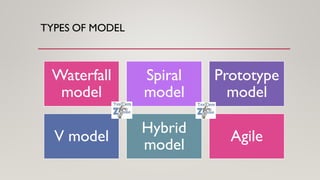
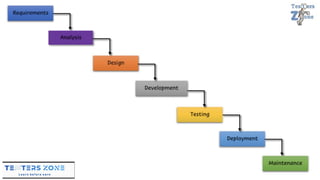
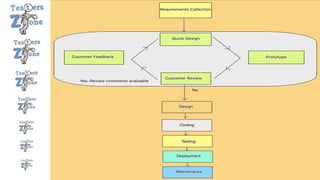
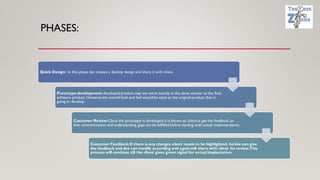
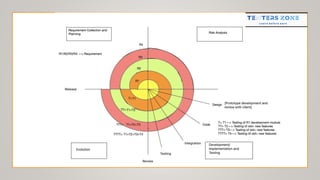
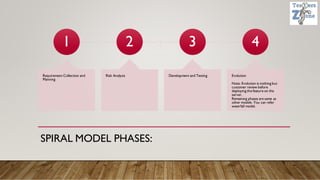
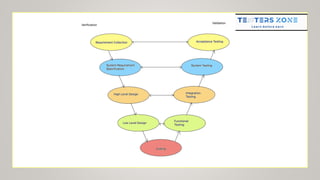
The document discusses various software development models, including the Waterfall, Spiral, Prototype, V, Agile, and Hybrid models. Each model is defined by its specific phases, advantages, and disadvantages, emphasizing client interaction and project management strategies. The document highlights when to use each model based on project requirements, complexity, and stakeholder involvement.