1. The document outlines the key characteristics and classifications of vertebrates.
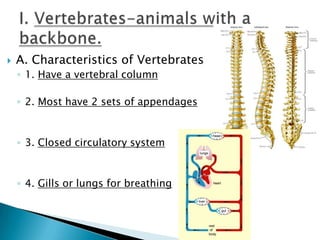
2. Vertebrates are defined as having a backbone and most have two sets of appendages. They have a closed circulatory system and breathe using gills or lungs.
3. Vertebrates are divided into 7 classes - jawless fish, cartilaginous fish, bony fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals - based on their physical traits and reproduction methods.