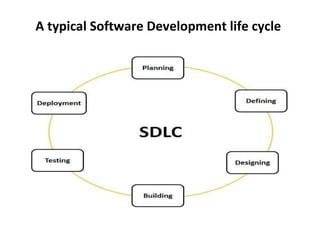
The document describes the six main phases of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC): 1) Planning and Requirement Analysis, 2) Defining Requirements, 3) Designing the product architecture, 4) Building or Developing the Product, 5) Testing the Product, and 6) Deployment in the Market and Maintenance. Each phase is explained in 1-2 sentences with an emphasis on gathering requirements, designing the architecture, coding, testing, and deploying the final product.