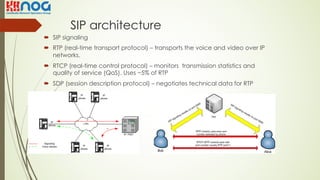
The document discusses Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and its relation to IP telephony, highlighting the differences in capacity and diversity between traditional telephony and IP networks. It details SIP architecture, signaling messages, and real-time transport protocols for voice and video transmission. Additionally, the document provides codec information, packetization periods, and features relevant to Voice over IP (VoIP) communications.





![SDP (session description protocol)
It’s a protocol that describes the media of a session.
Session description
v= (protocol version number, currently only 0)
o= (originator and session identifier : username, id, version number, network address)
s= (session name : mandatory with at least one UTF-8-encoded character)
c=* (connection information—not required if included in all media)
b=* (zero or more bandwidth information lines)
Media description (if present)
m= (media name and transport address, and set of codecs)
i=* (media title or information field)
c=* (connection information — optional if included at session level)
b=* (zero or more bandwidth information lines)
k=* (encryption key)
a=* (zero or more media attribute lines — overriding the Session attribute lines, with codec and sampling rate)
[Request]
v=0
o=Makara 2890844526 2890844526 IN IP4 10.120.42.3
s= KHNOG
c=IN IP4 10.120.42.3
m=audio 49170 RTP/AVP 0 8 97 (Real-time protocol, Audio-video profile)
a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000
a=rtpmap:8 PCMA/8000
a=rtpmap:97 iLBC/8000
m=video 51372 RTP/AVP 31 32
a=rtpmap:31 H261/90000
a=rtpmap:32 MPV/90000
[Answer]
v=0
o=Vibol 2808844564 2808844564 IN IP4 10.120.32.12
s=KHNOG
c=IN IP4 10.120.32.12
m=audio 49174 RTP/AVP 0
a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000
m=video 49170 RTP/AVP 32
a=rtpmap:32 MPV/90000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sipsessioninitiationprotocol-170223020837/85/SIP-Session-Initiation-Protocol-7-320.jpg)