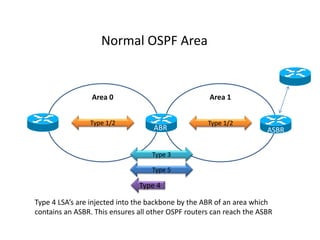
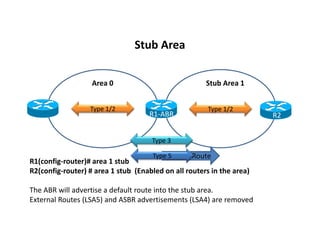
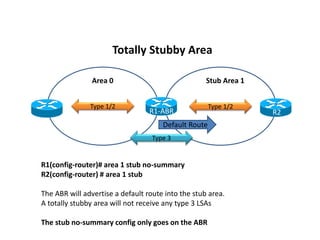
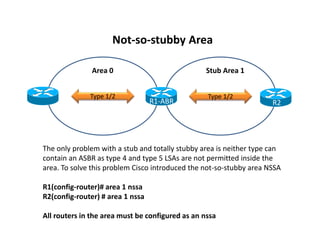
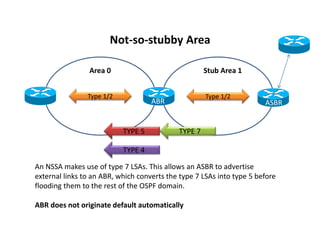
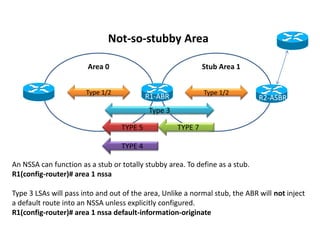
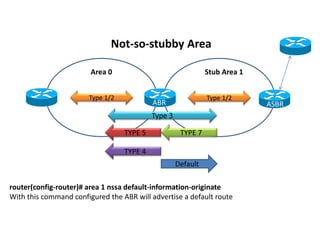
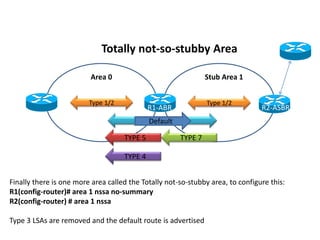
OSPF stub areas, totally stubby areas, and not-so-stubby (NSSA) areas are specialized area types that control the routing information distributed within the area. Stub areas allow only Type 1 and 2 LSAs, and the ABR will advertise a default route into the stub area. NSSAs function similarly but also allow an ASBR to advertise external routes using Type 7 LSAs, which the ABR converts to Type 5 LSAs. A totally stubby area receives no Type 3 LSAs, while a totally NSSA area also filters Type 3 LSAs and relies on a default route from the ABR.