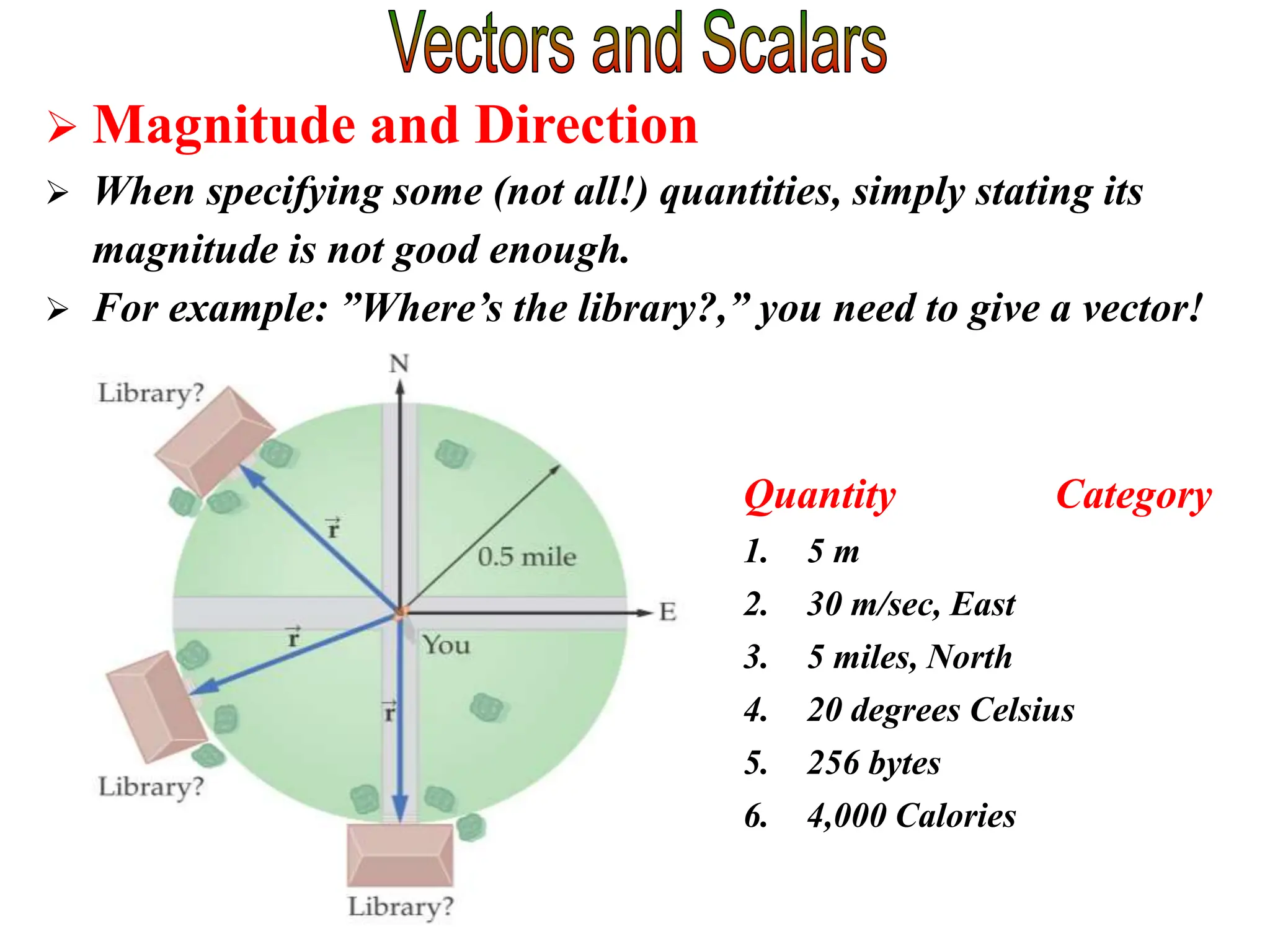
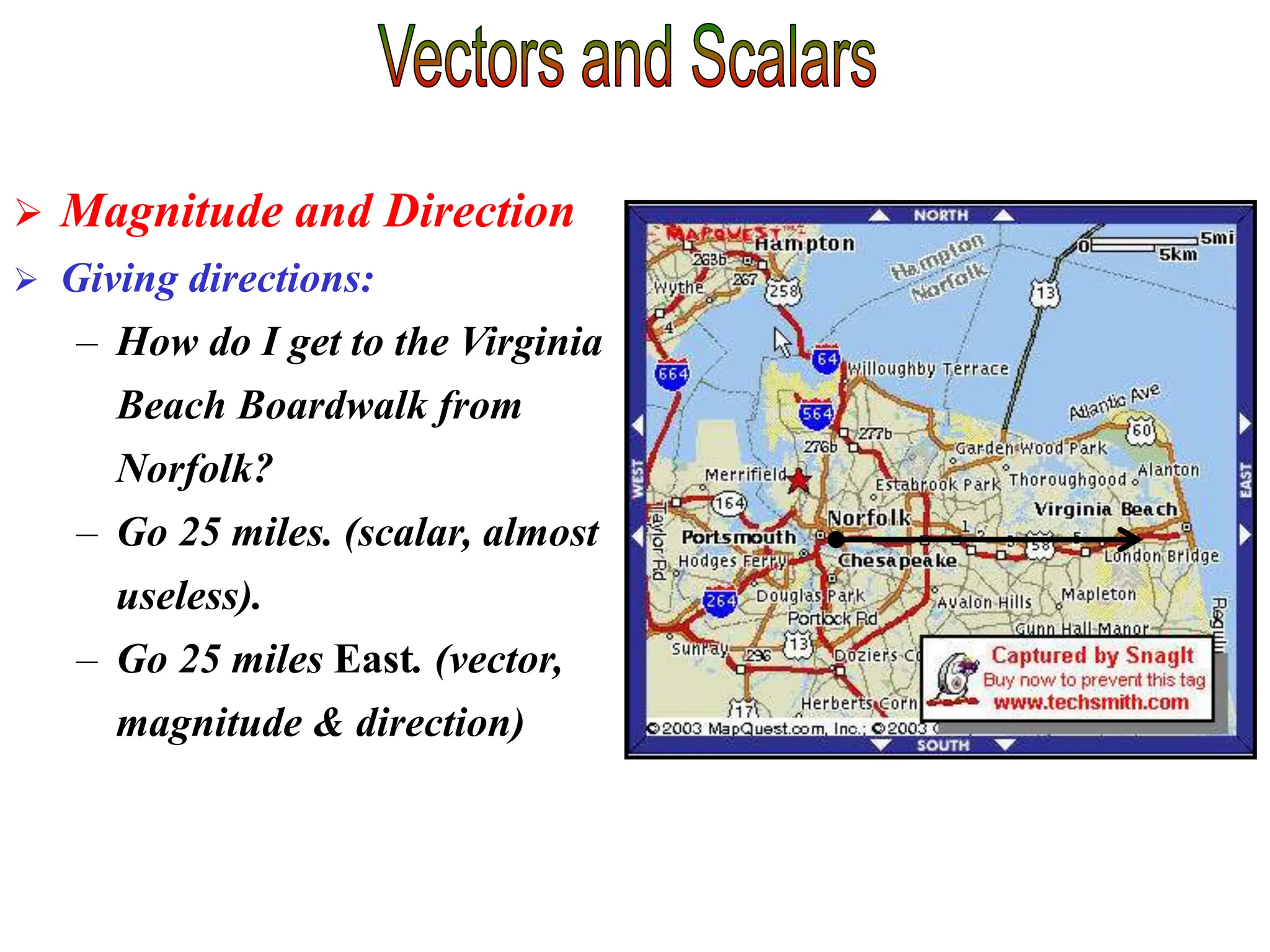
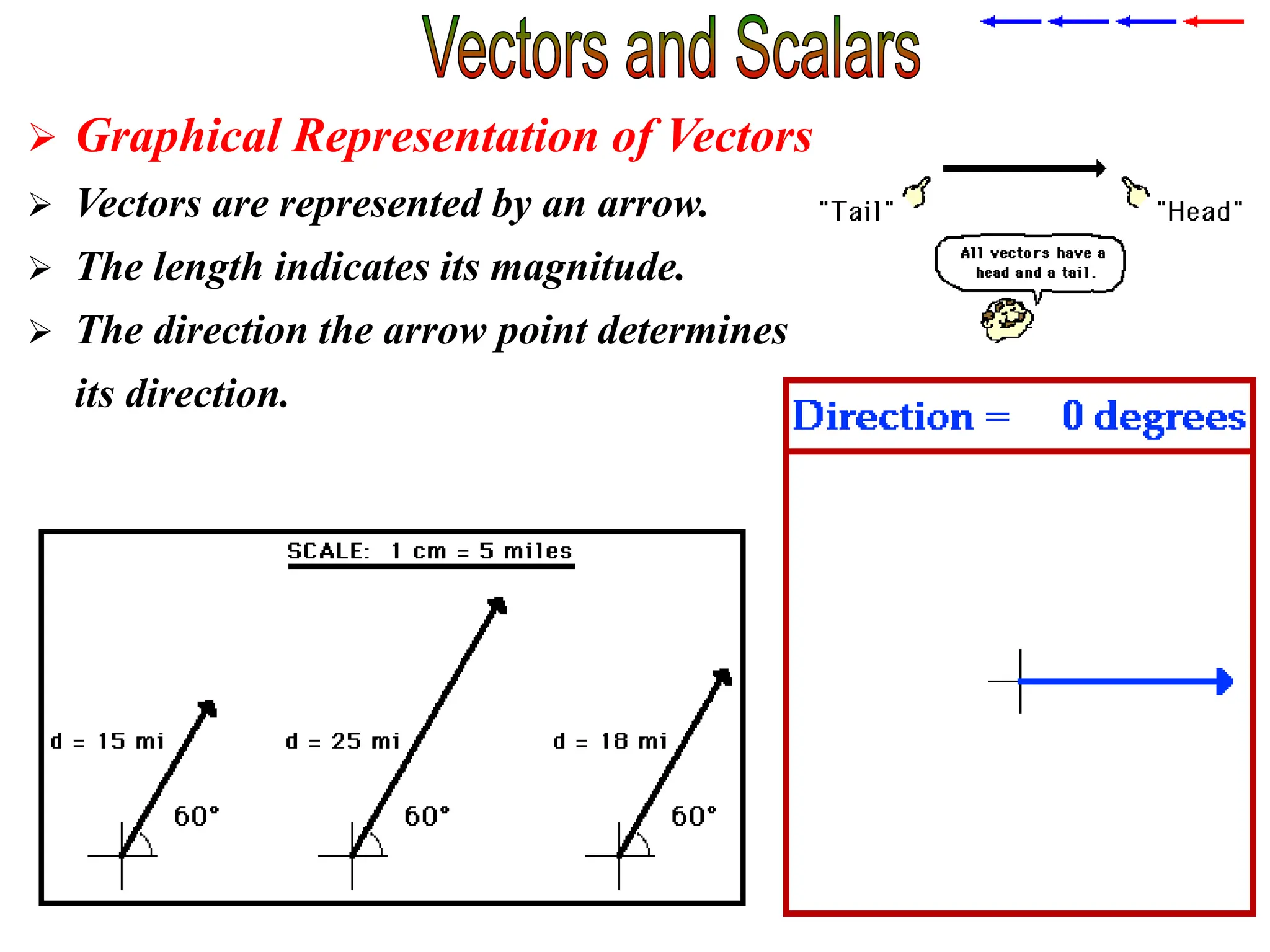
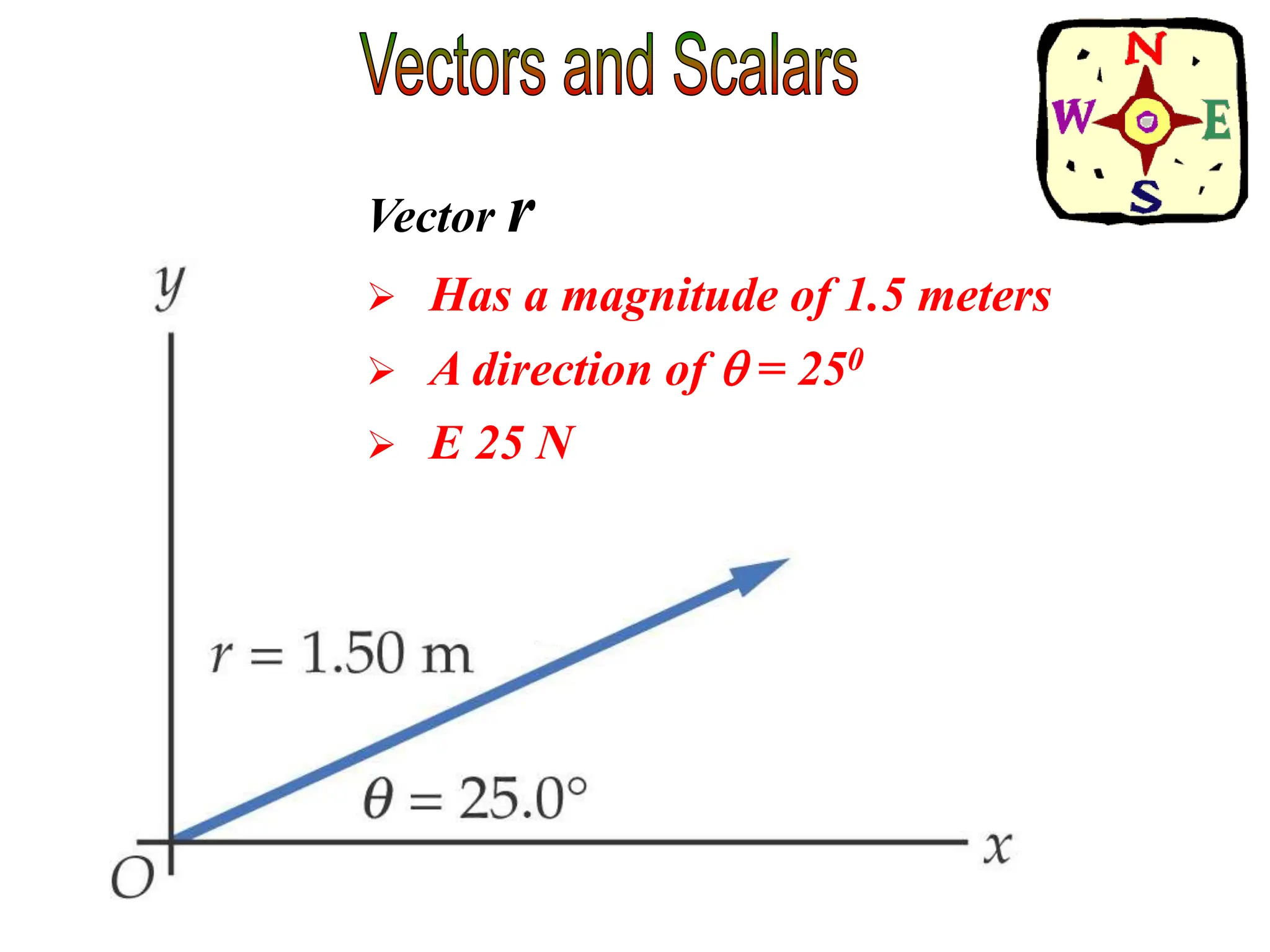
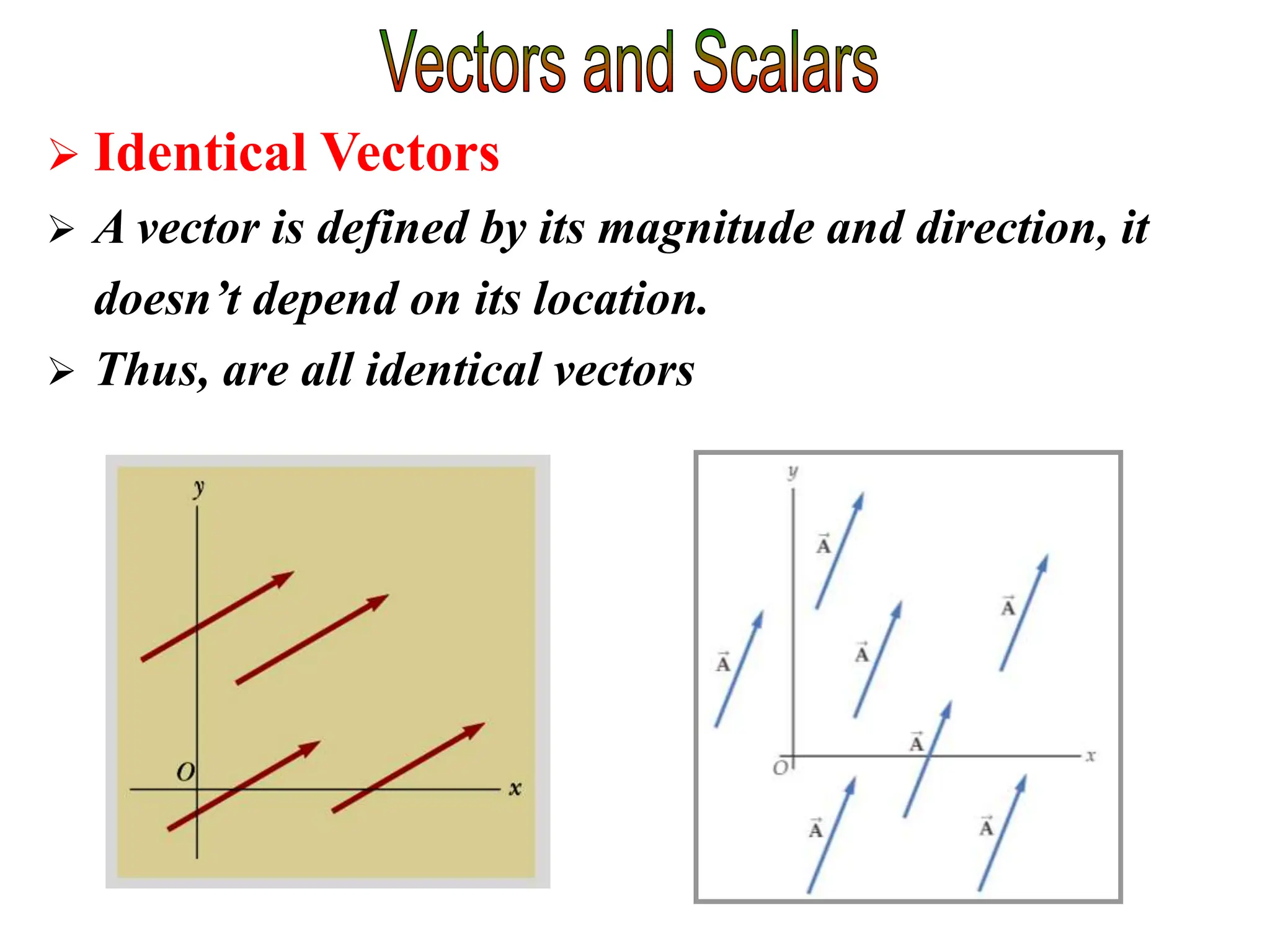
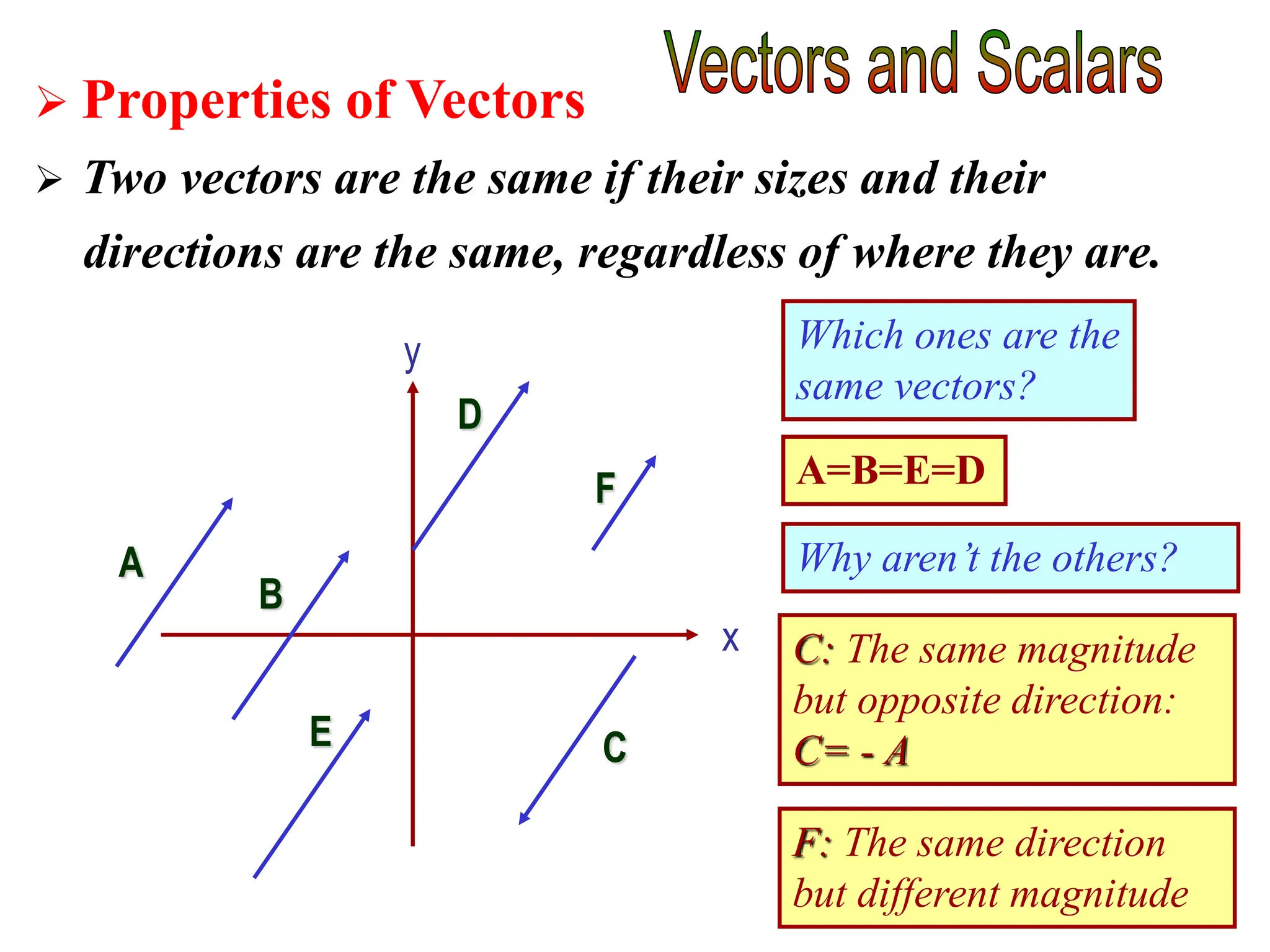
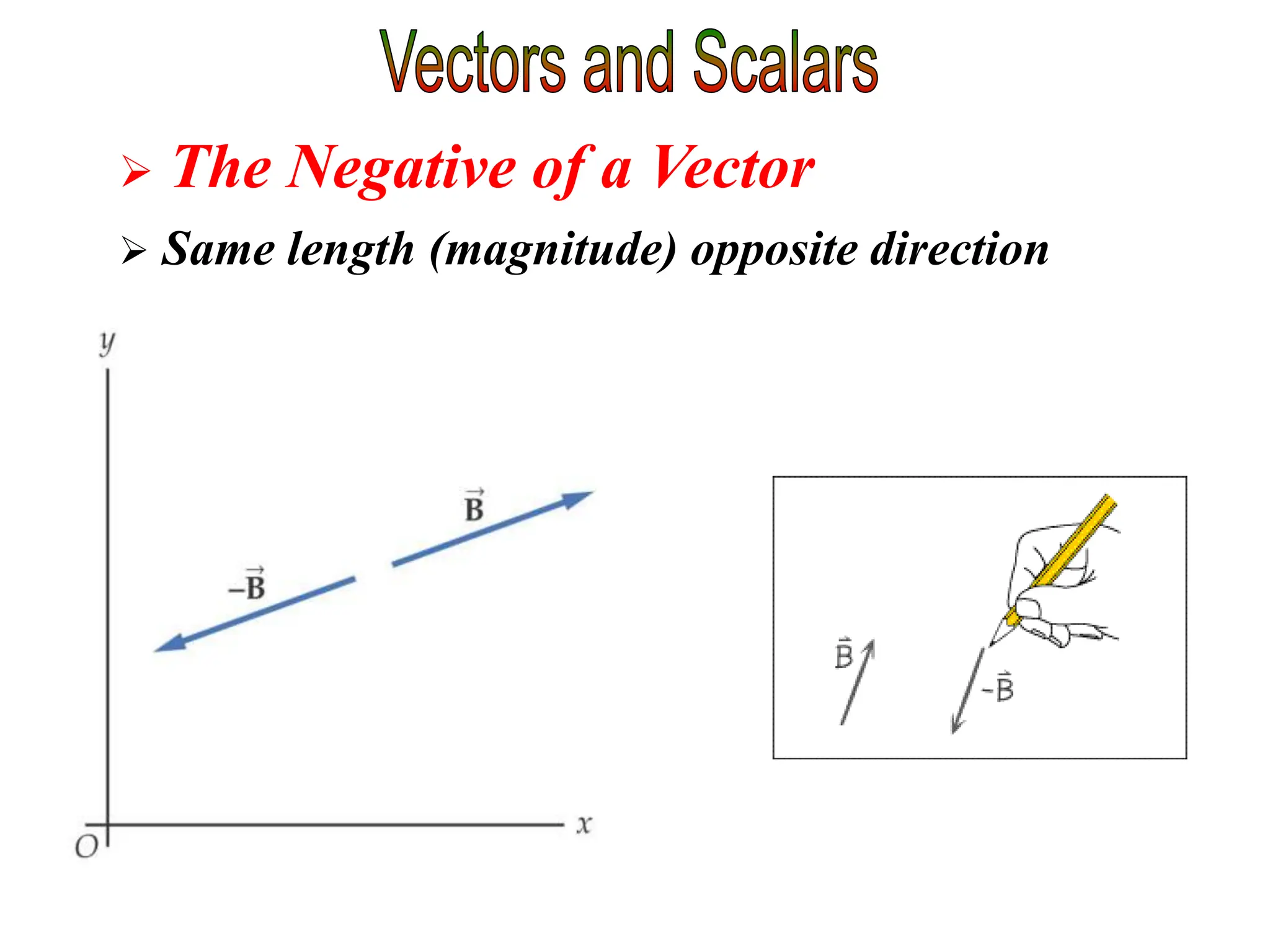
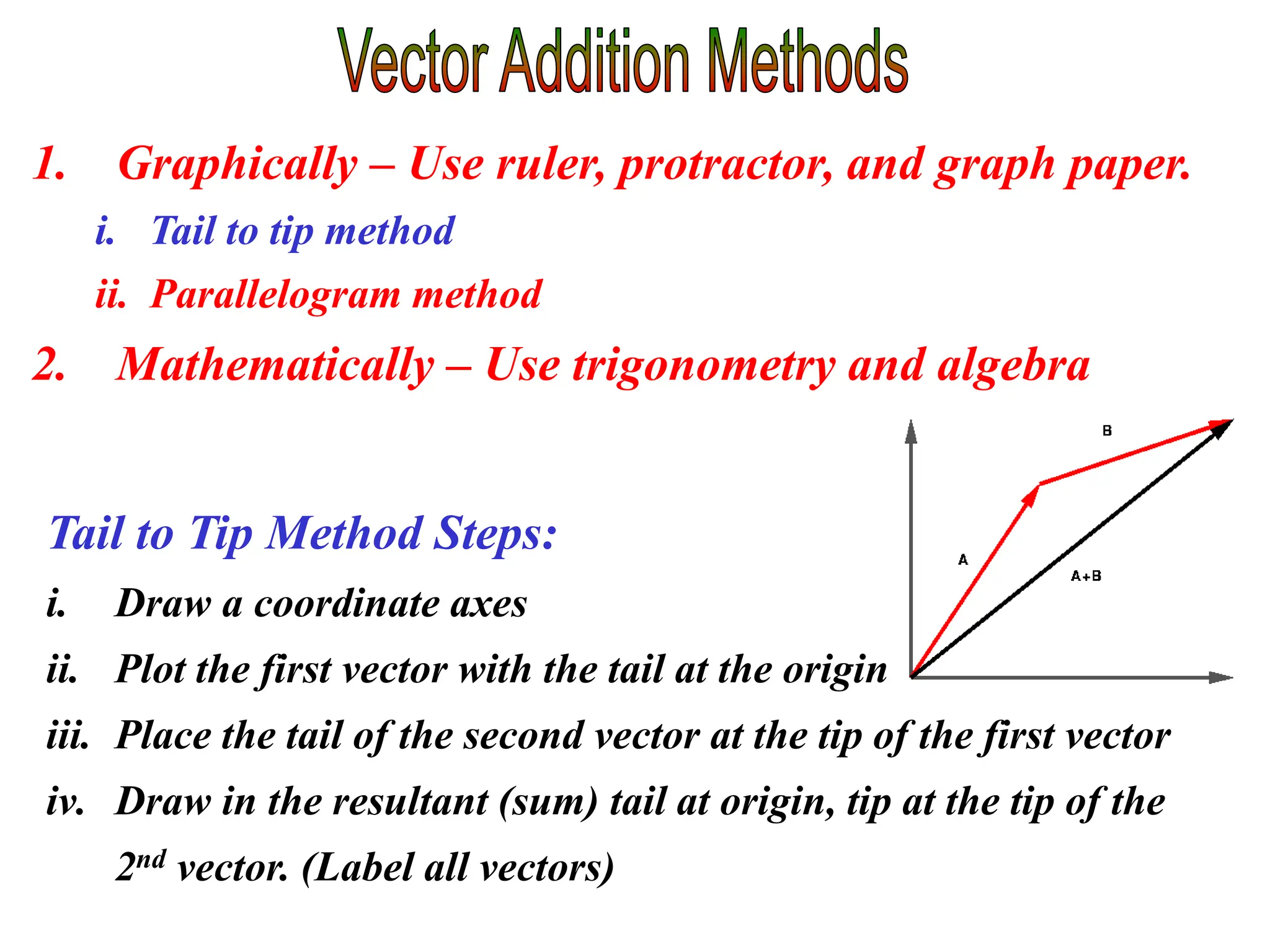
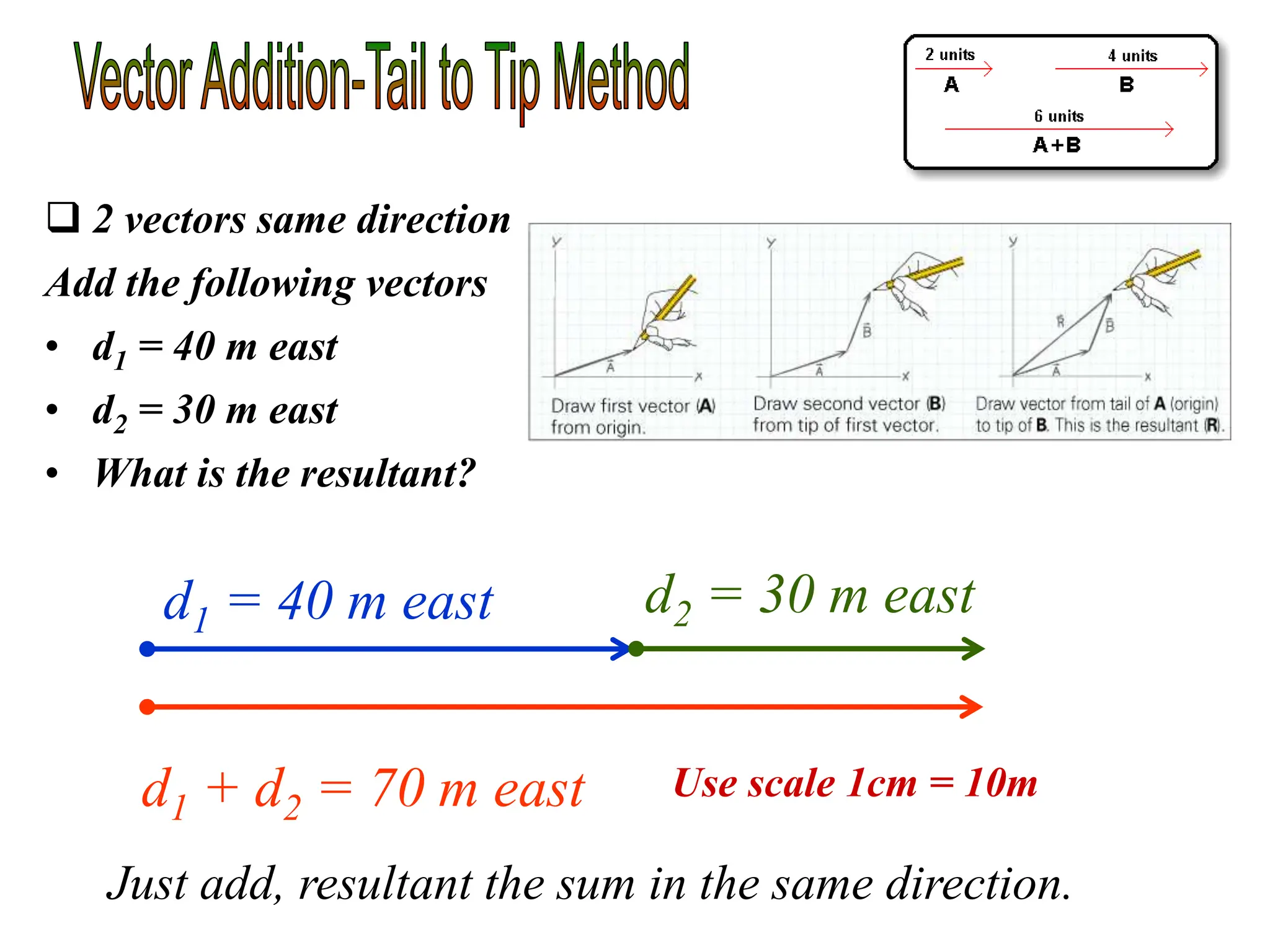
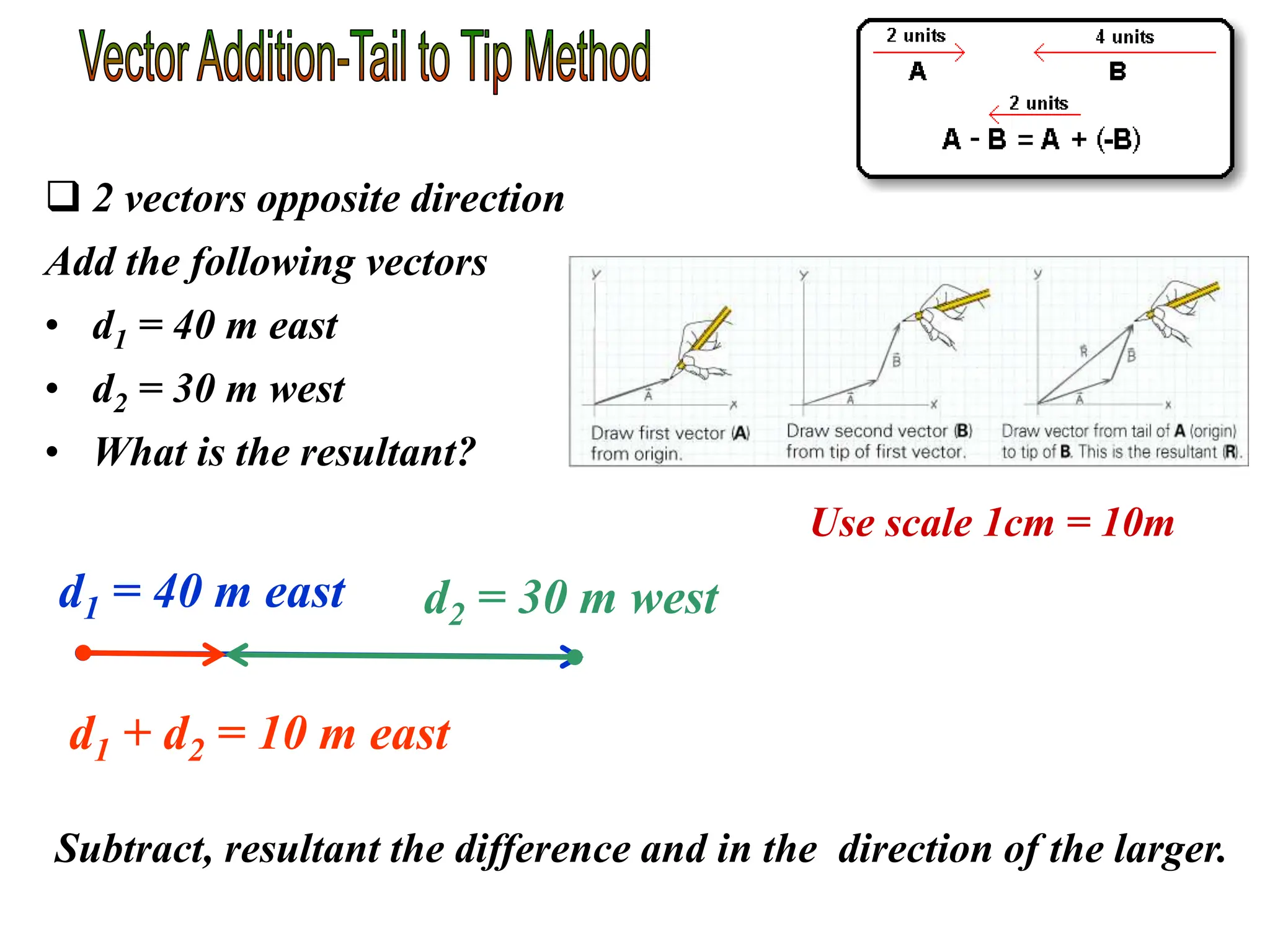
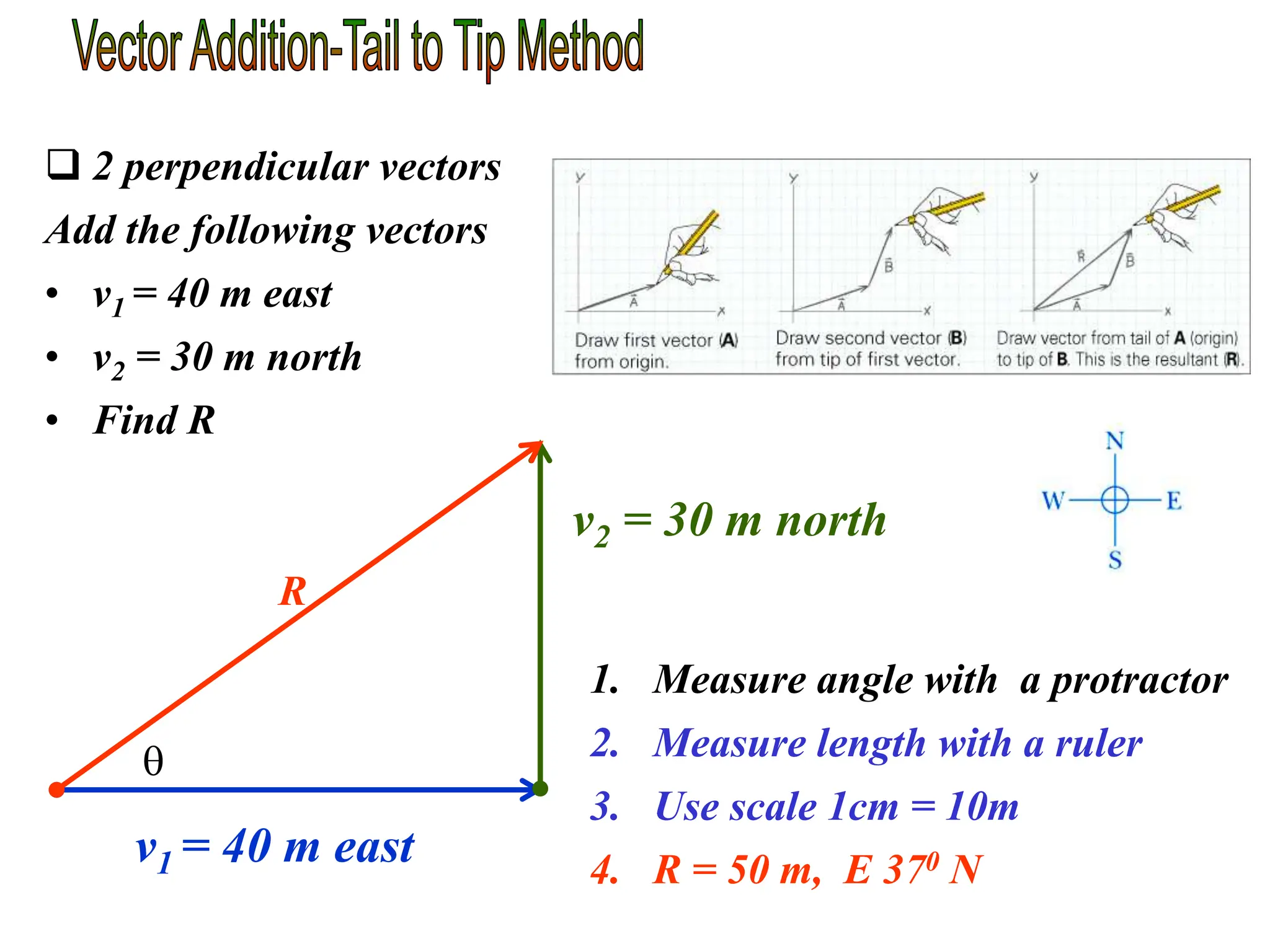
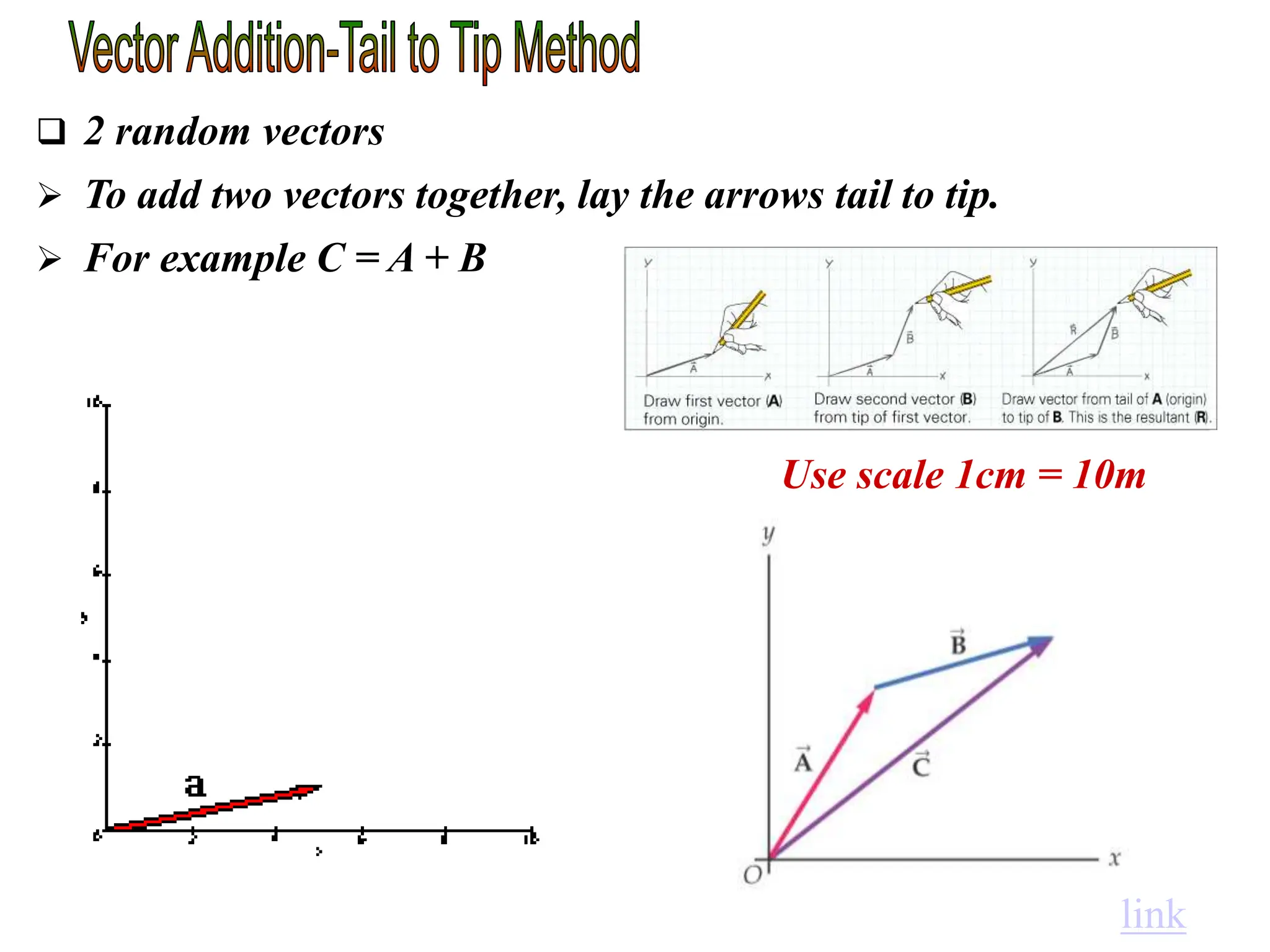
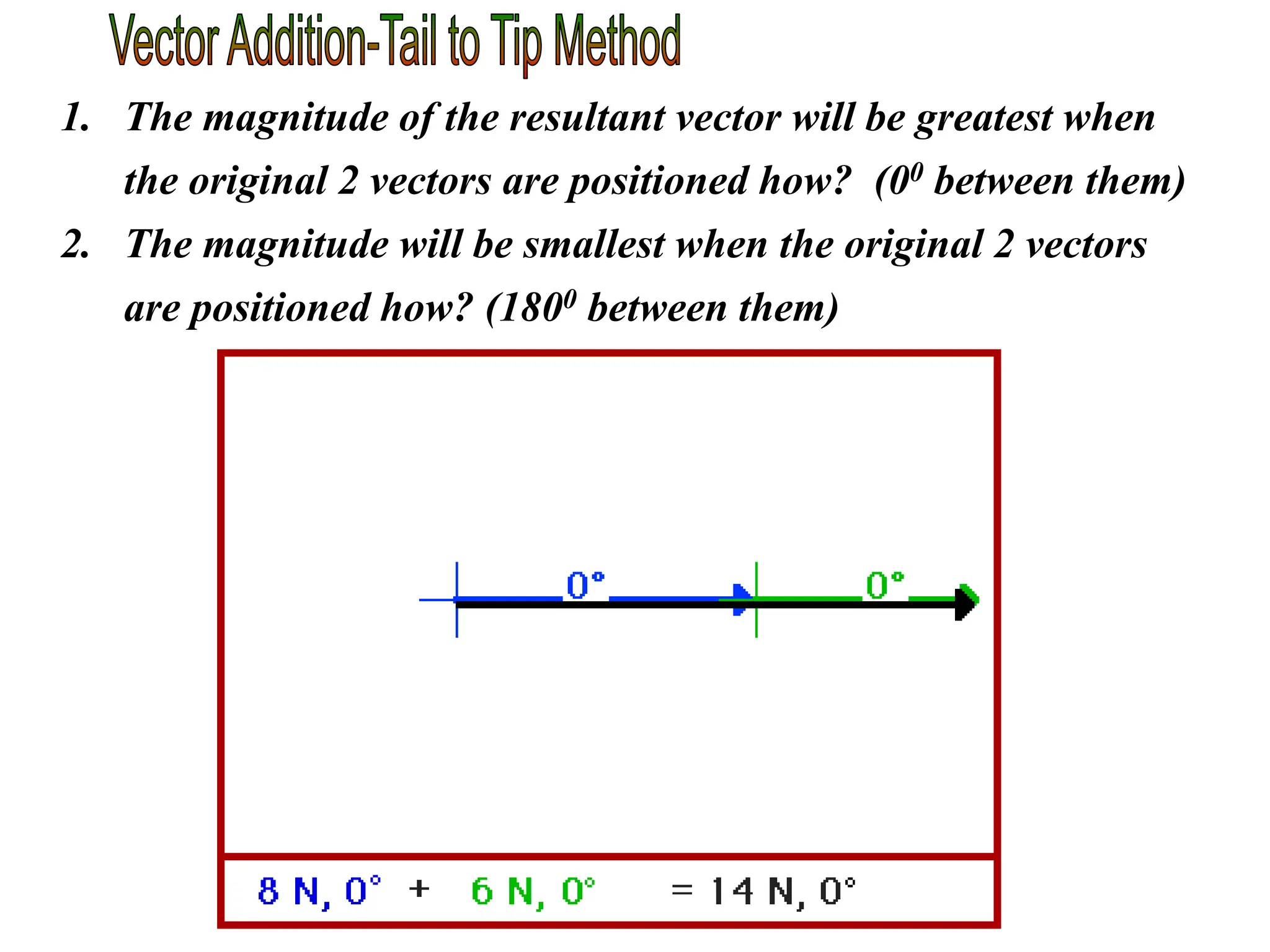
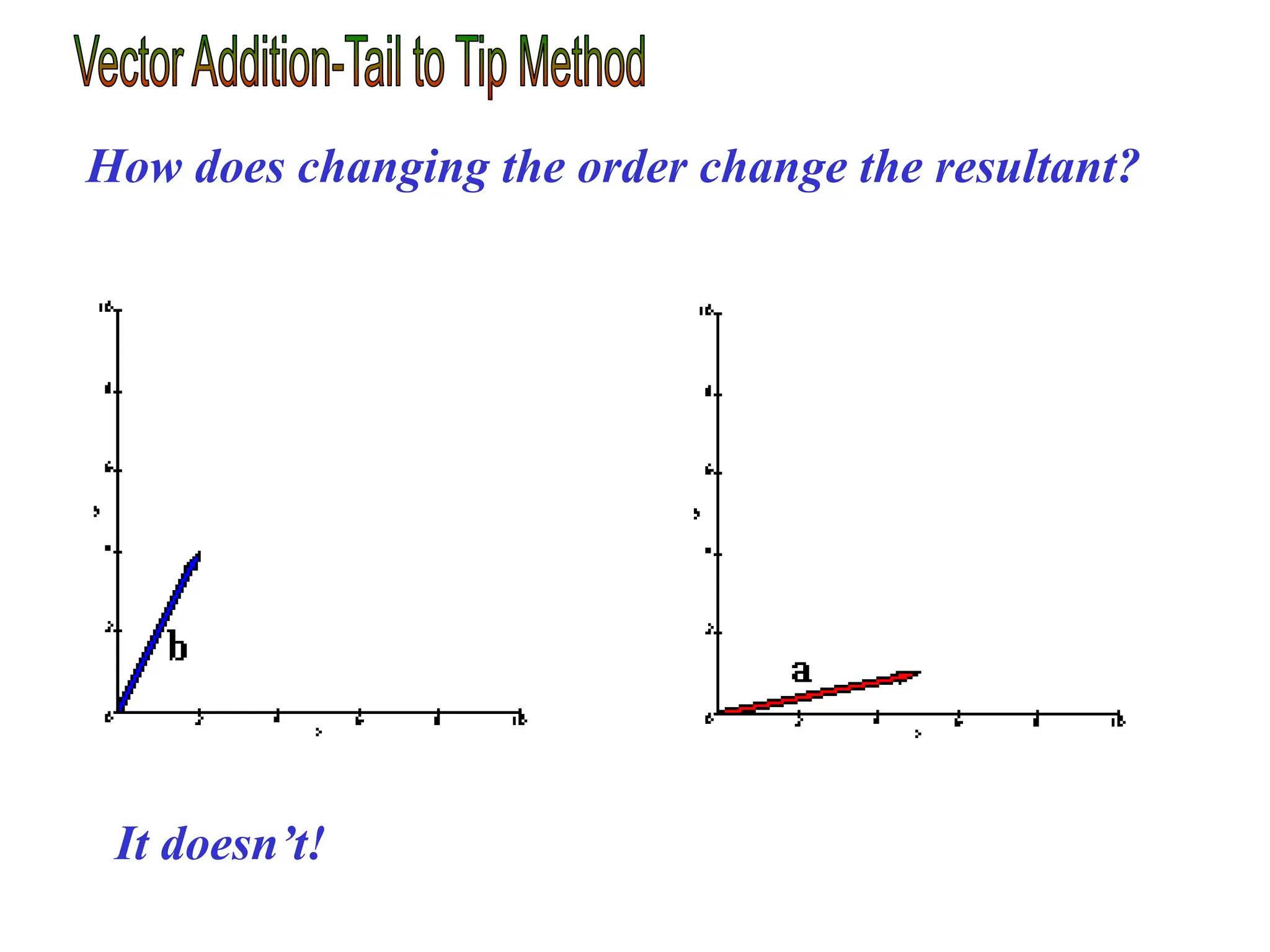
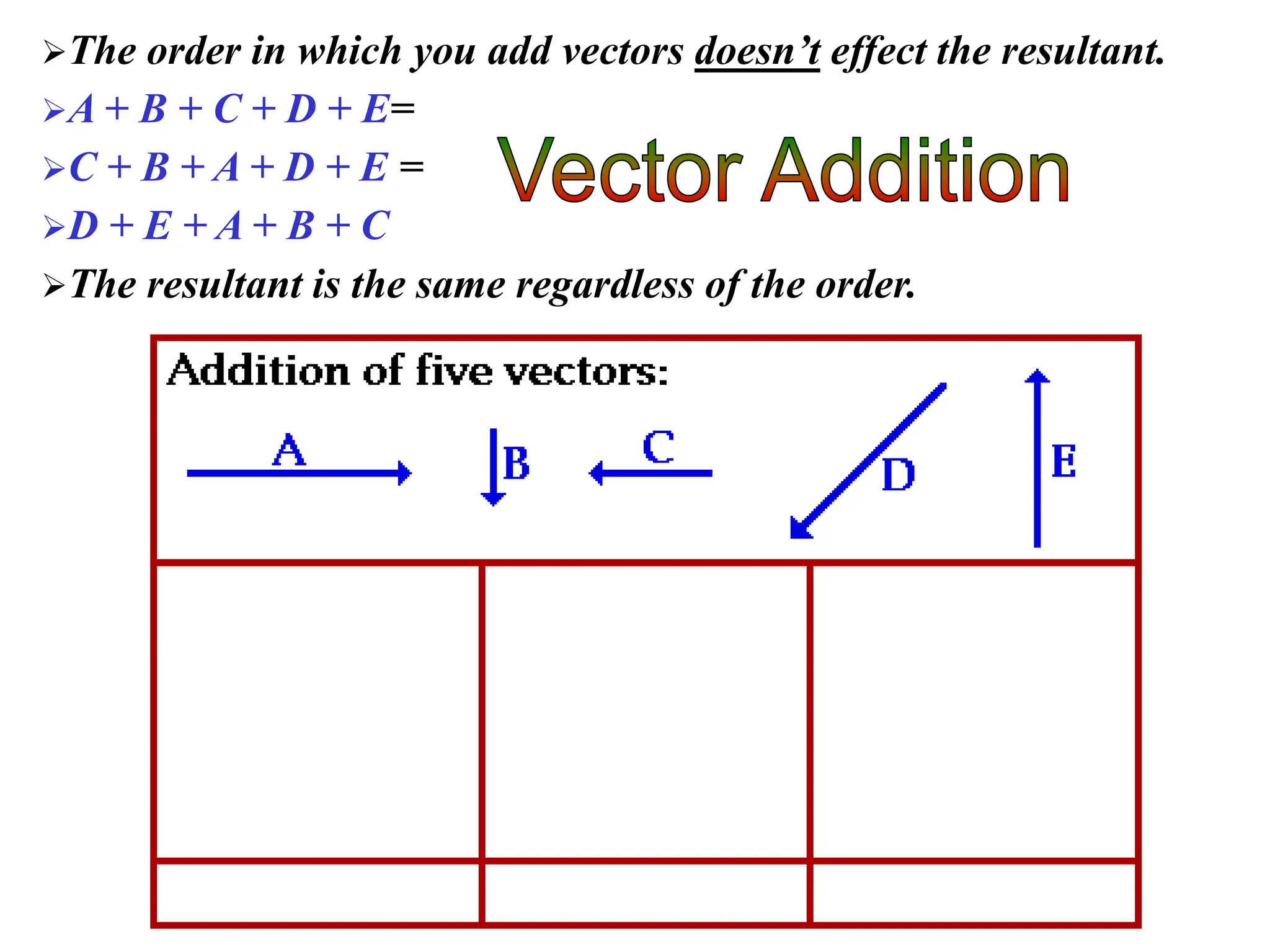
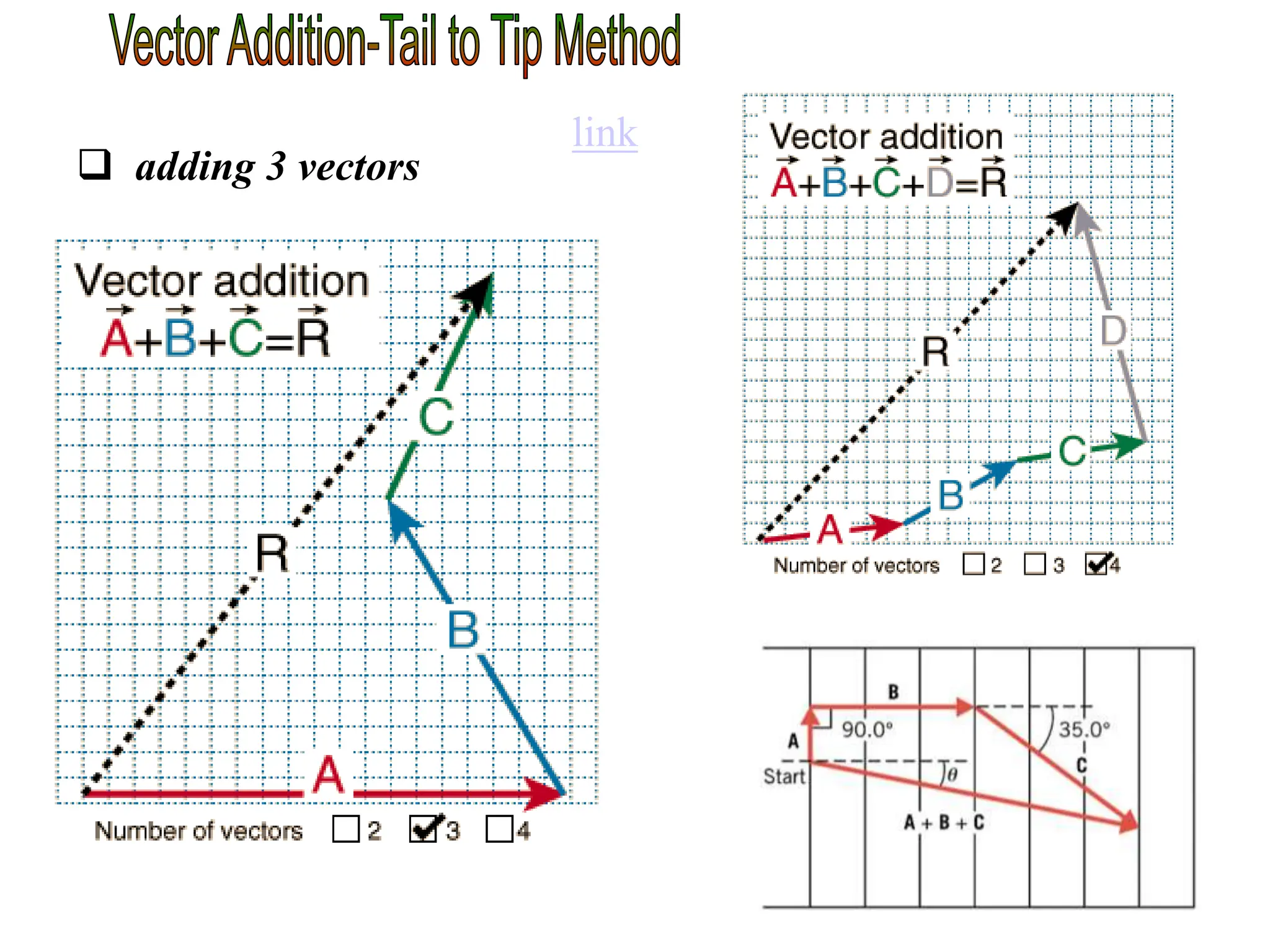
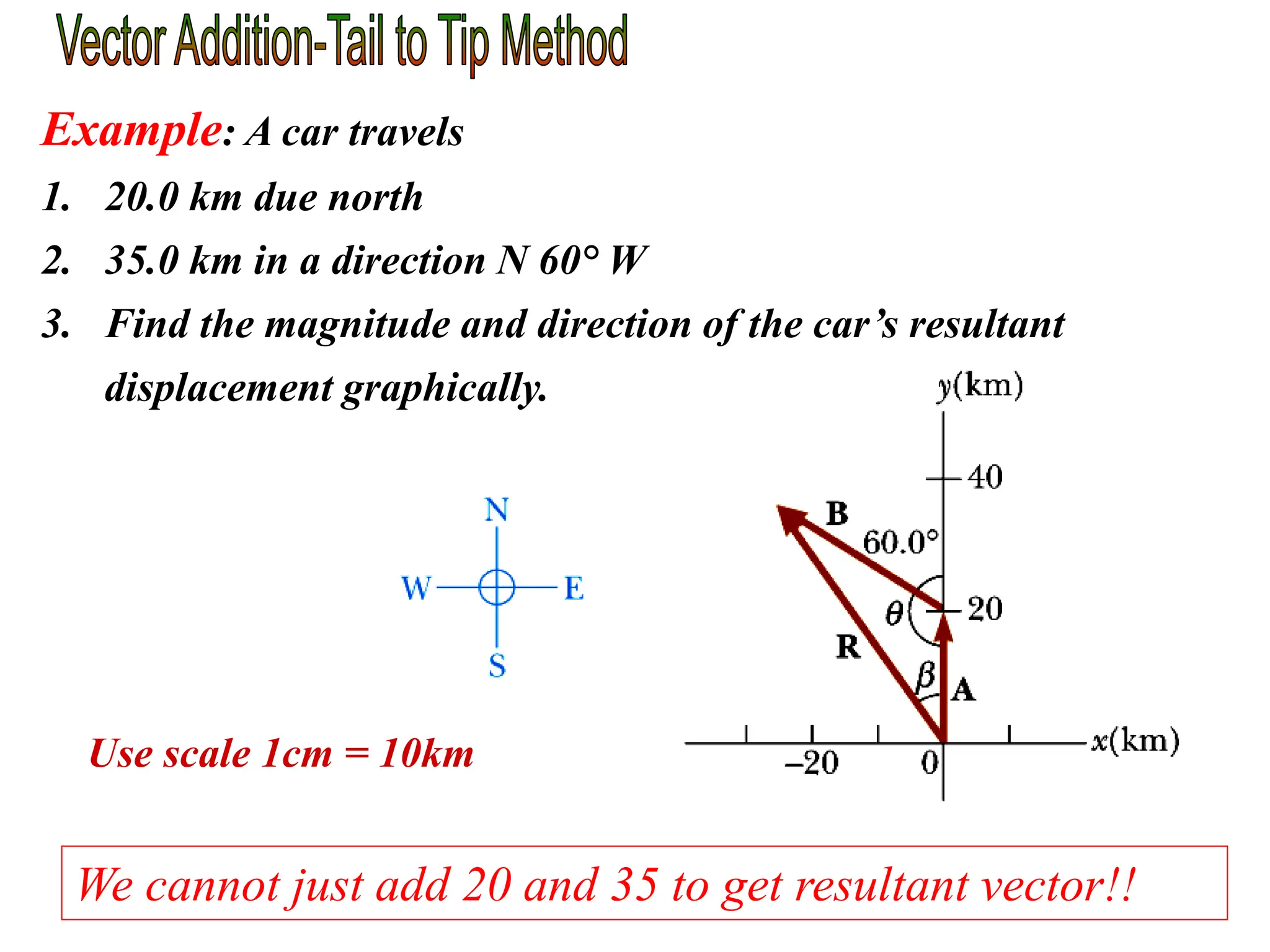
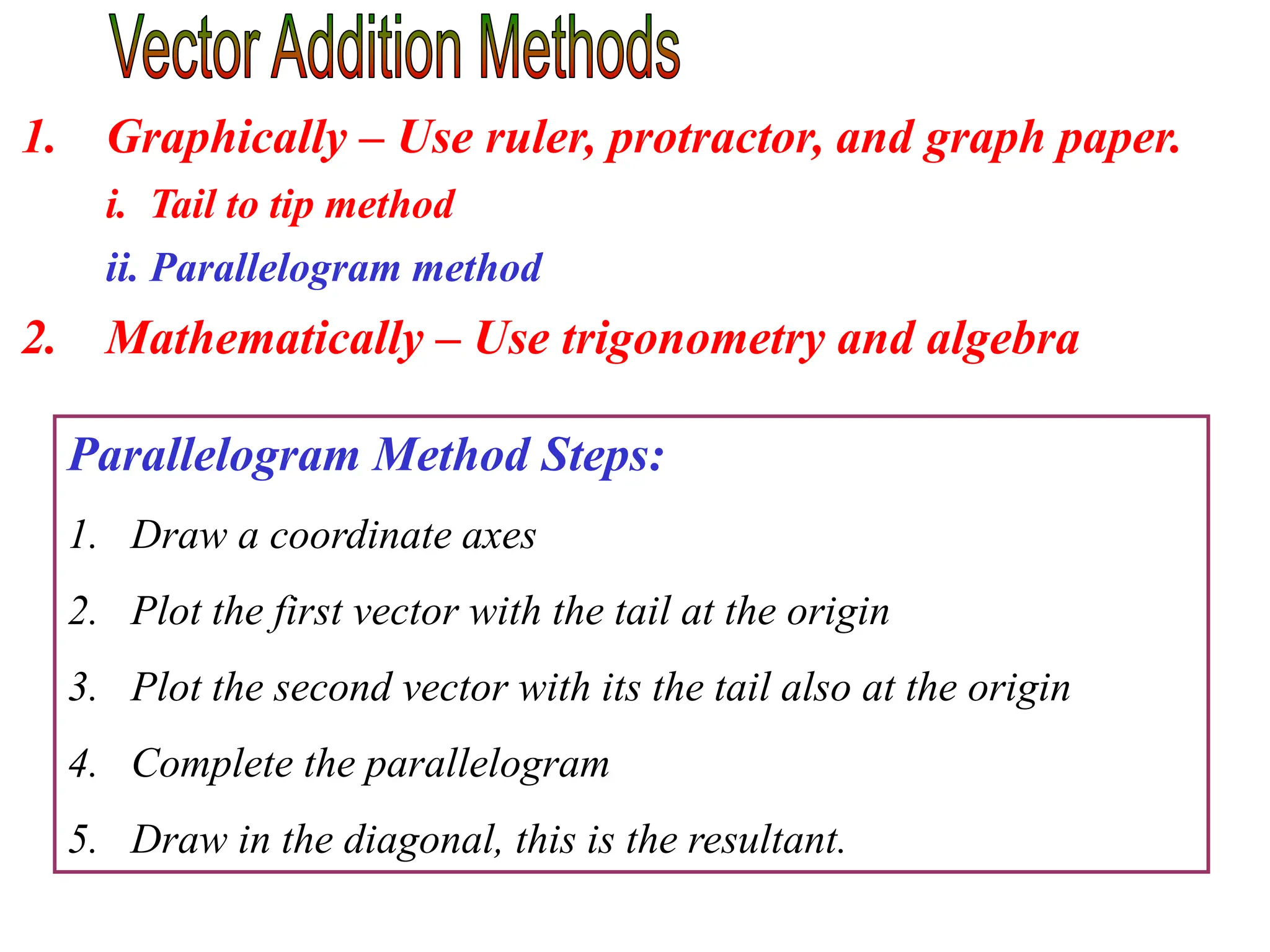
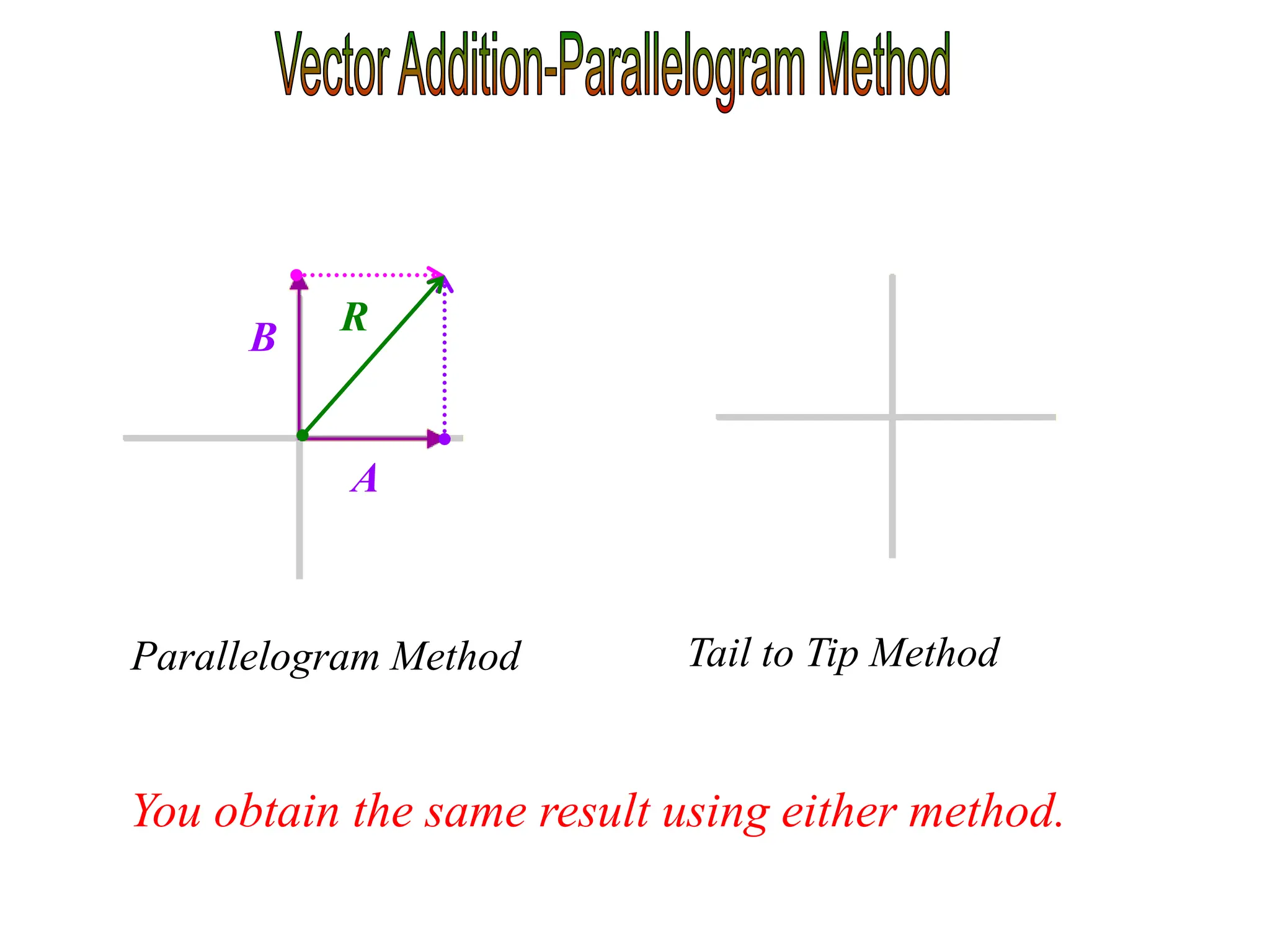
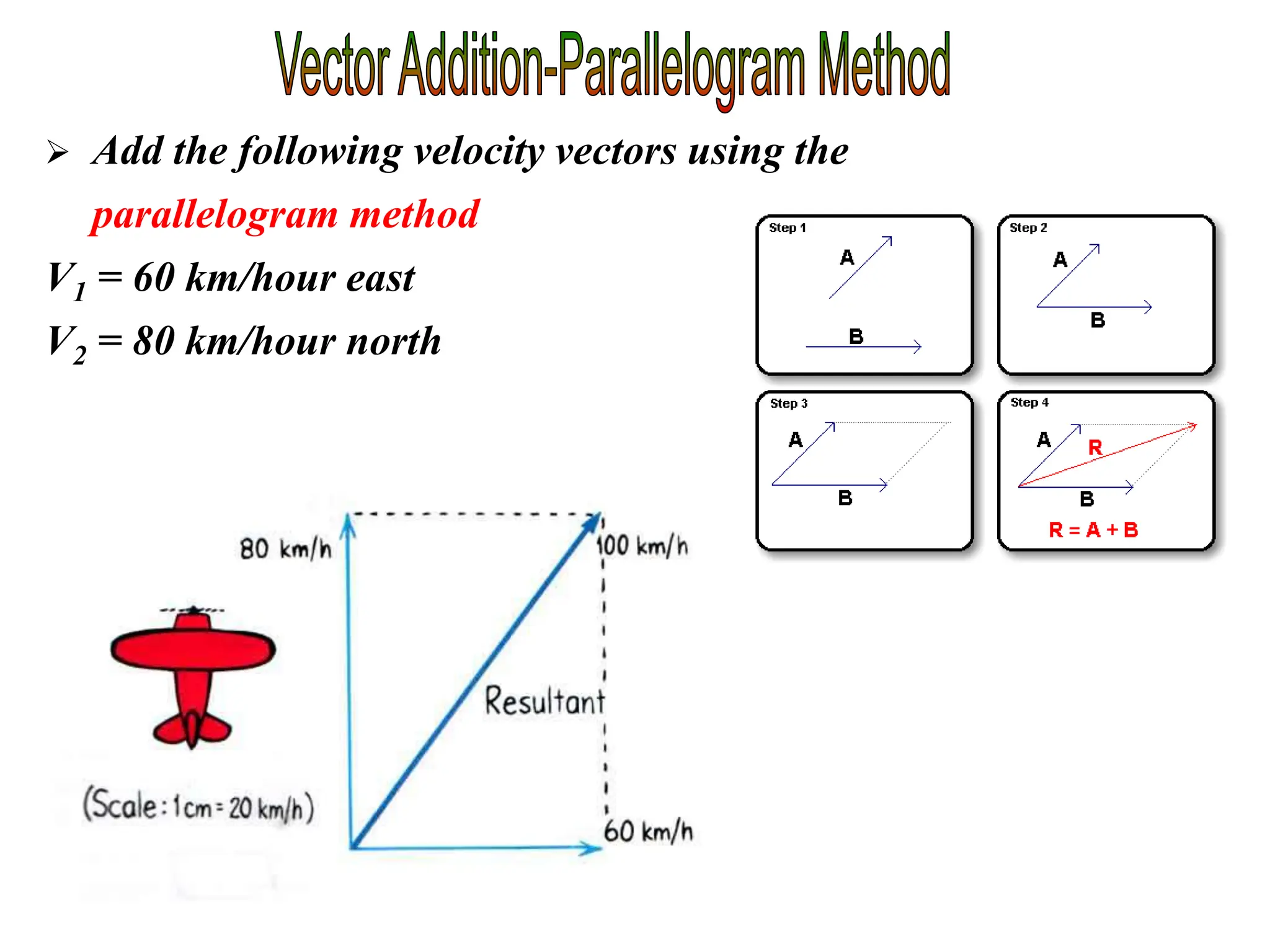
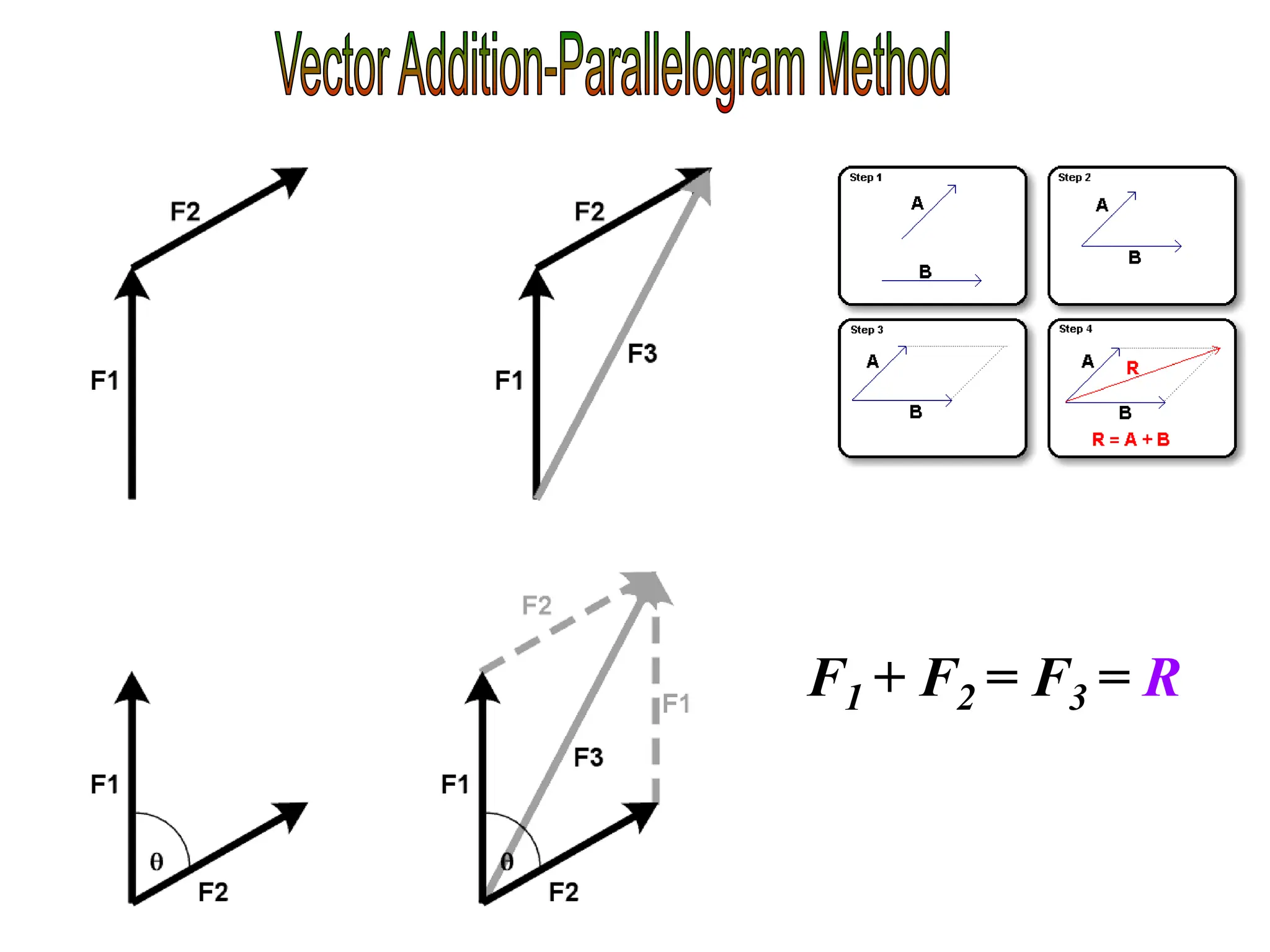
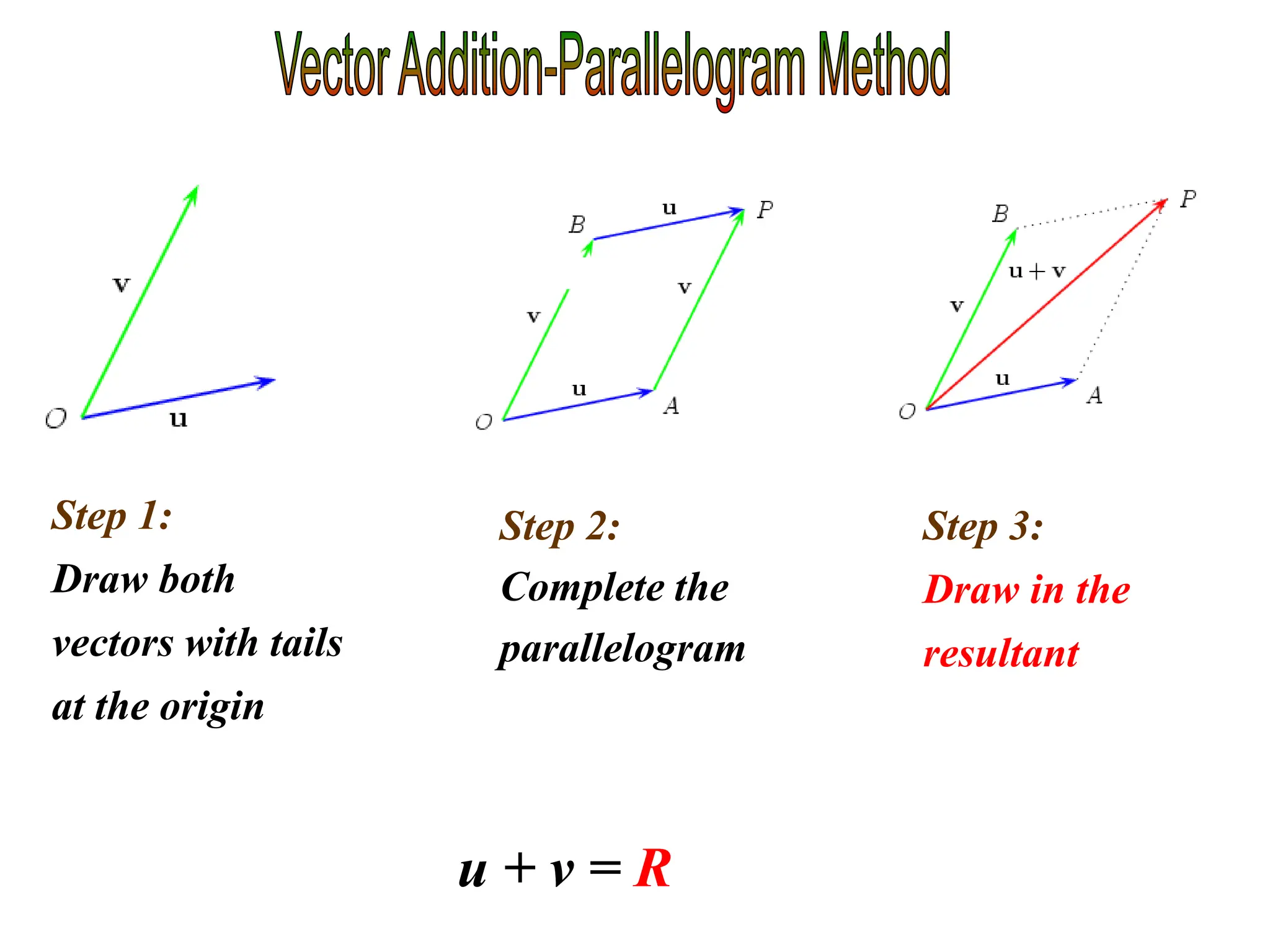
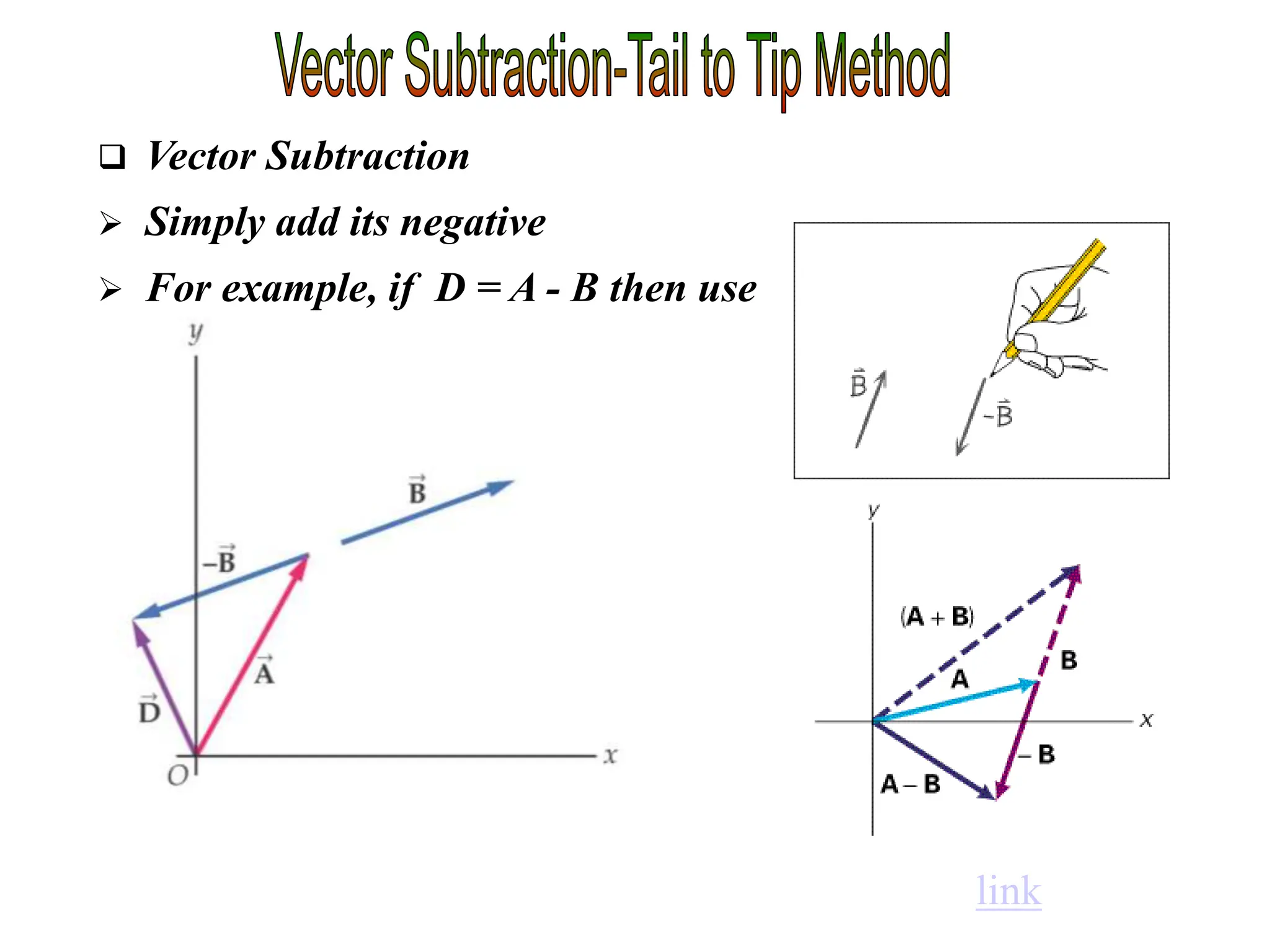
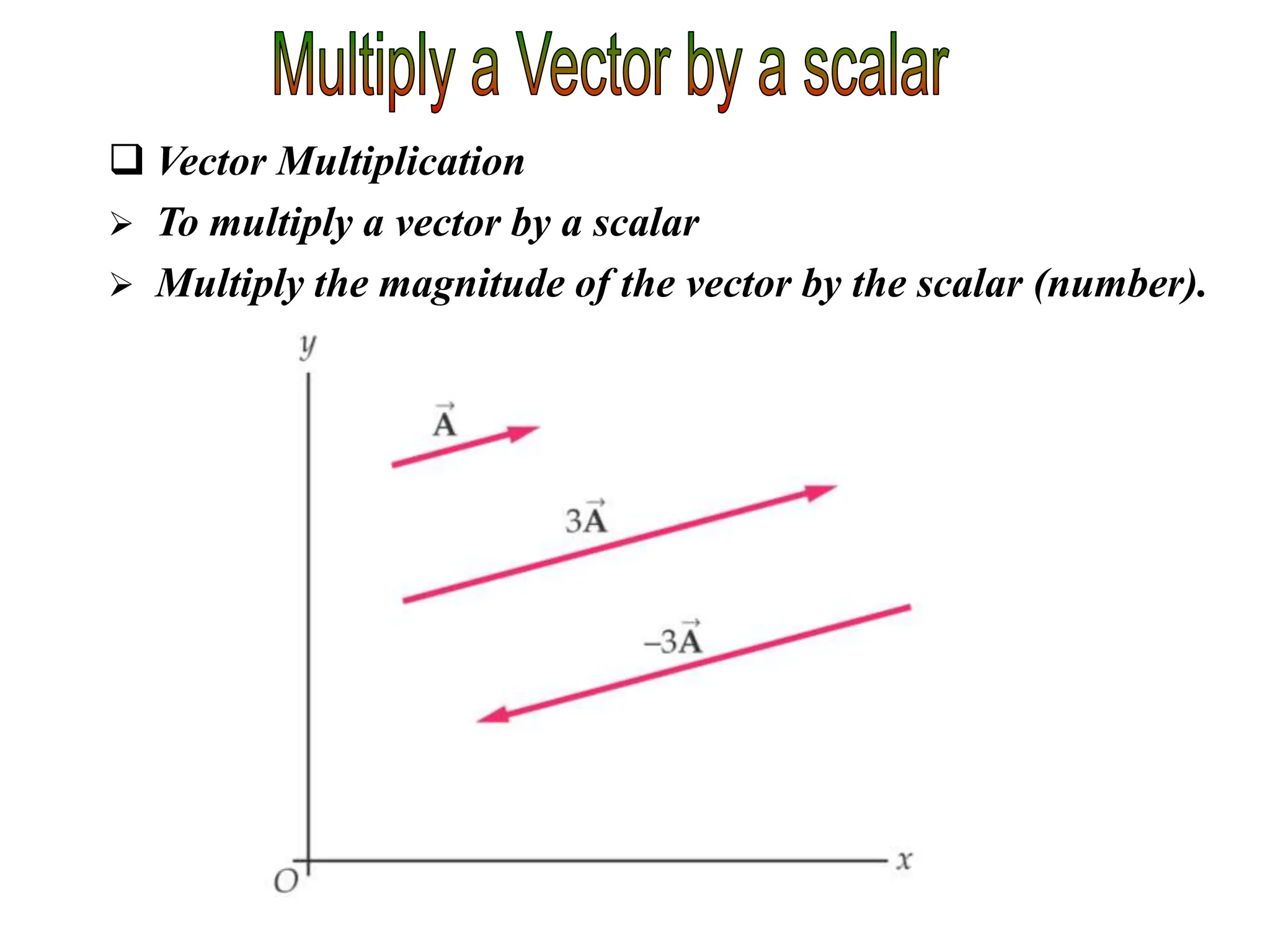
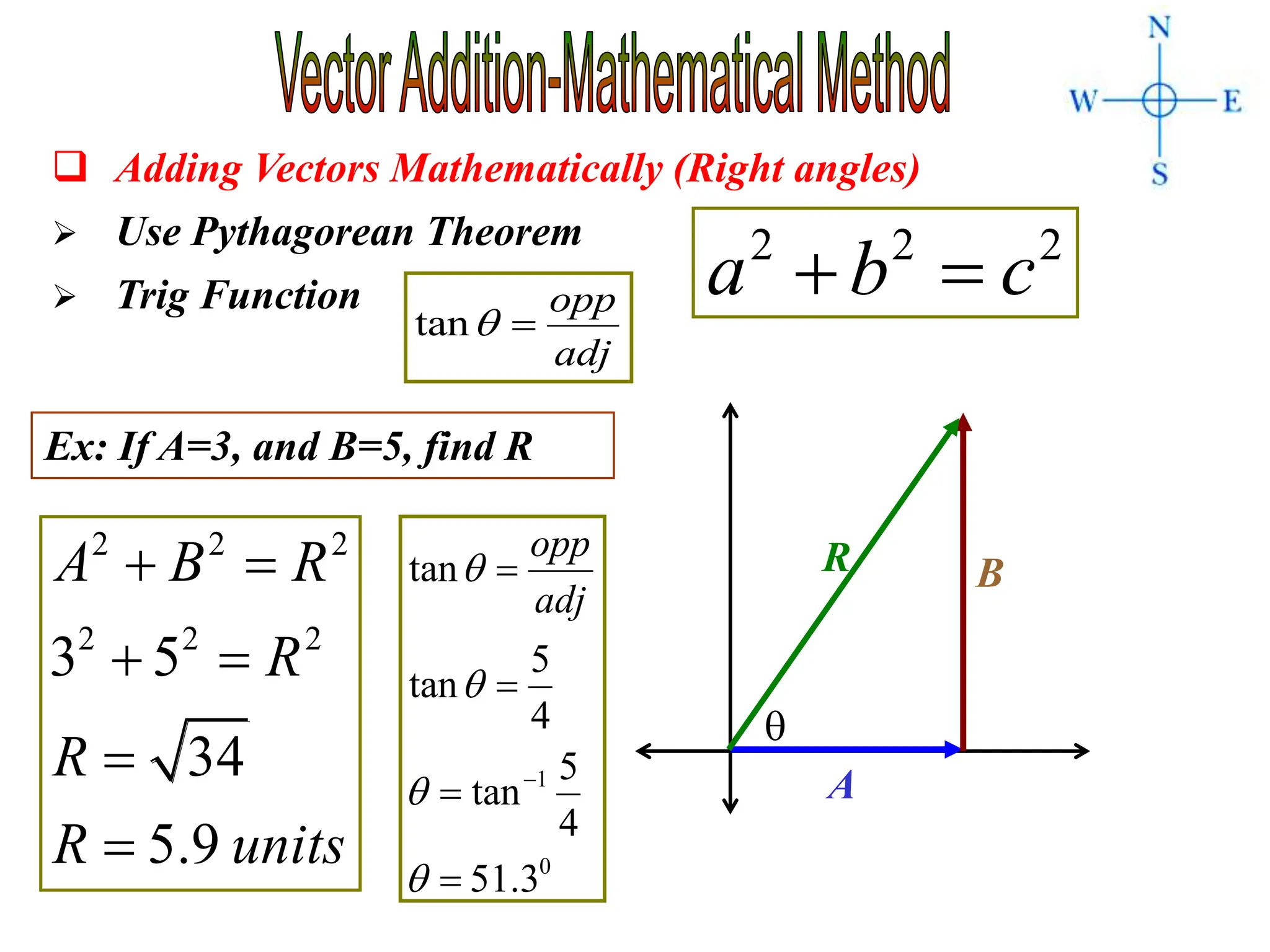
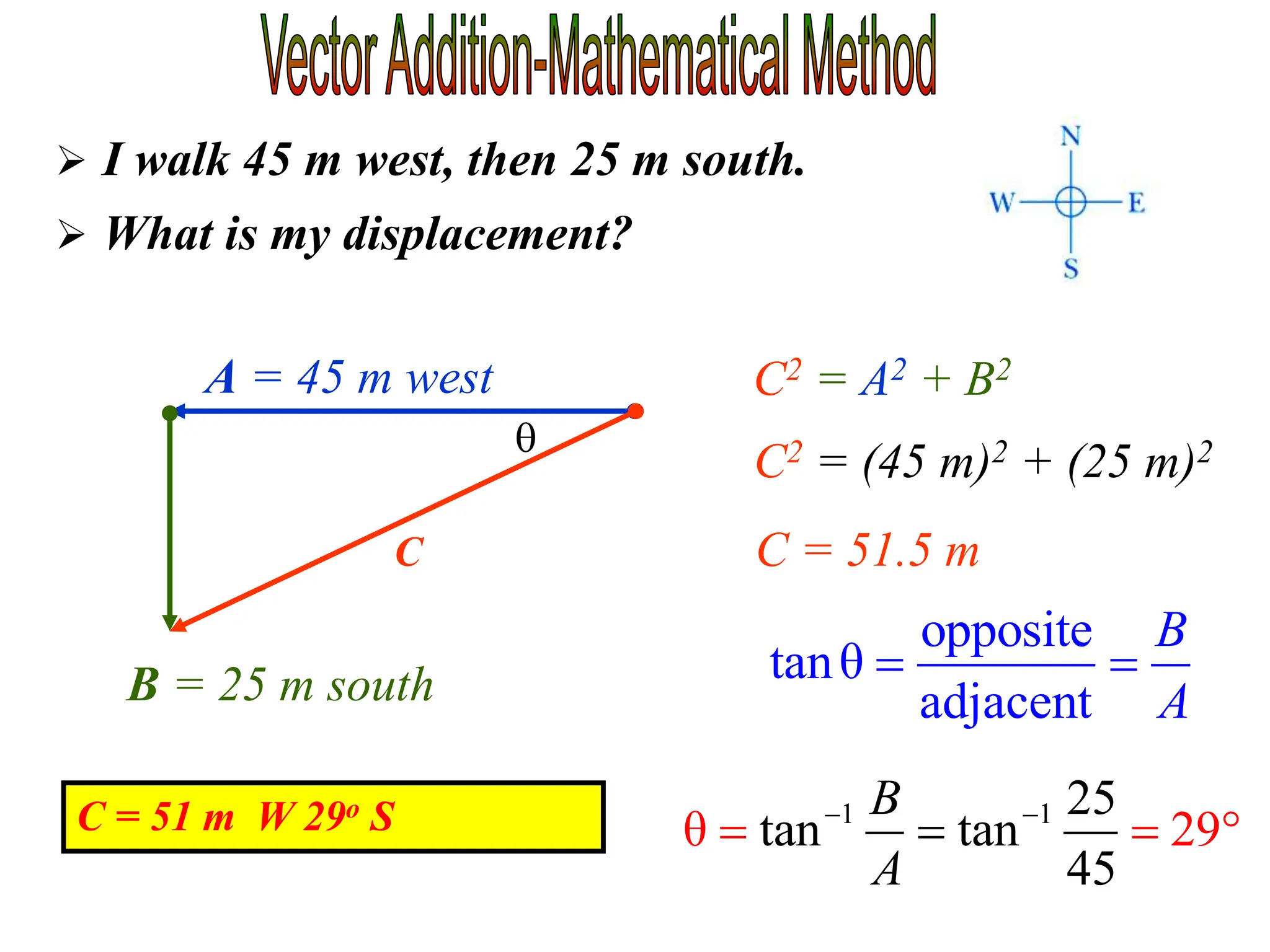
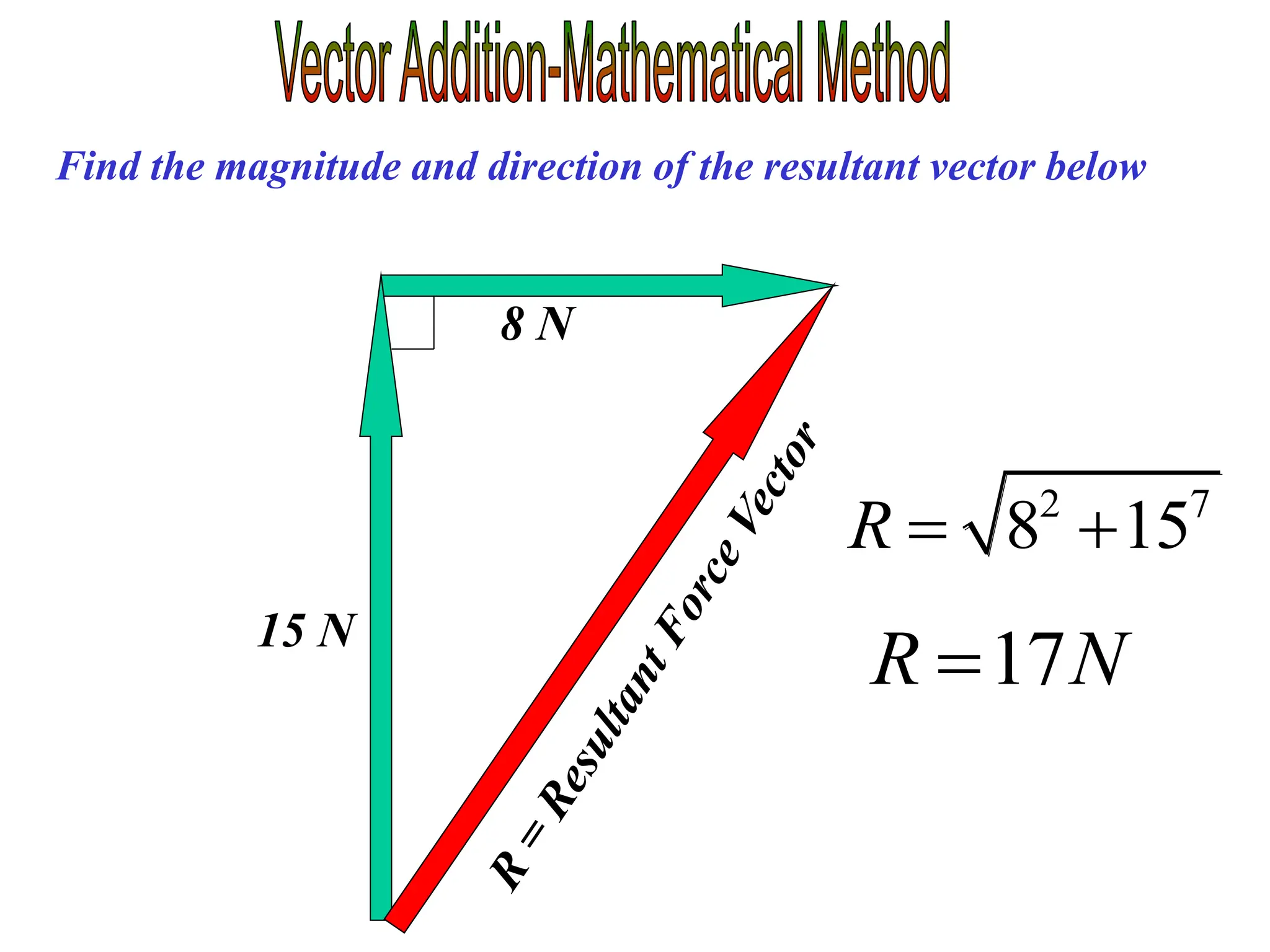
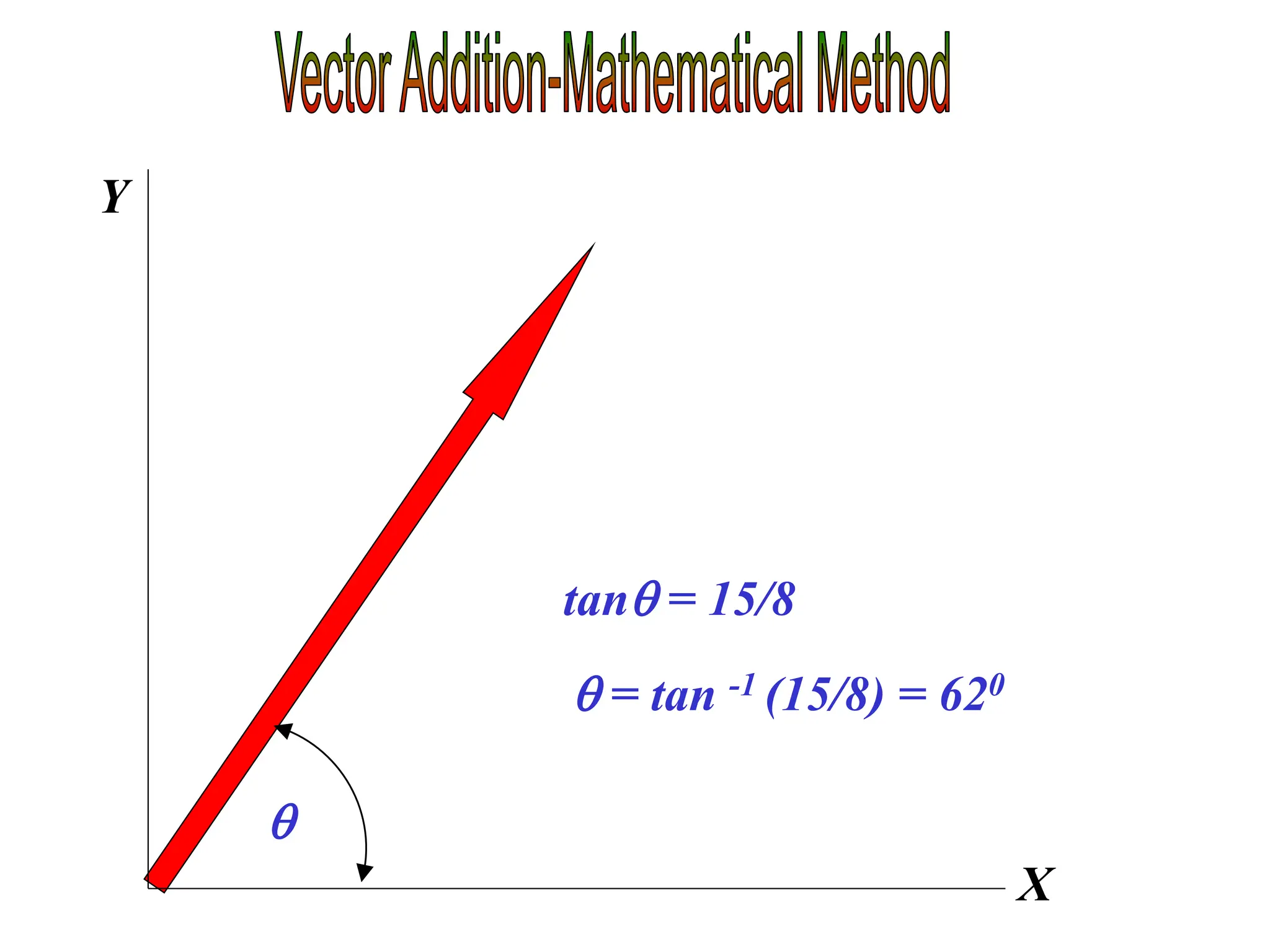
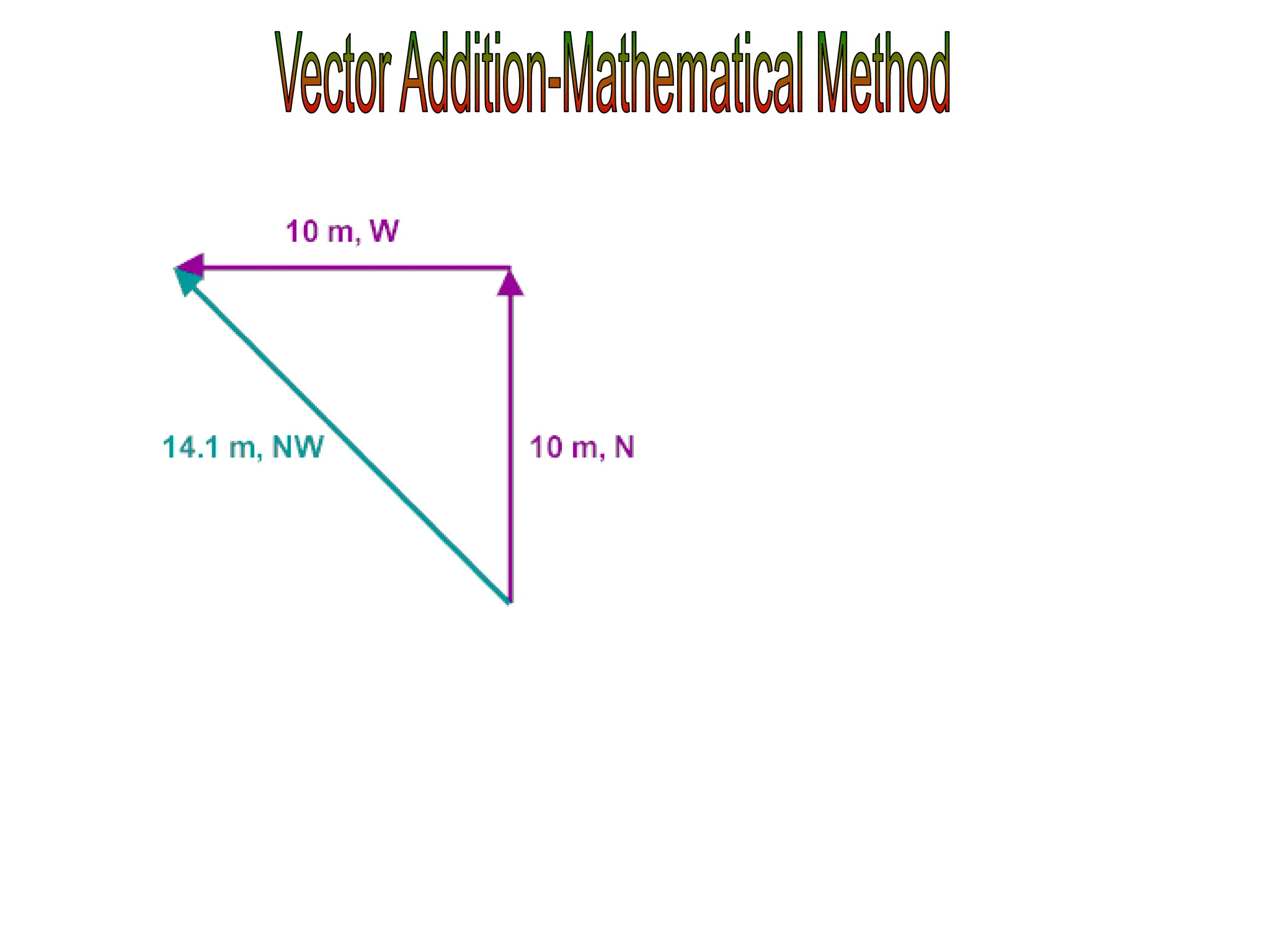
This document discusses scalars and vectors. It defines a scalar as a quantity with only magnitude and a vector as a quantity with both magnitude and direction. Examples of scalars include distance and temperature, while examples of vectors include displacement and velocity. The document also discusses how to represent vectors graphically with arrows and how to add vectors using the tail-to-tip method or parallelogram method, including adding perpendicular and random vectors. It provides examples of how to calculate vector addition and subtraction both graphically and mathematically.