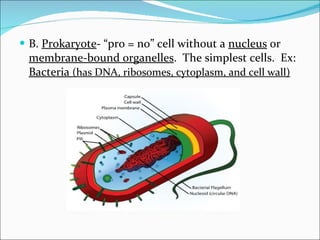
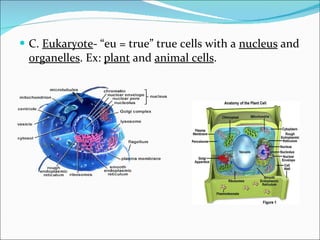
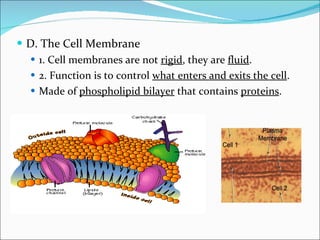
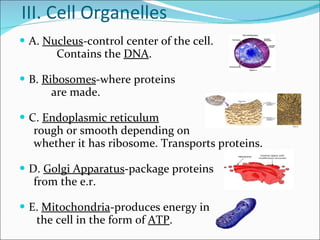
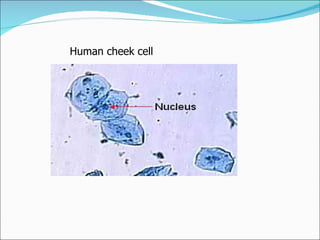
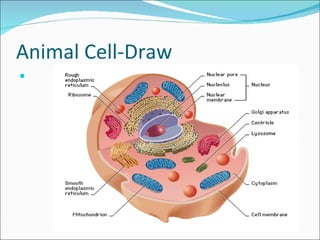
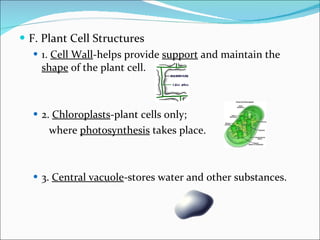
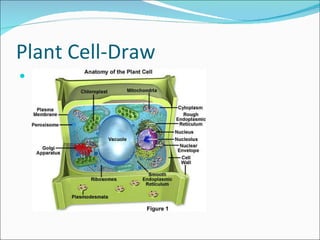
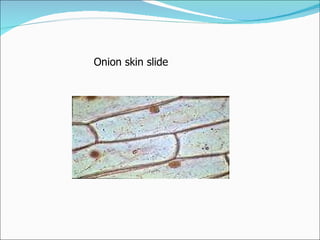
Cell structure can be observed under microscopes. Cells are the basic units of structure and function of living things. There are two main types of cells: prokaryotes which lack nuclei and organelles, and eukaryotes which have nuclei and organelles. The cell membrane controls what enters and exits the cell and is made of a phospholipid bilayer containing proteins. Major cell organelles include the nucleus which contains DNA, ribosomes which produce proteins, and mitochondria which generate energy.