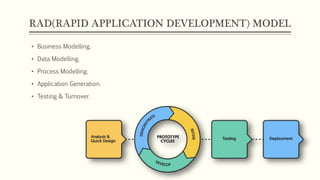
The document discusses various software engineering models for an advanced employee management system, detailing the incremental model as the selected approach due to its flexibility and ability to handle changing requirements. It contrasts this with the rejected waterfall model, citing its rigid structure and difficulty in accommodating changes. The document highlights each model's advantages and disadvantages, aiming to determine the most suitable design and implementation strategy.