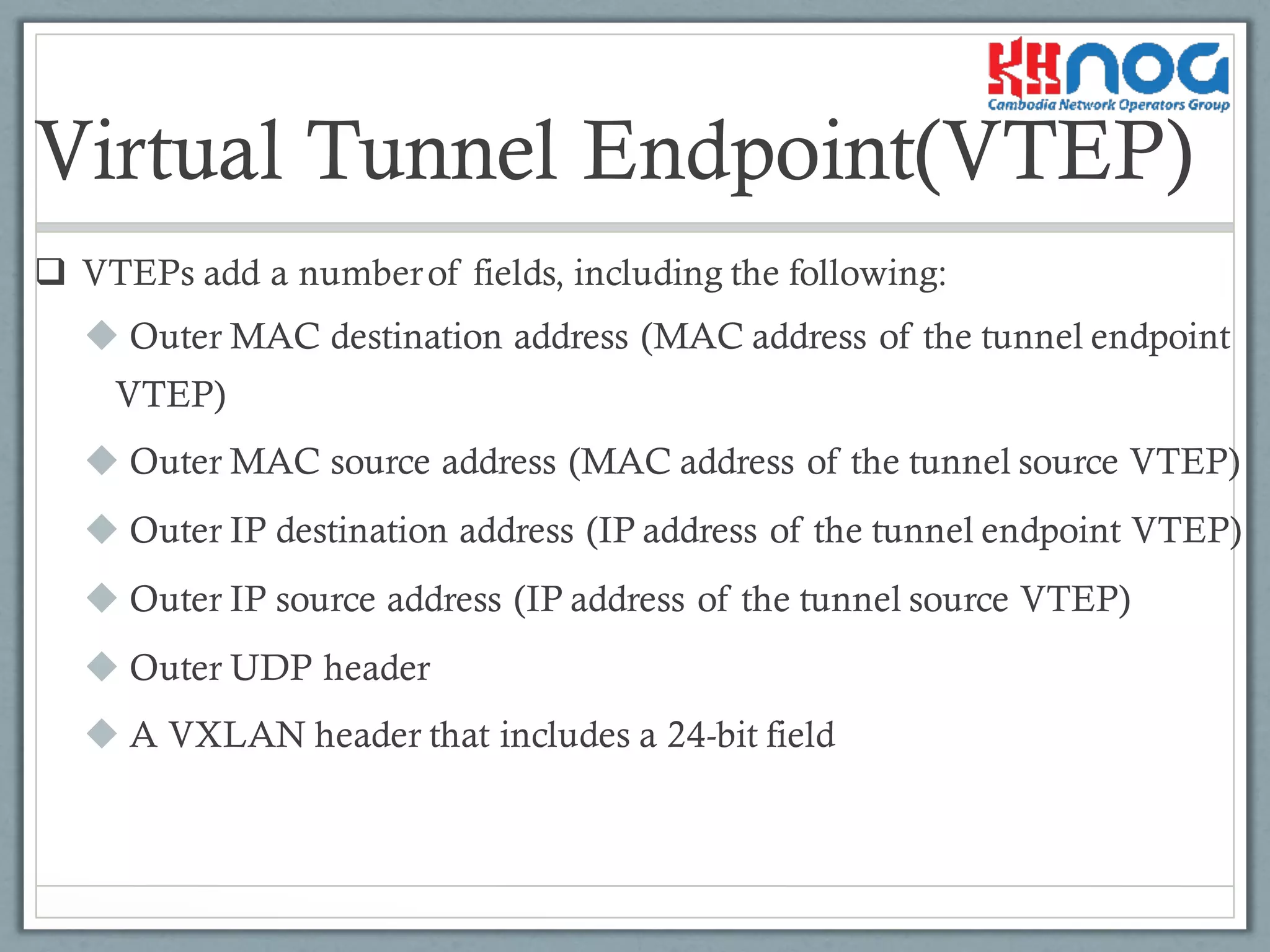
VTEPs are devices for VXLAN traffic encapsulation and decapsulation; they can be hosts or network devices.
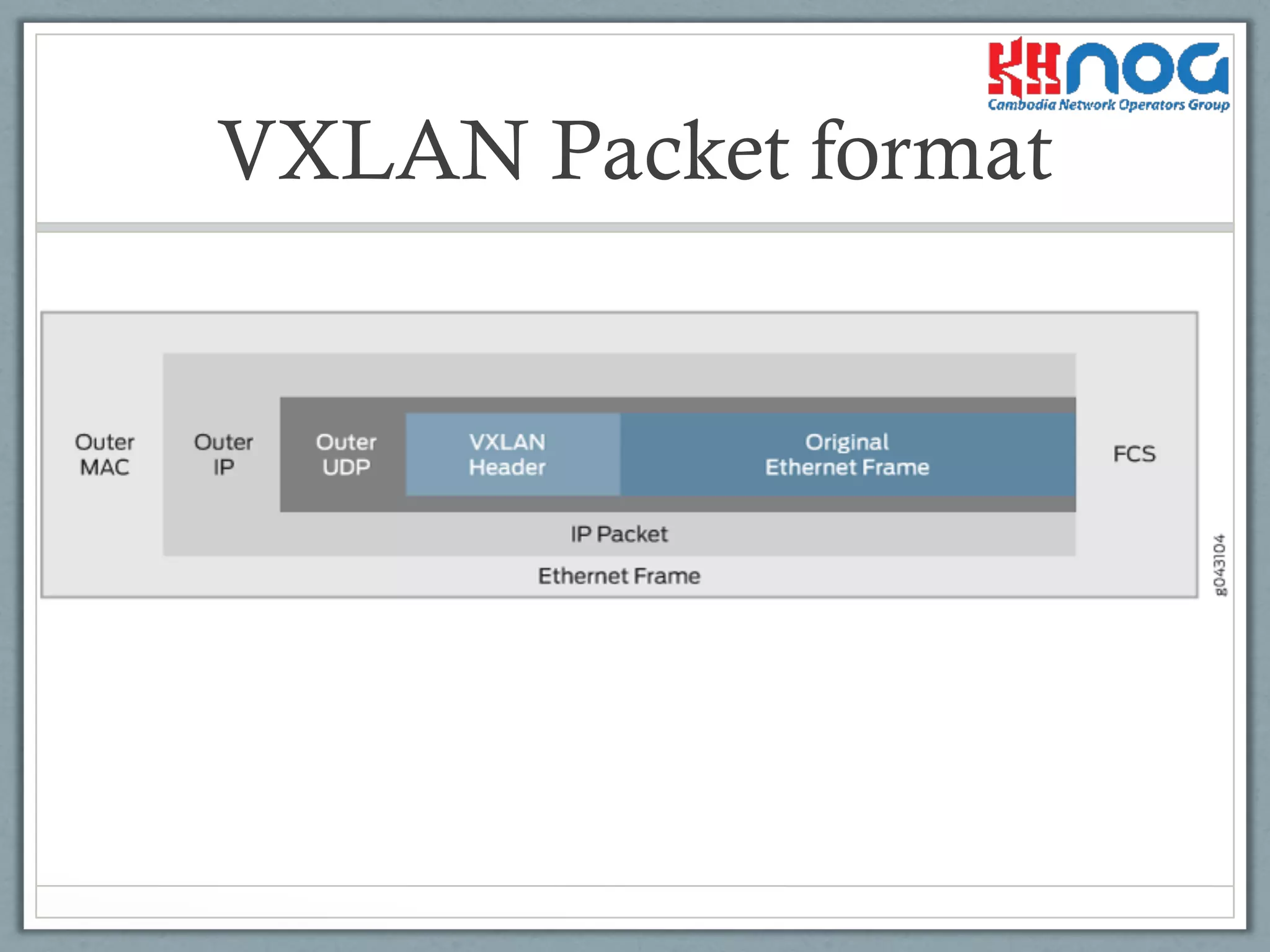
VTEPs add fields for MAC and IP addresses, an outer UDP header, and a VXLAN header.
Describes VXLAN packet forwarding based on labels with encapsulation and normal IP routing.
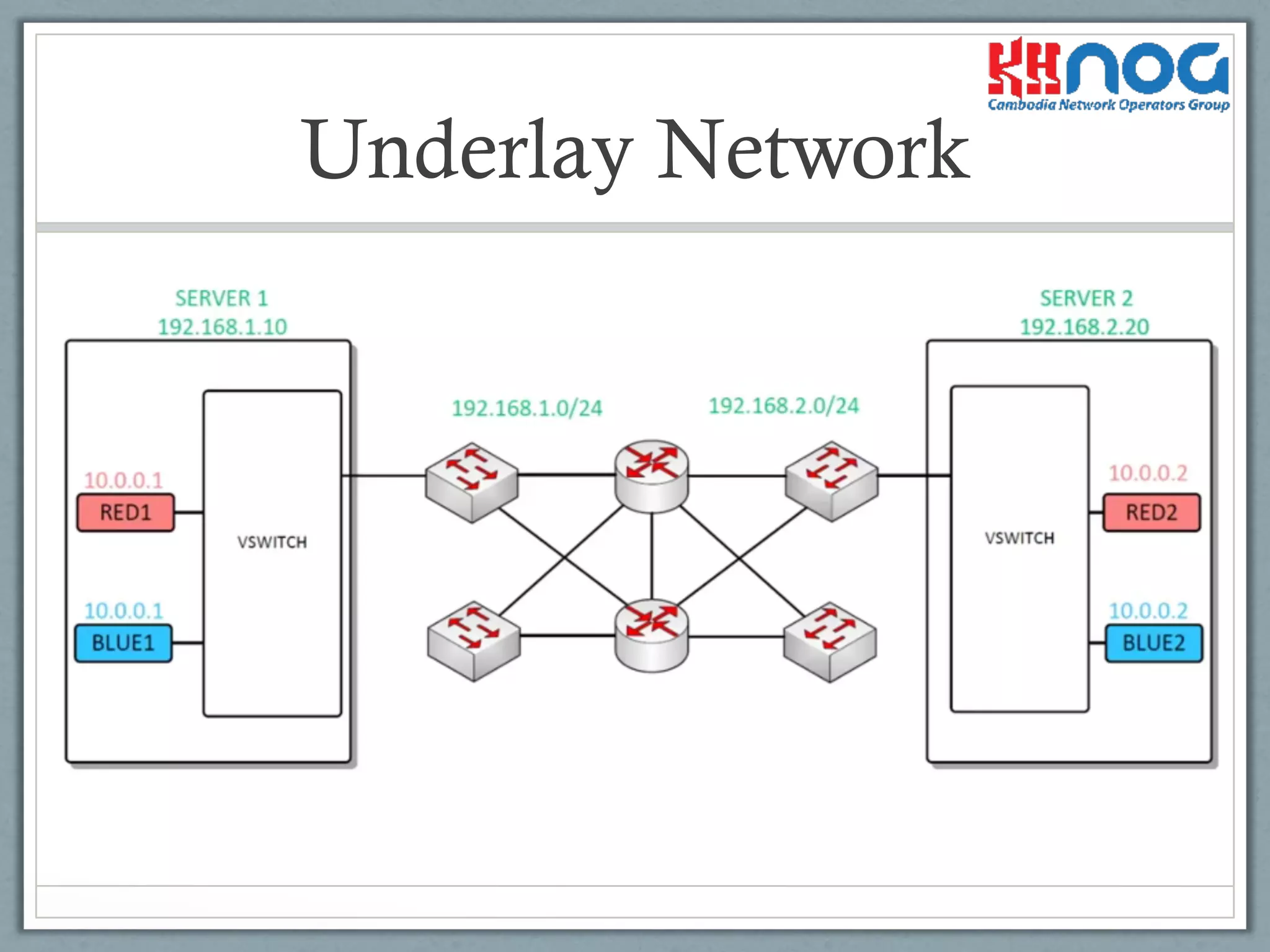
Representation of the underlying network that VXLAN operates over.
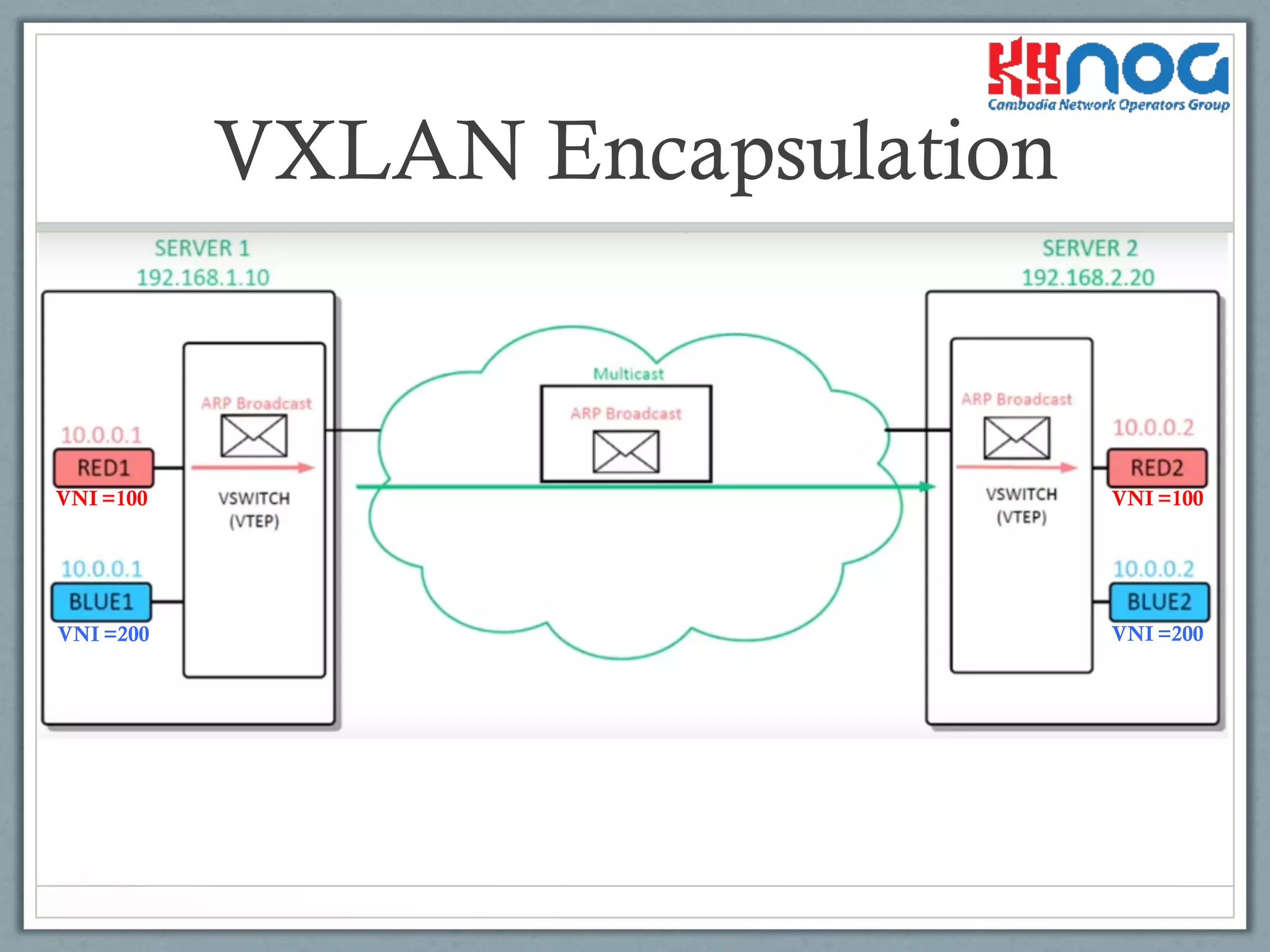
Illustration of how different VNI values are managed in VXLAN encapsulation.
Representation of the network that overlays the underlay network using VXLAN technology.
Provides links to resources such as RFCs and documentation related to VXLAN.












