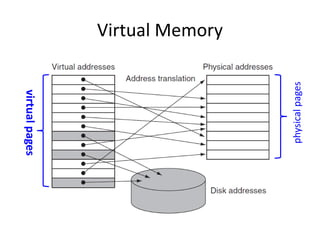
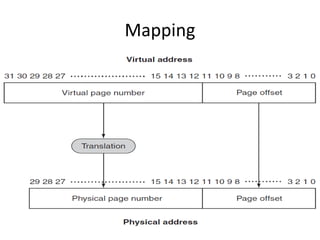
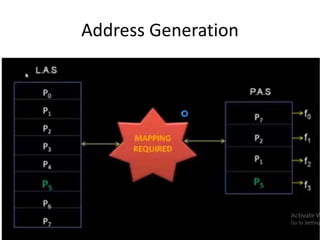
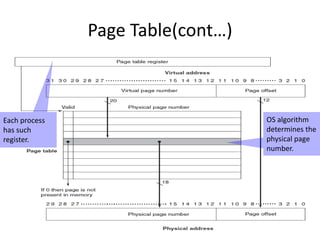
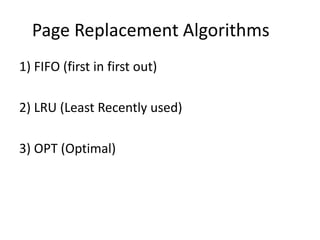
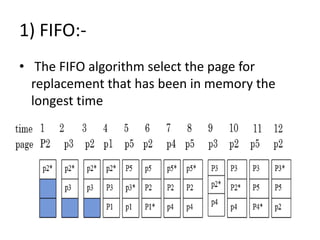
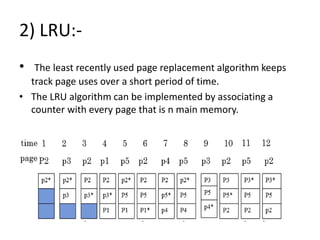
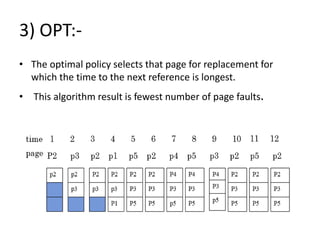
Virtual memory allows a program to use more memory than the physical memory available by storing inactive memory pages on disk. It divides programs into pages of equal size and maps pages to frames using a page table. When a page is accessed that is not in memory, a page fault occurs and an algorithm like FIFO or LRU selects a frame to replace based on what page has been in memory longest or least recently used. This allows more programs to run simultaneously by swapping pages in and out of physical memory.