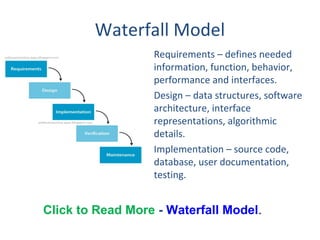
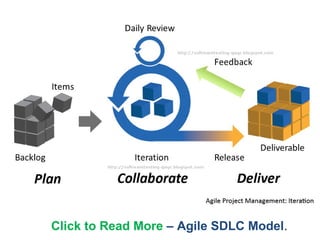
The document discusses several software development life cycle (SDLC) models including waterfall, iterative waterfall, V-shaped, RAD, incremental, spiral, and agile models. It also covers agile methods like Scrum and extreme programming. The document defines the capability maturity model (CMM) which measures an organization's software process maturity across five levels from initial to optimizing.