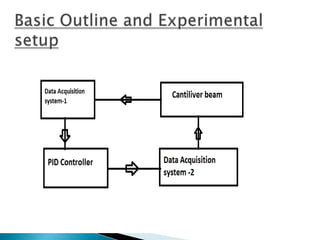
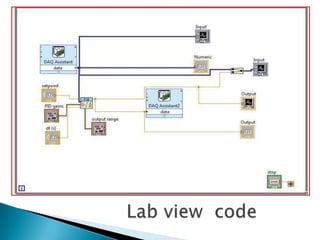
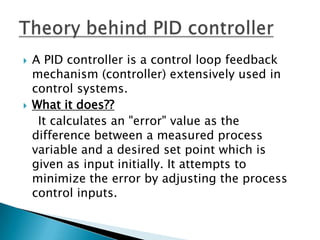
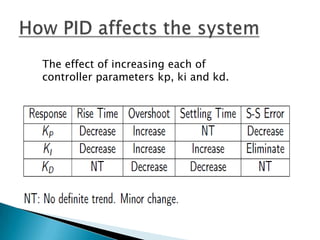
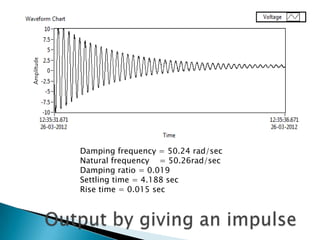
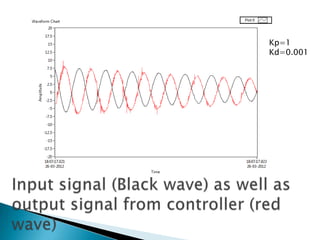
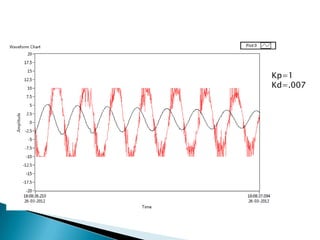
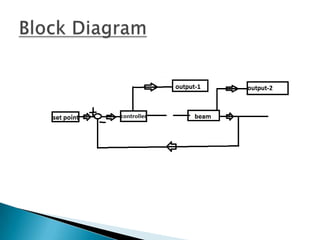
The document outlines a study on active and passive vibration control techniques, detailing the use of PID controllers in managing vibrations in a structure. It discusses material specifications, experimentation, and controller tuning methods, emphasizing the need for amplifiers to actuate the control systems effectively. Experimental results highlight the parameters for designing a PID controller and the challenges encountered in the setup.