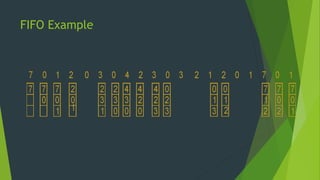
The document discusses different page replacement algorithms used in operating systems. It explains that paging allows processes to have non-contiguous physical address spaces by retrieving data from secondary storage in blocks called pages. When a process tries to access a page not currently in memory, a page fault occurs and the operating system must handle it. If all memory pages are in use, one must be replaced to load the requested page. Common algorithms discussed are FIFO, LRU, and optimal page replacement. FIFO replaces the oldest page, but ignores locality. LRU tracks recent usage and replaces the least recently used page, avoiding Belady's Anomaly but being expensive to implement.