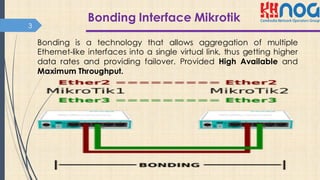
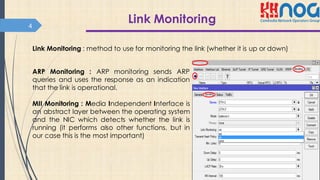
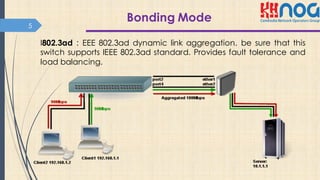
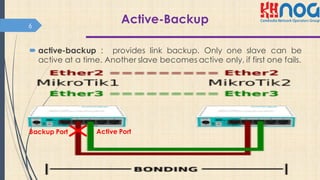
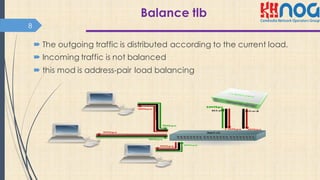
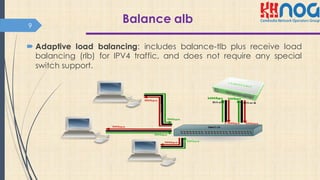
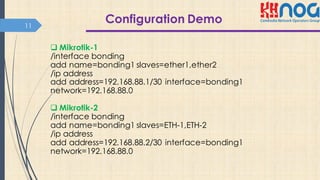
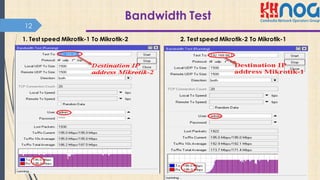
This document discusses bonding interfaces in Mikrotik routers. It begins with an overview of bonding and its benefits of higher throughput and failover. It then covers the different options for link monitoring and bonding modes, including active-backup, load balancing, and broadcast modes. It provides an example configuration of bonding two Ethernet interfaces together. Finally, it proposes testing the bonded bandwidth and provides references for further reading.