Embed presentation
Download to read offline



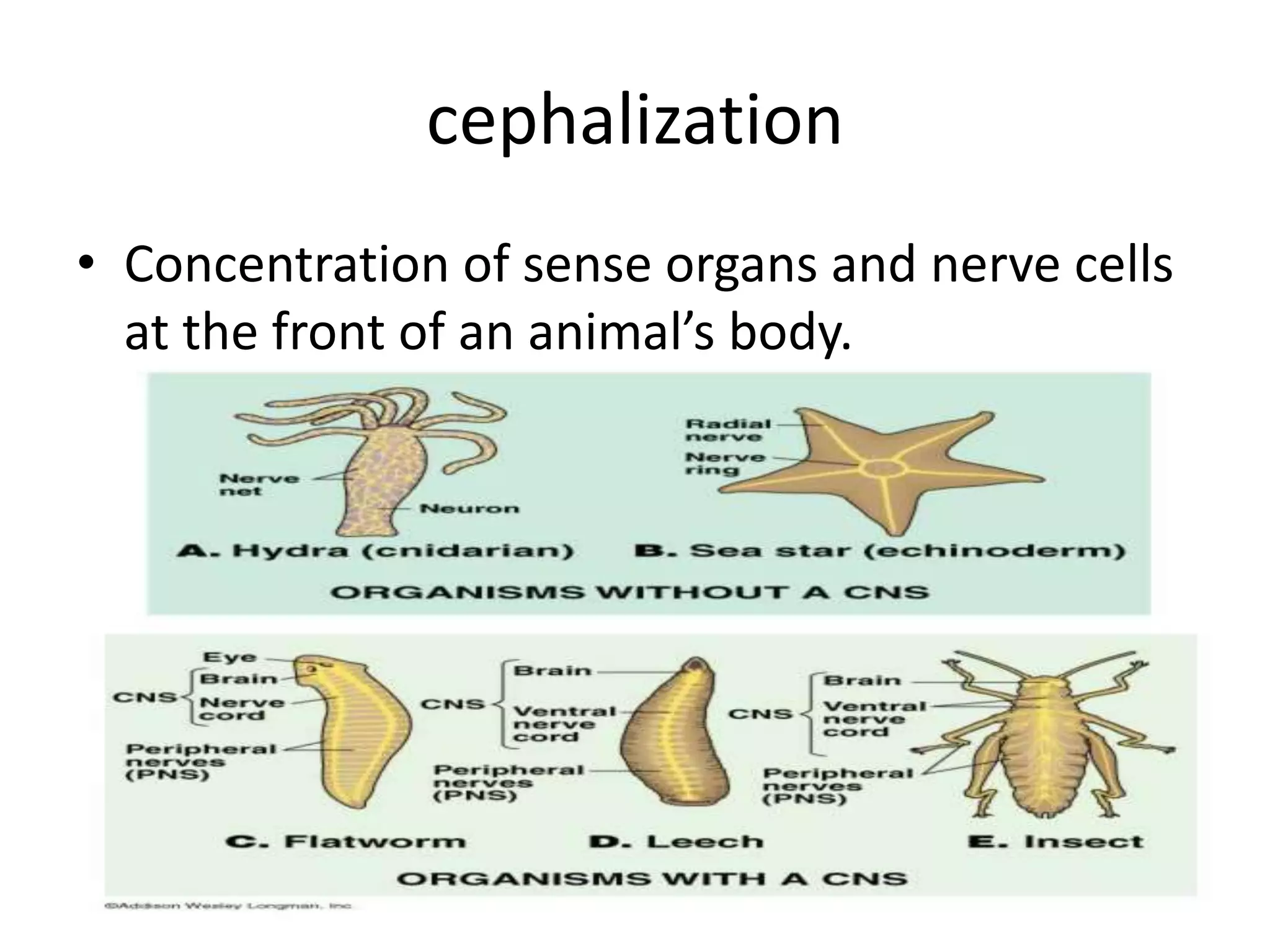




Radial and bilateral symmetry, cephalization, and the presence of a coelom are important characteristics in invertebrate evolution. Radial symmetry is seen in organisms like sea anemones where body parts repeat around the center, while bilateral symmetry is a single dividing line making two halves in worms and arthropods. Cephalization concentrated sense organs and nerves at the front, allowing more sophisticated responses. A true coelom is a fluid-filled cavity lined with mesoderm tissue, found in more complex phyla.







