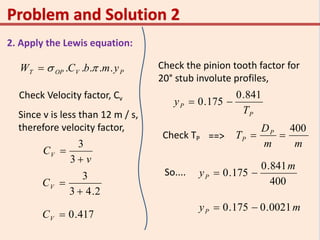
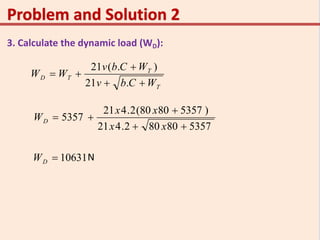
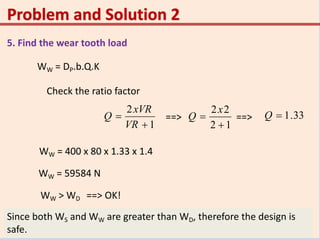
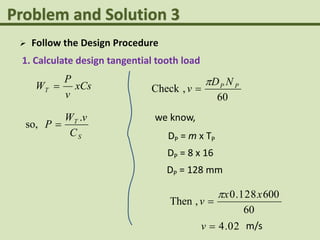
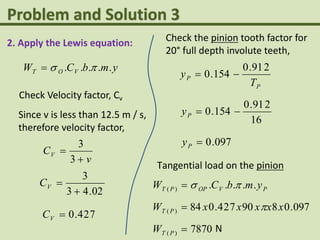
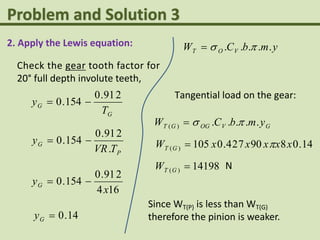
This problem involves designing a gear drive system to meet specific power, speed, and ratio requirements.
1. The key specifications are: 15 kW power at 1200 rpm driving a compressor at 300 rpm, with a gear ratio of 4:1. The shafts are 400mm apart. The pinion is forged steel with 210 MPa allowable stress, and the gear is cast steel with 140 MPa stress.
2. A two-stage gear train layout is proposed to achieve a 9:1 ratio from an input of 960 rpm to transmit 2 kW power. The shafts are 200mm apart with coaxial input/output.
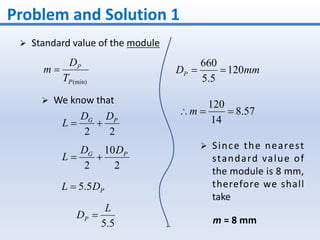
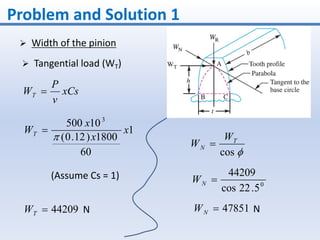
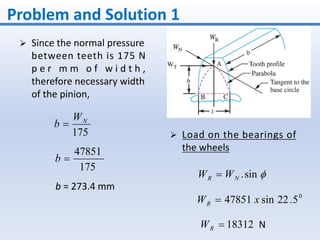
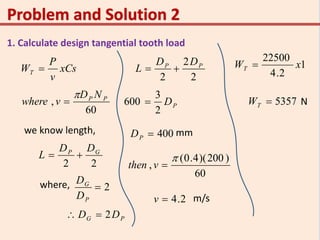
3. The solution involves calculating the module, pitch diameter, number