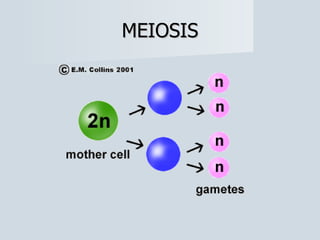
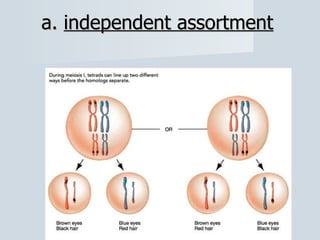
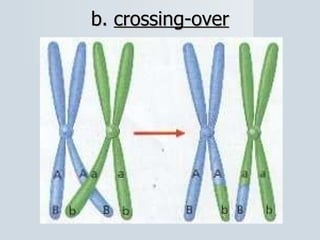
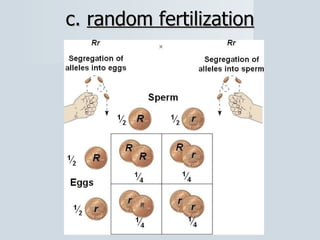
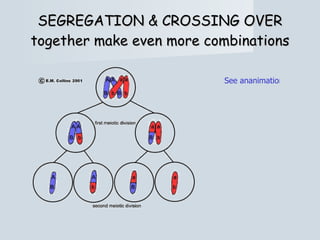
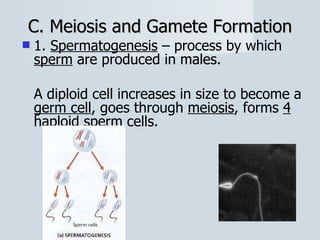
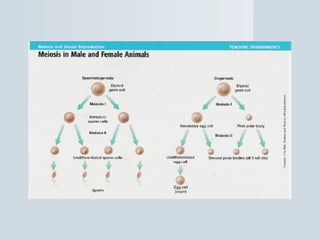
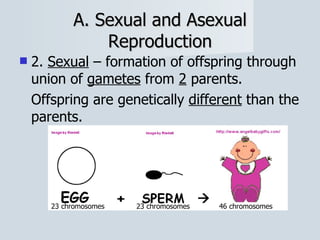
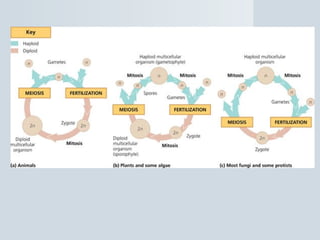
Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes in cells from diploid to haploid, forming four haploid gametes from one diploid cell. This occurs through the processes of independent assortment, crossing over, and random fertilization, which contribute to genetic variation and allow for evolution. Meiosis produces either sperm cells in males through spermatogenesis or egg cells in females through oogenesis, where the cytoplasm unequally divides. Sexual reproduction then involves the union of haploid gametes from two parents to form a diploid zygote, resulting in offspring that are genetically different from the parents.