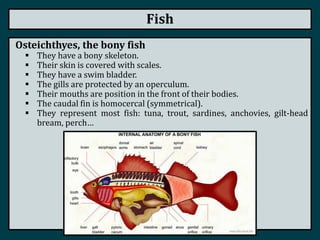
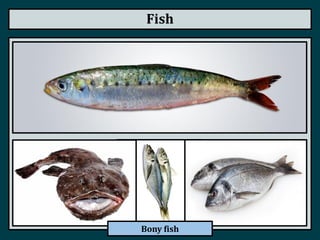
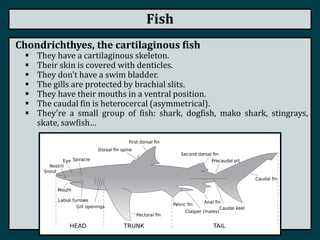
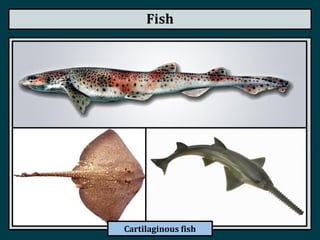
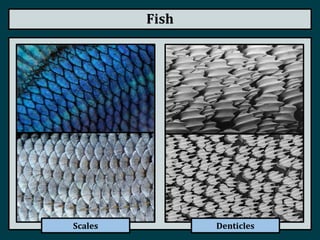
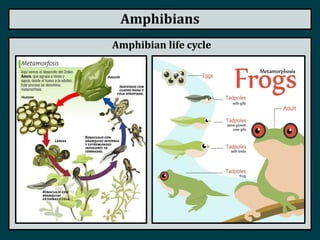
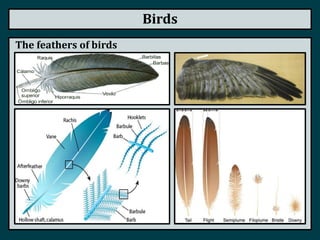
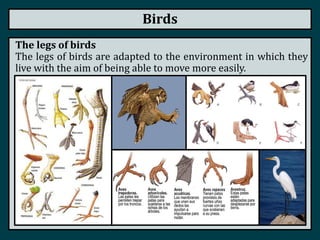
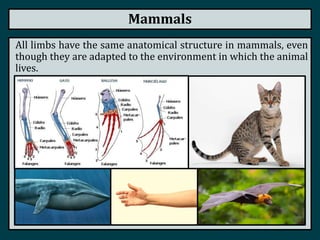
This document summarizes the classification of vertebrate animals. It describes five groups: fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. For each group, it outlines key distinguishing characteristics, such as their skeletal structure, skin/scales, limbs, reproduction methods, temperature regulation, habitats and examples of common animals in each group. It also describes some subgroups within each main category, such as bony fish vs. cartilaginous fish, and anurans vs. urodeles for amphibians.