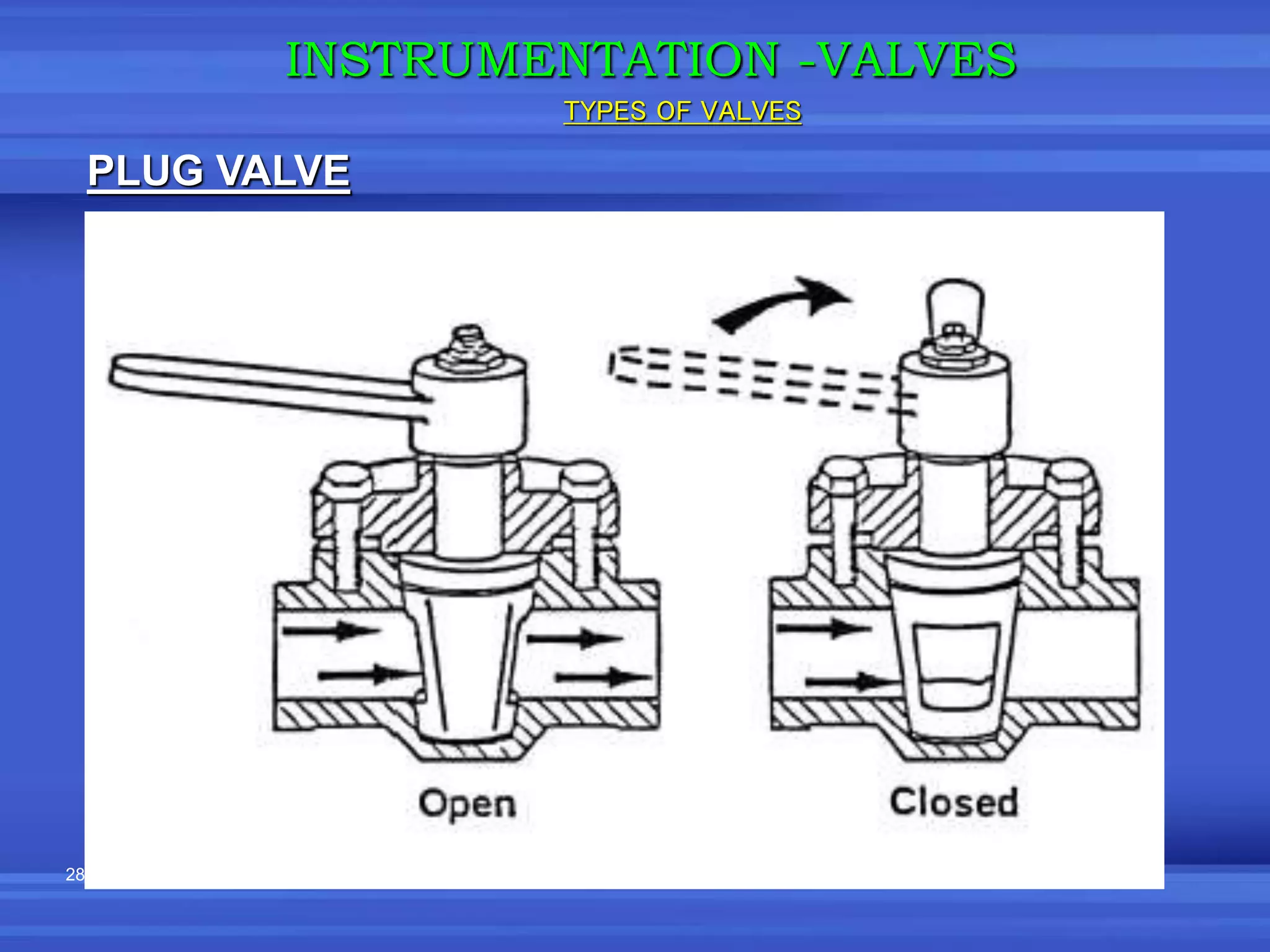
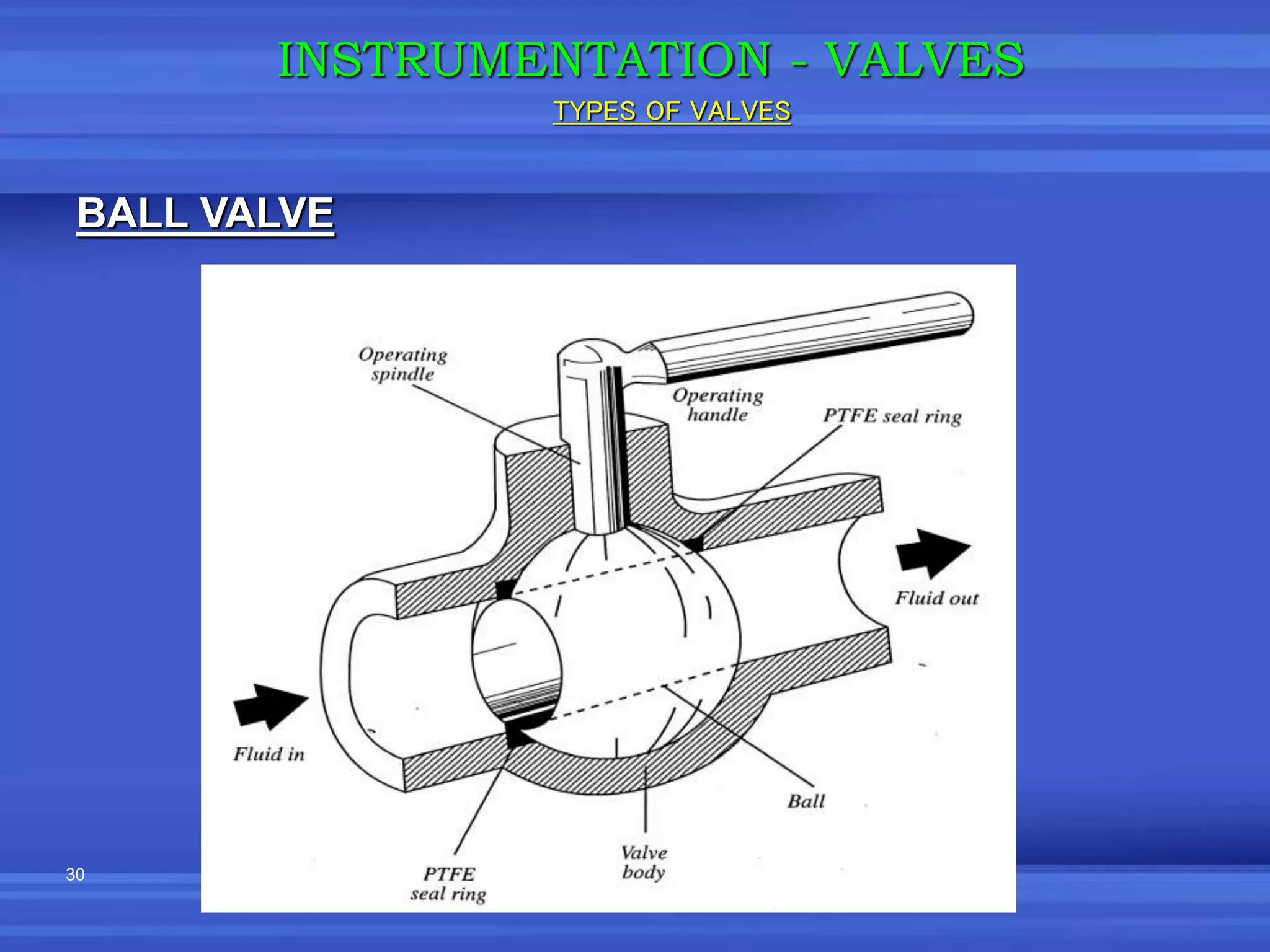
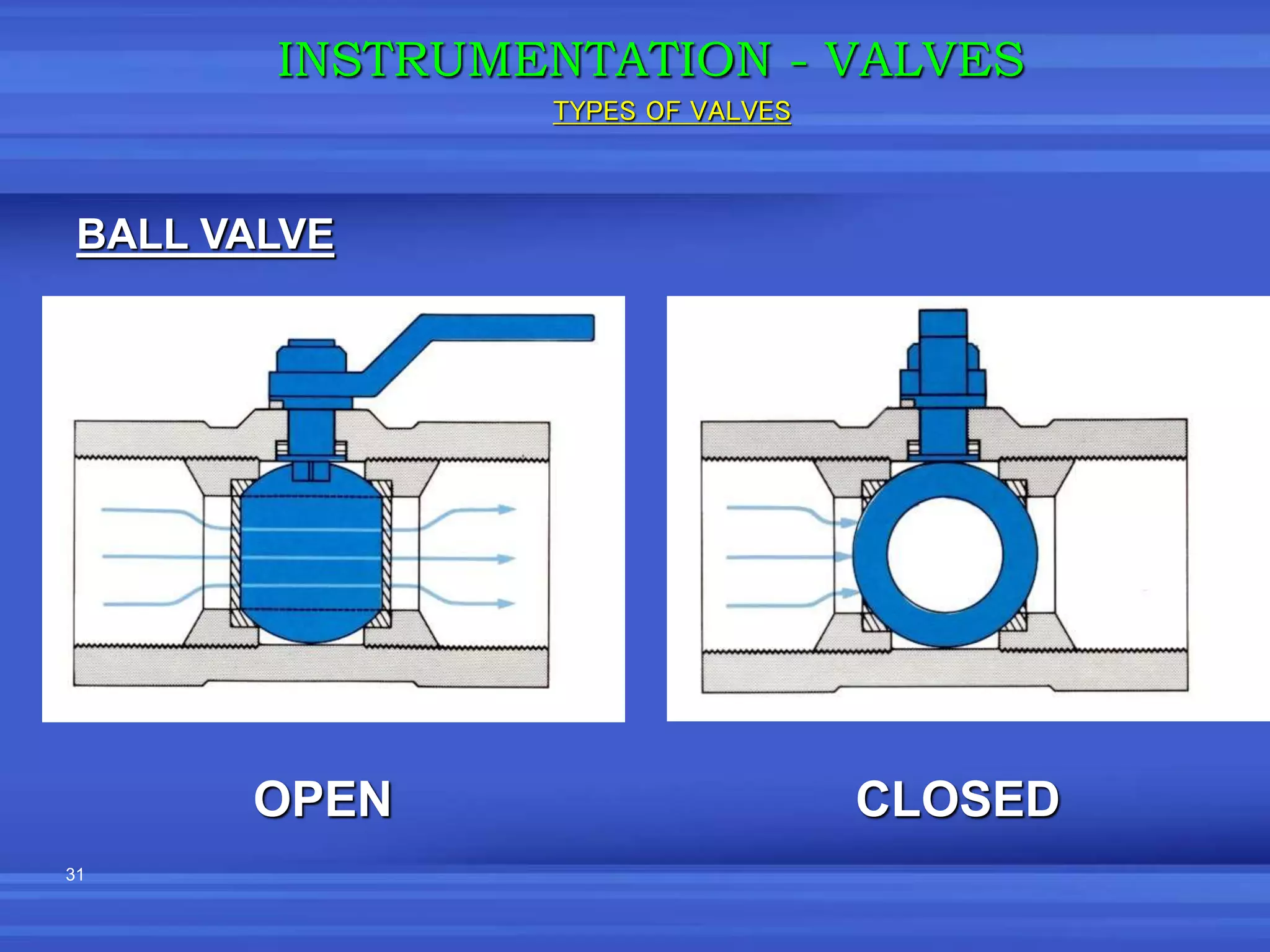
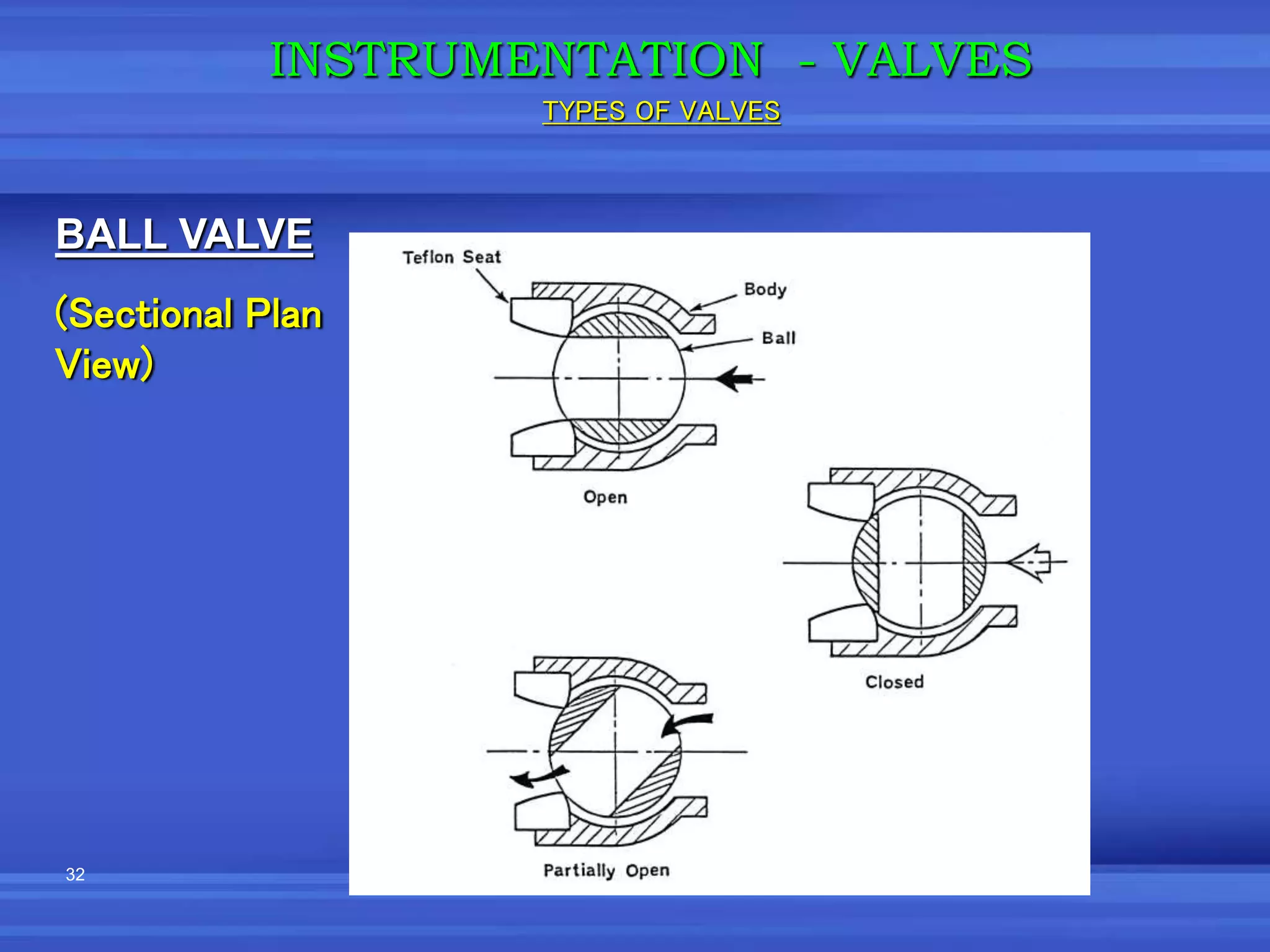
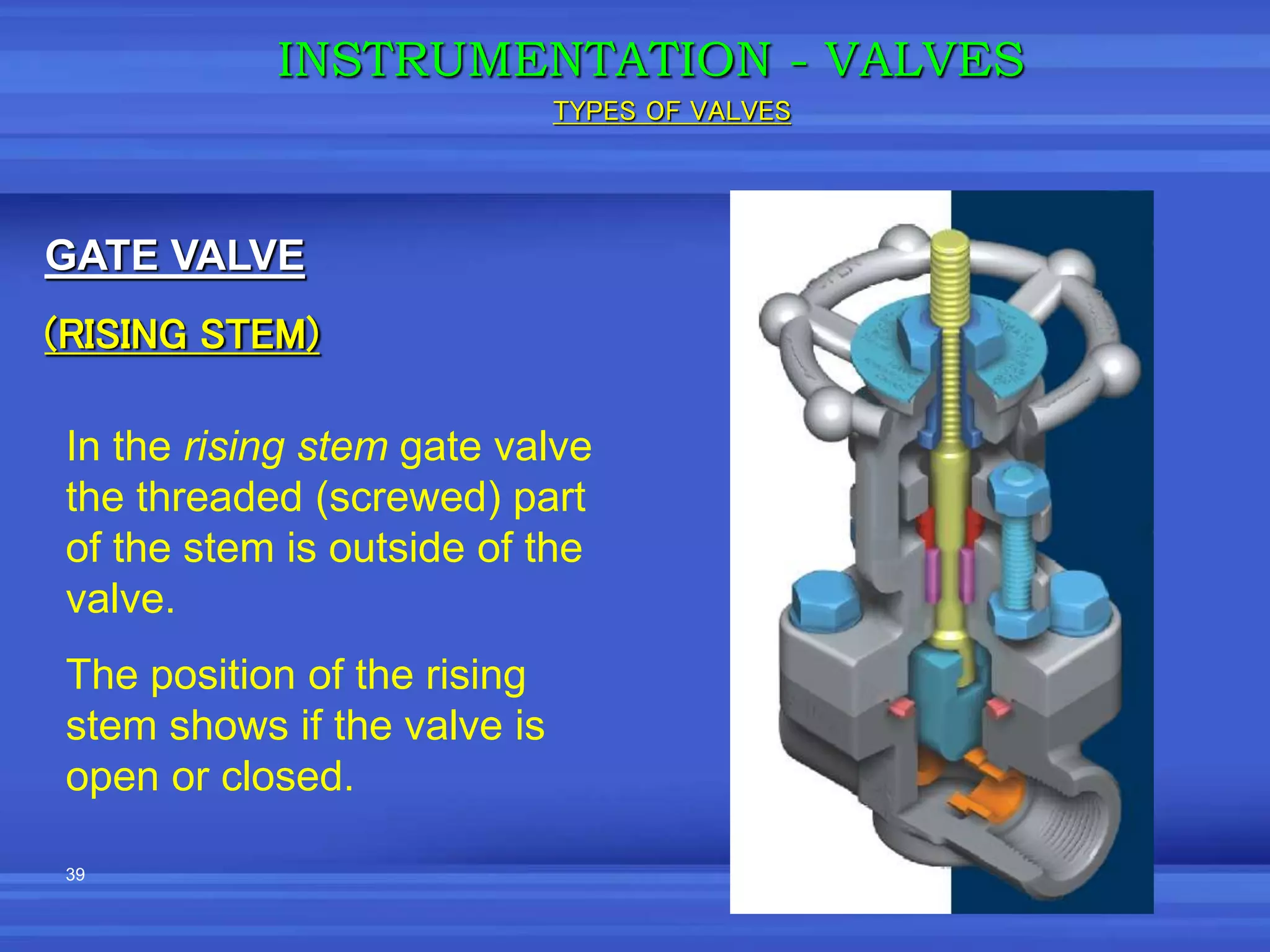
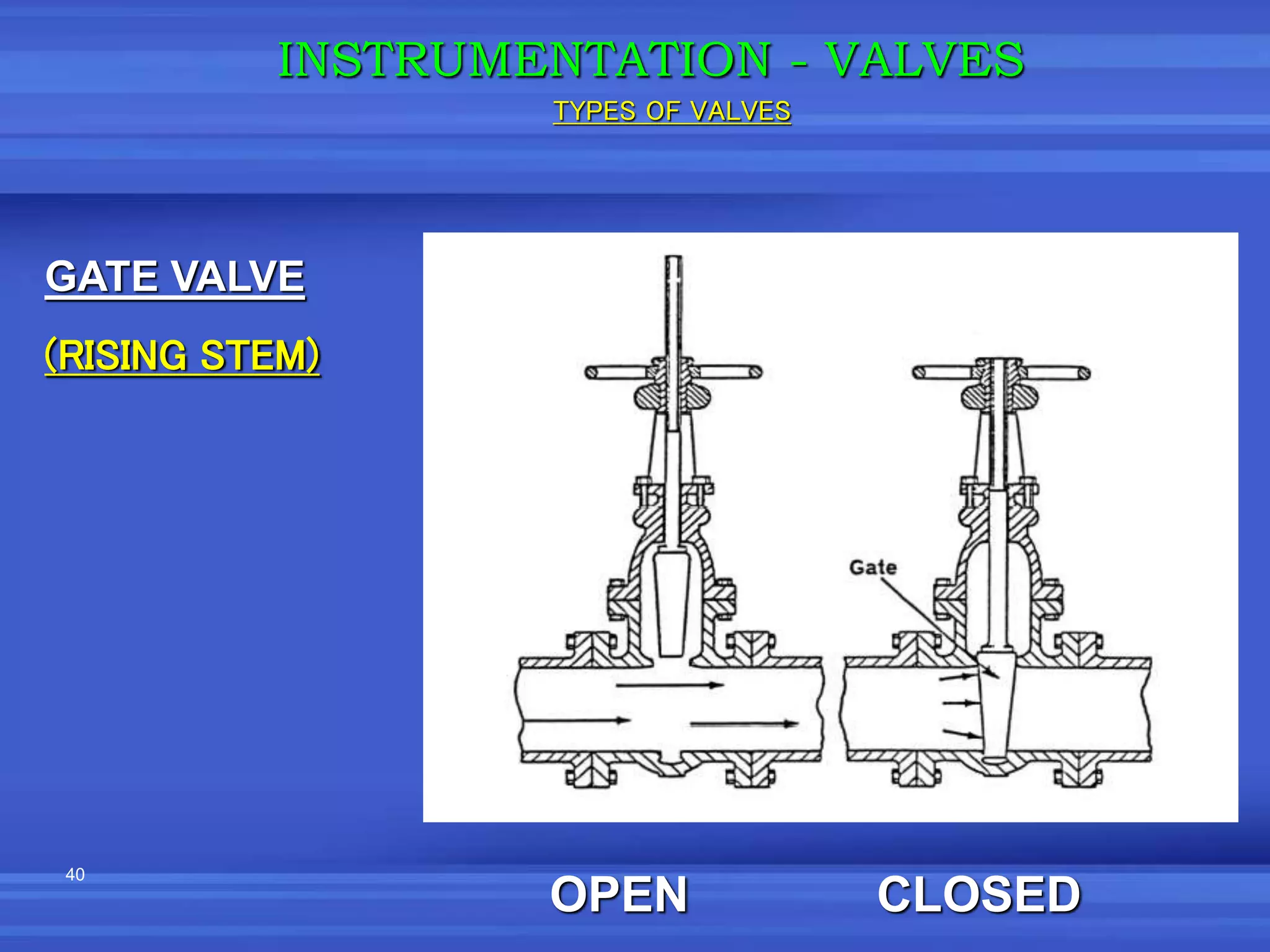
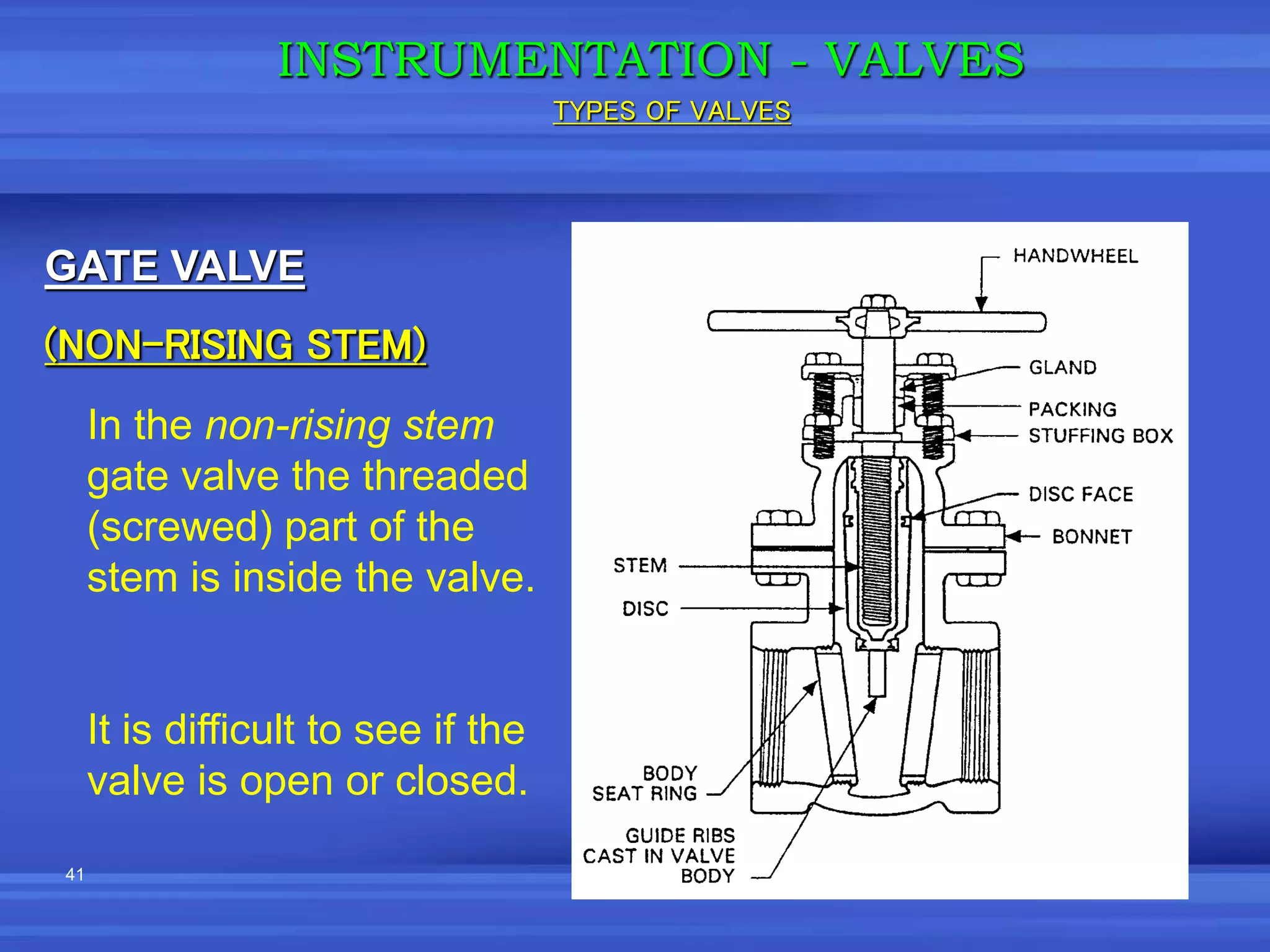
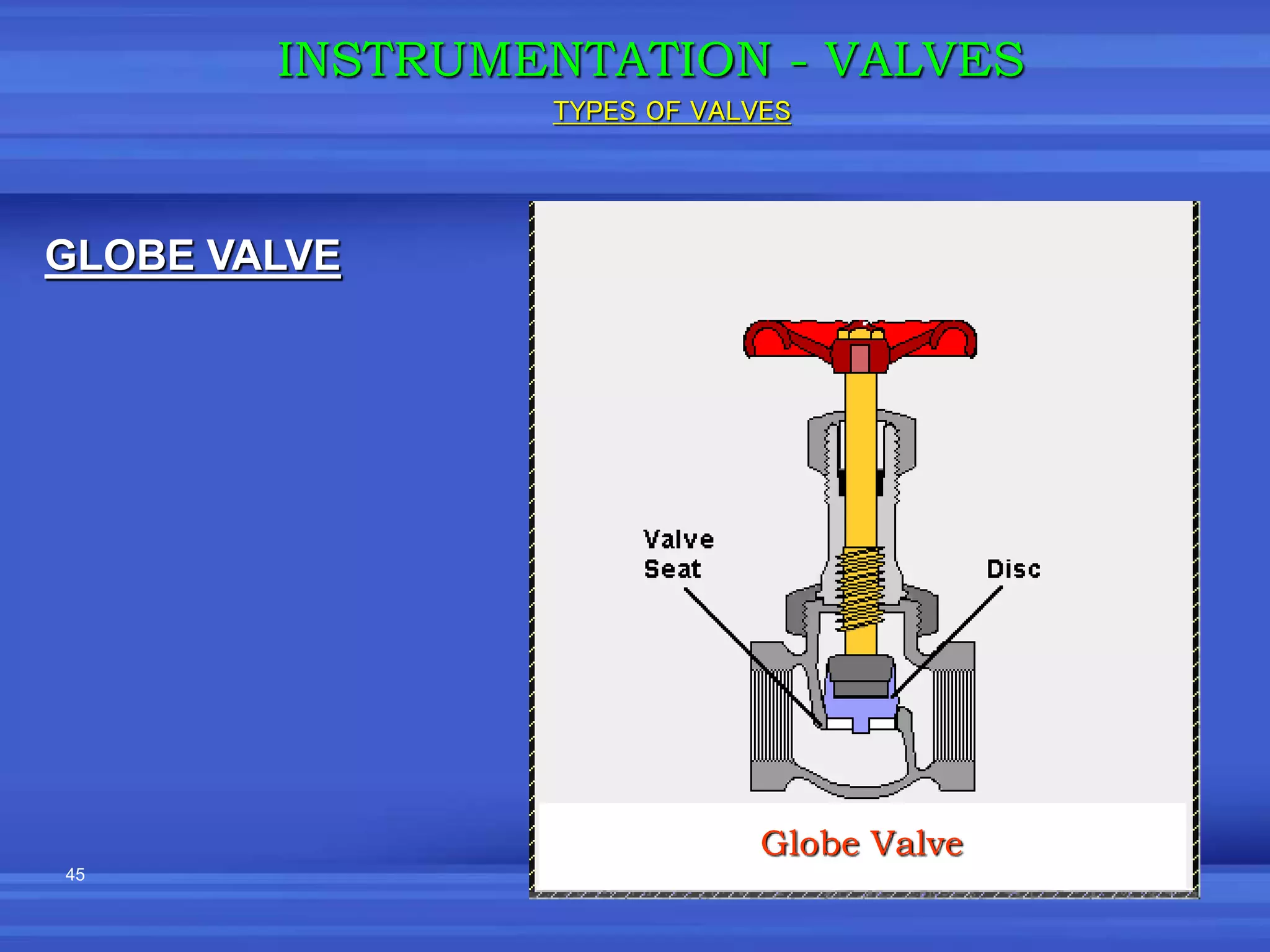
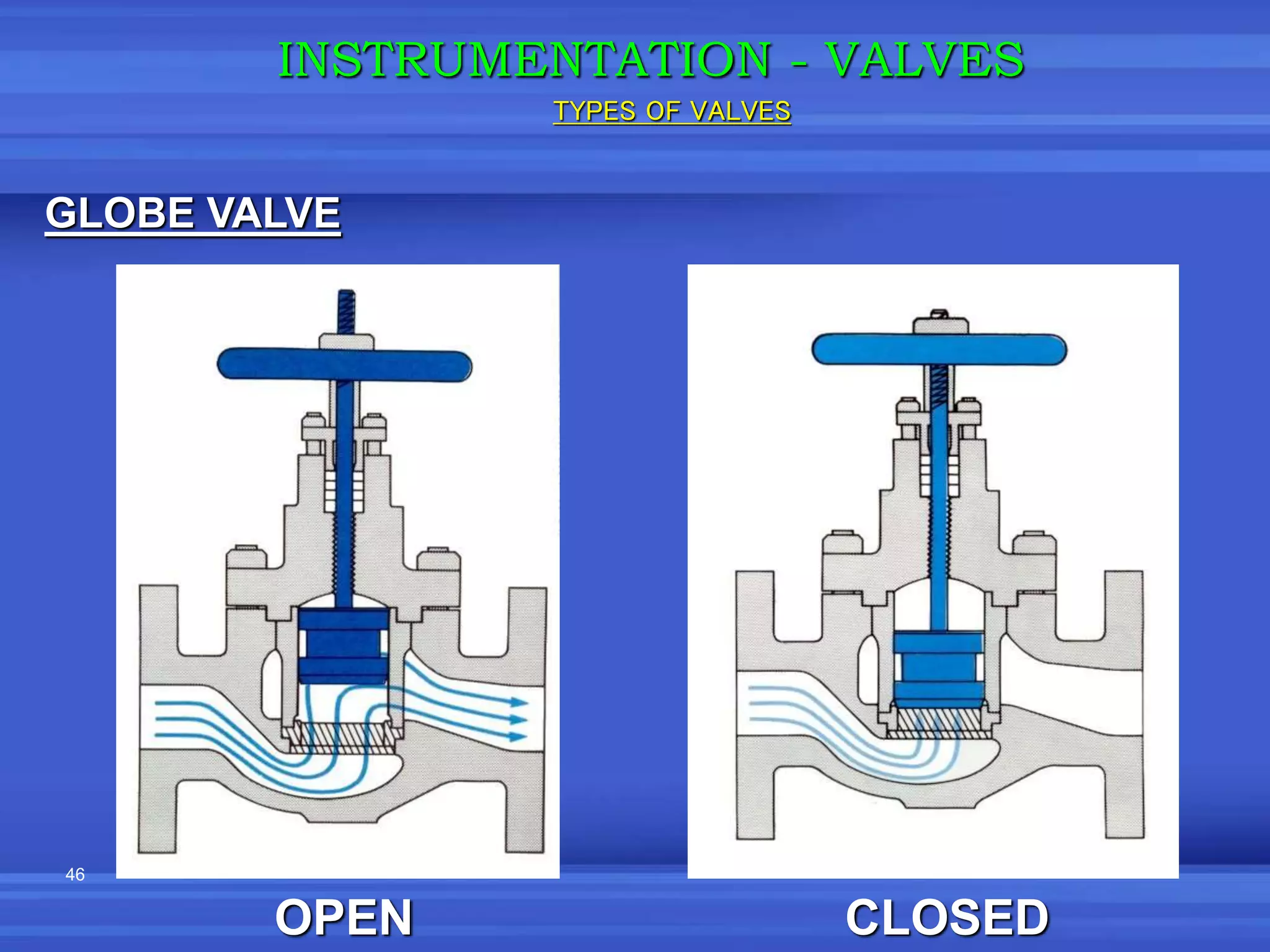
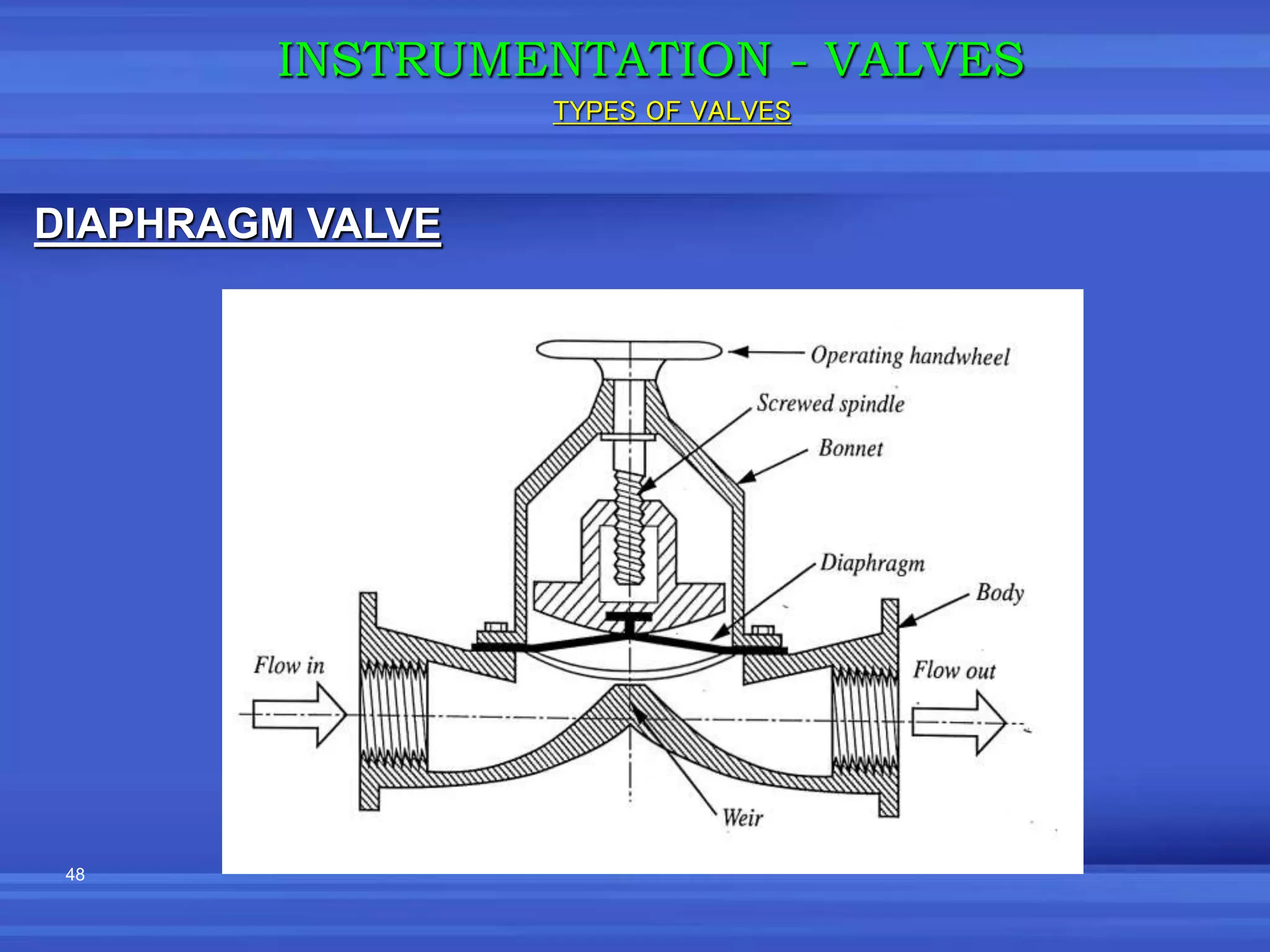
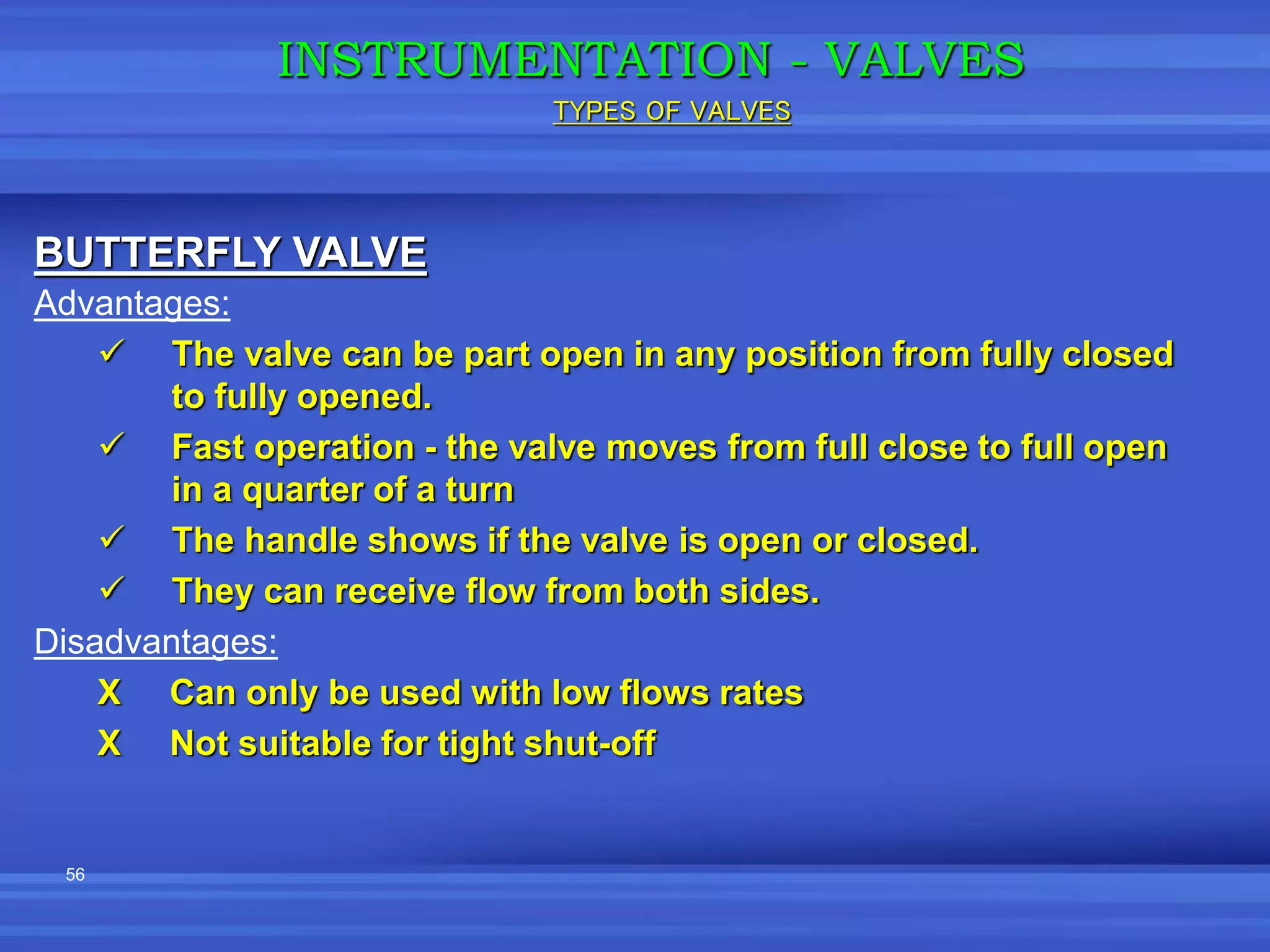
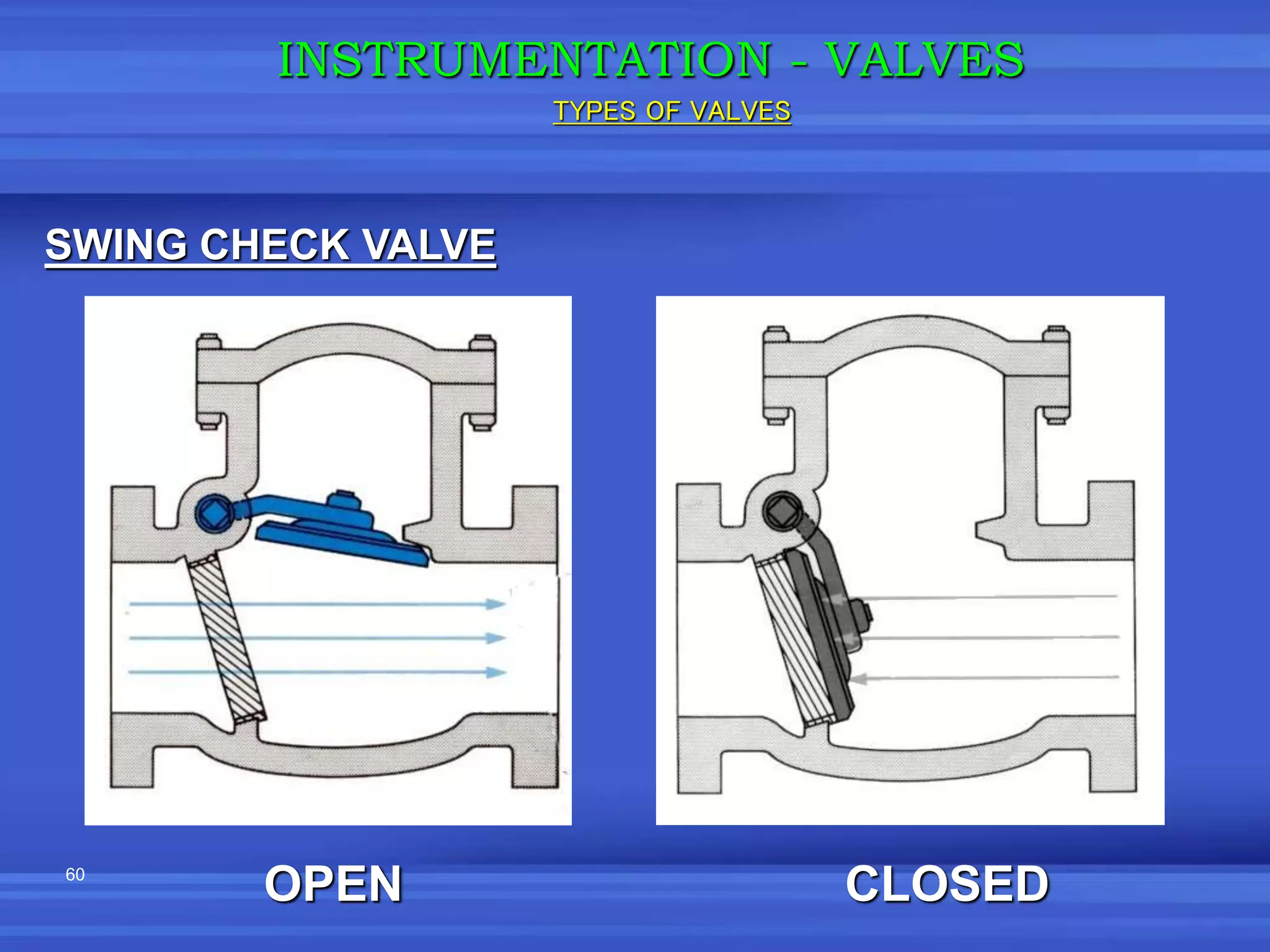
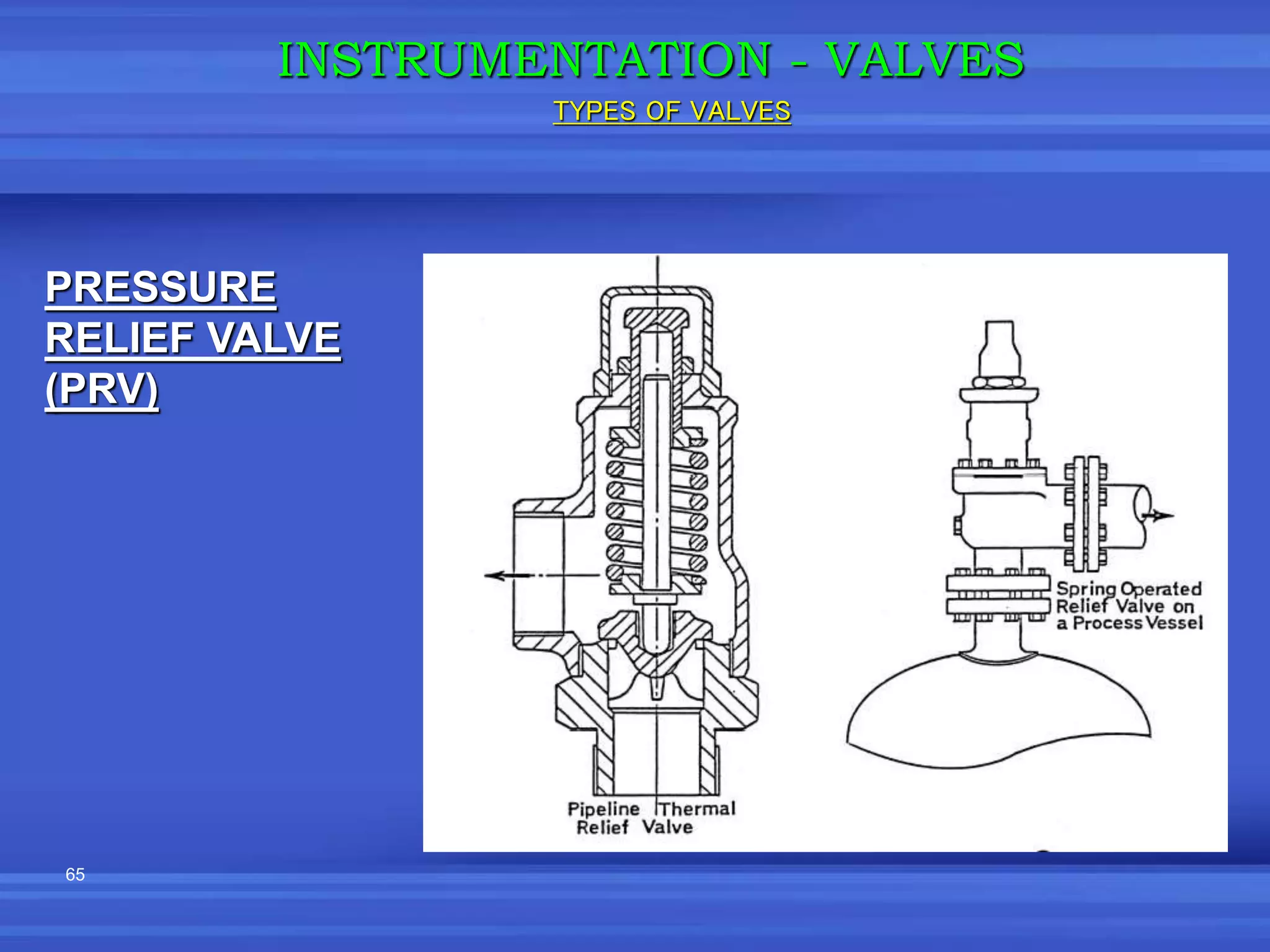
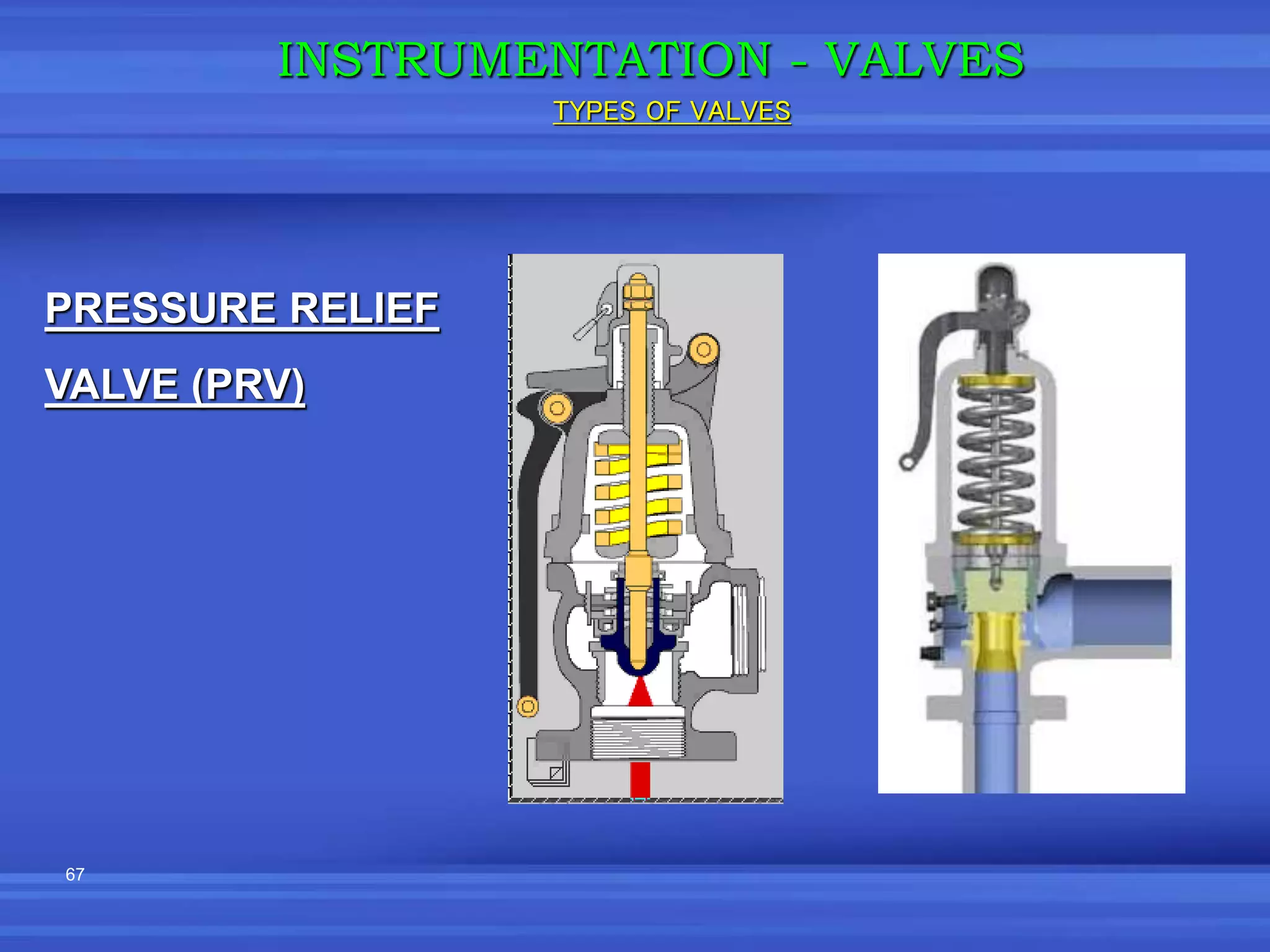
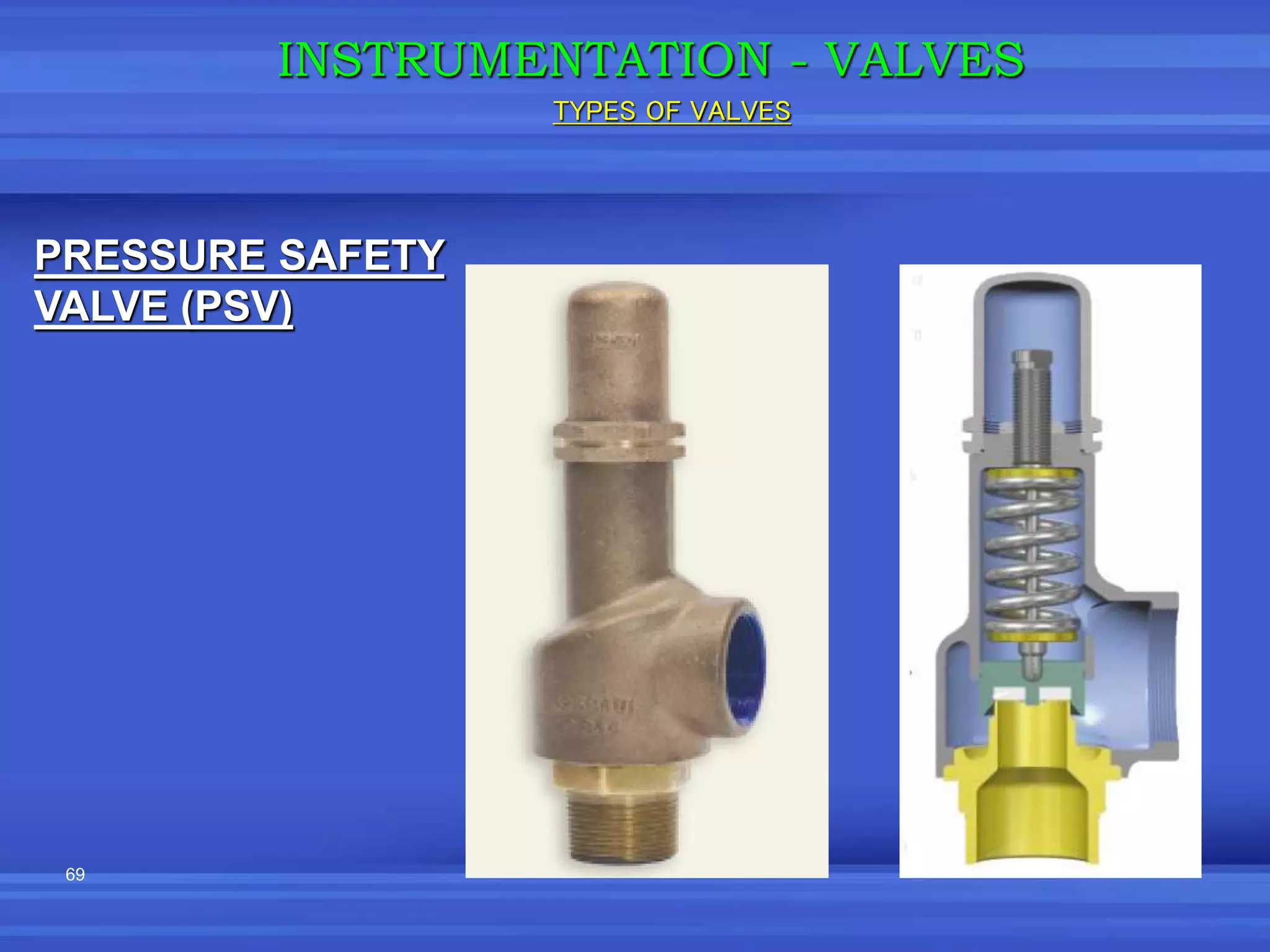
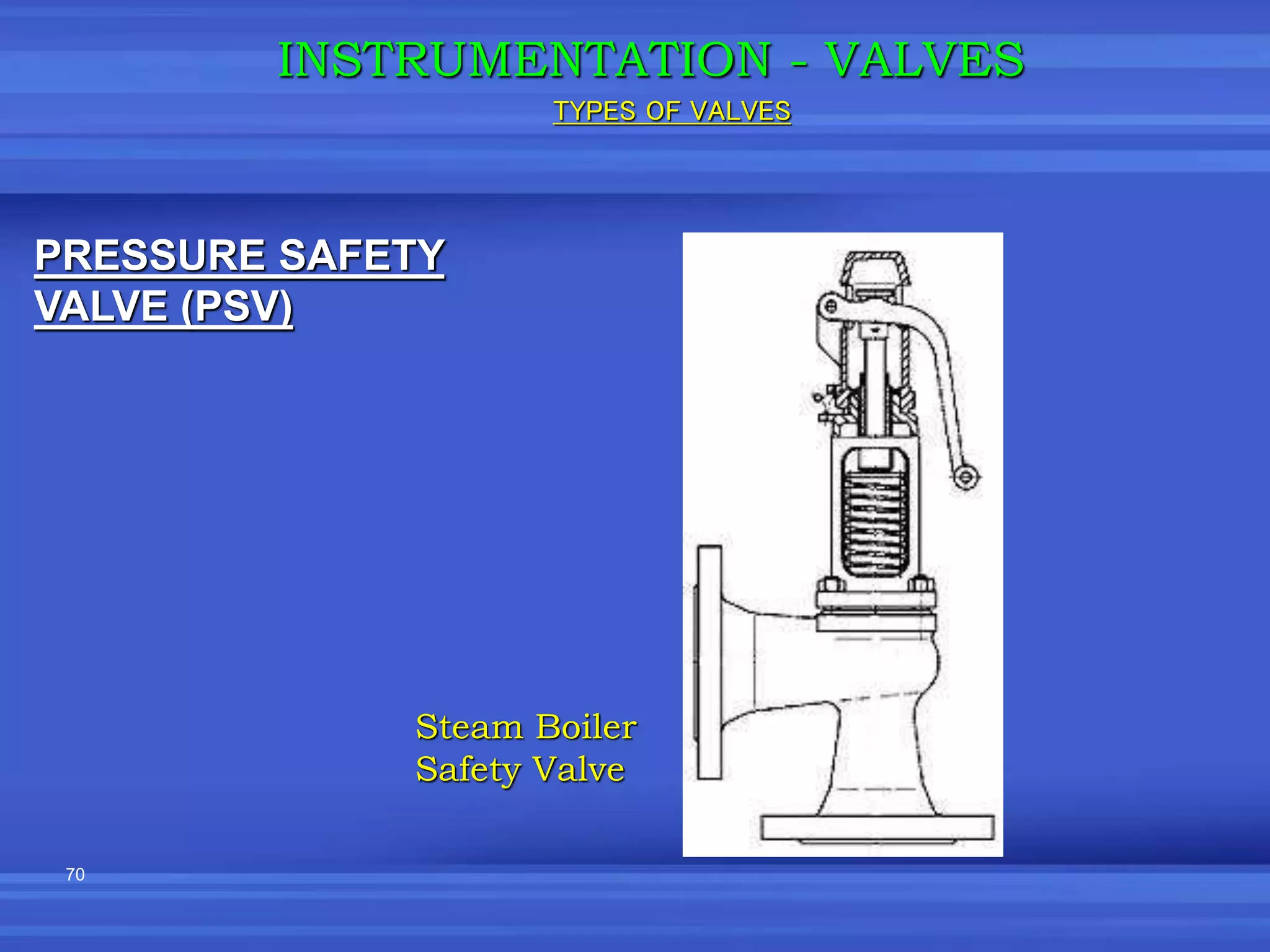
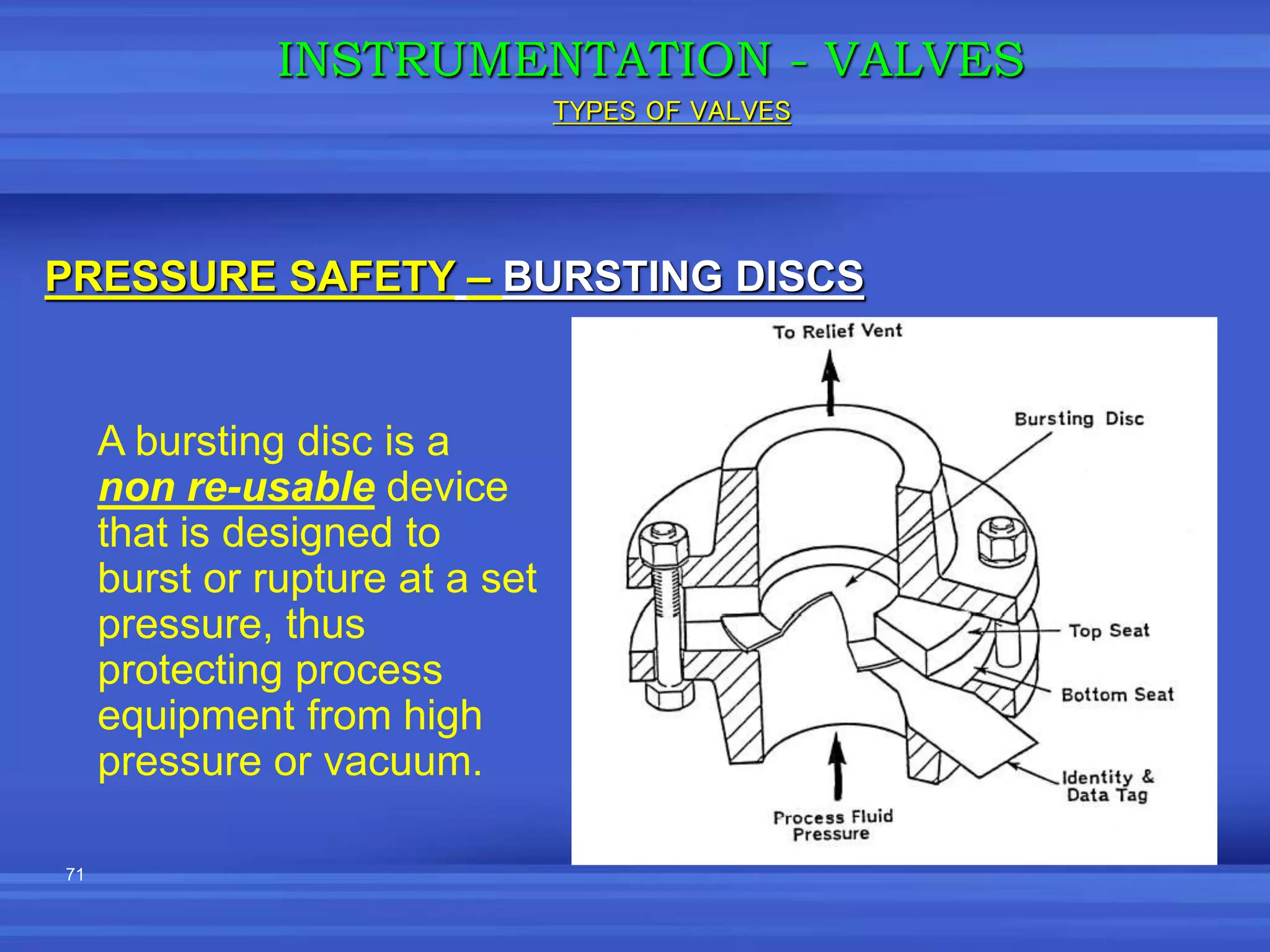
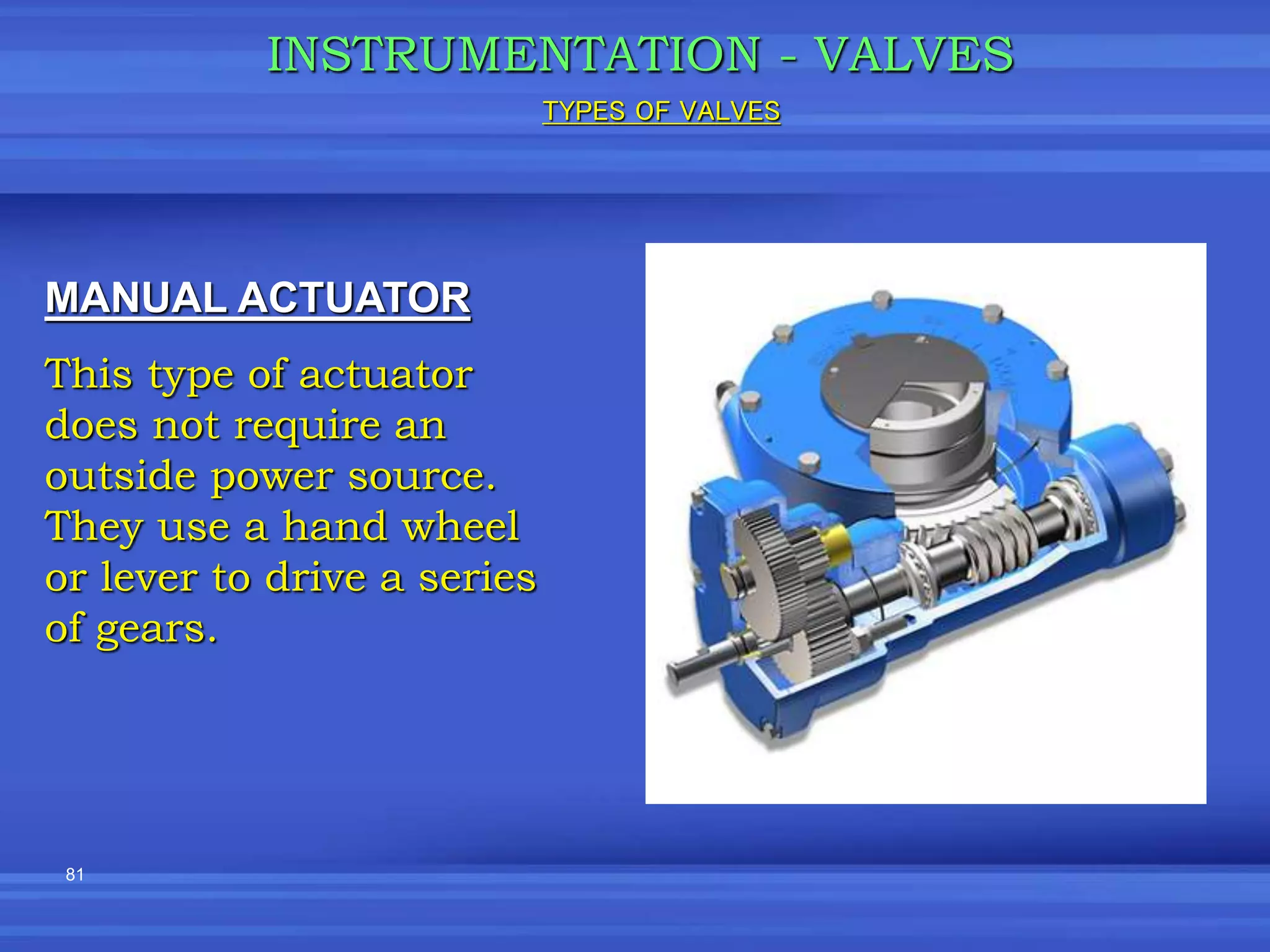
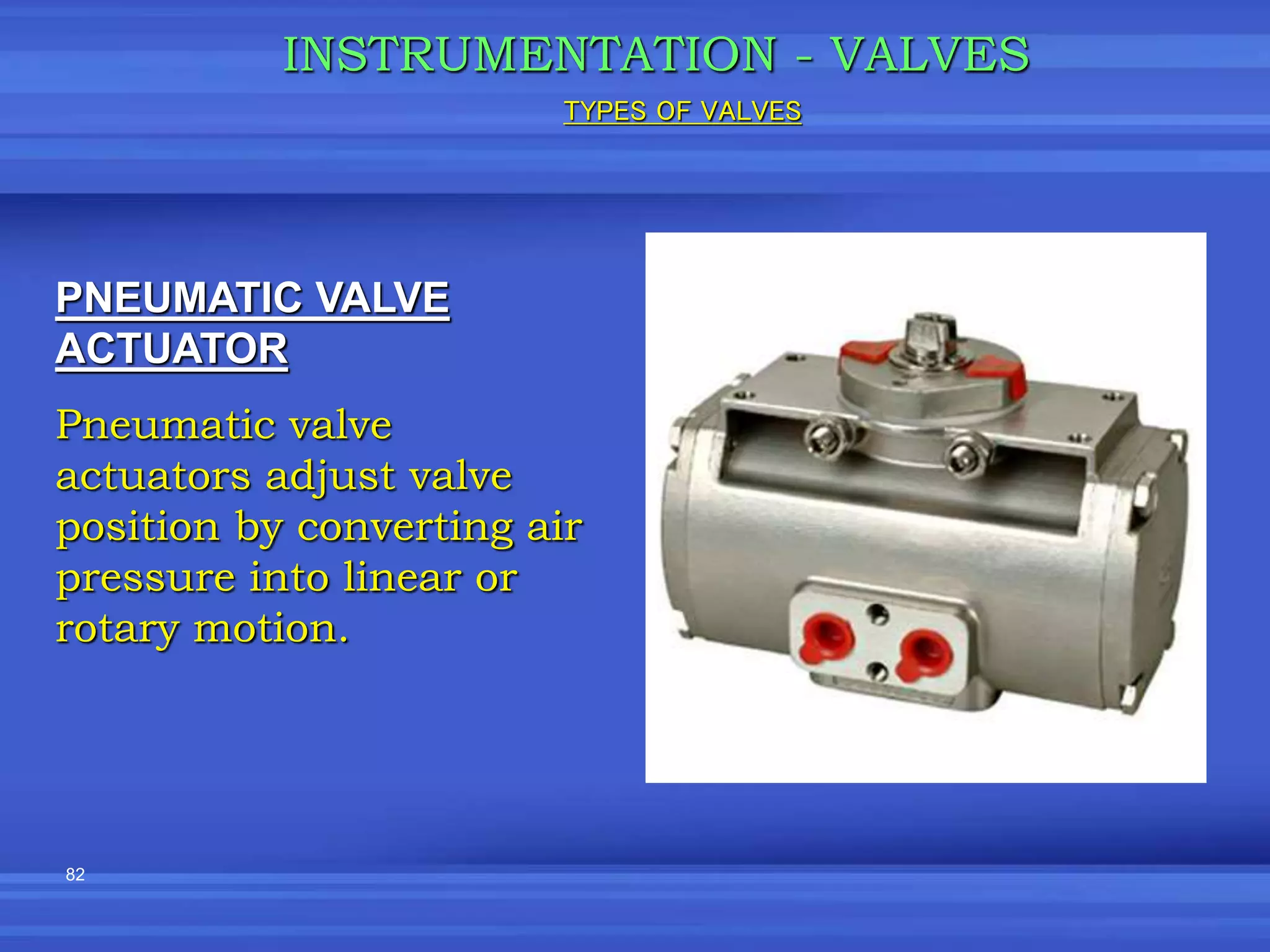
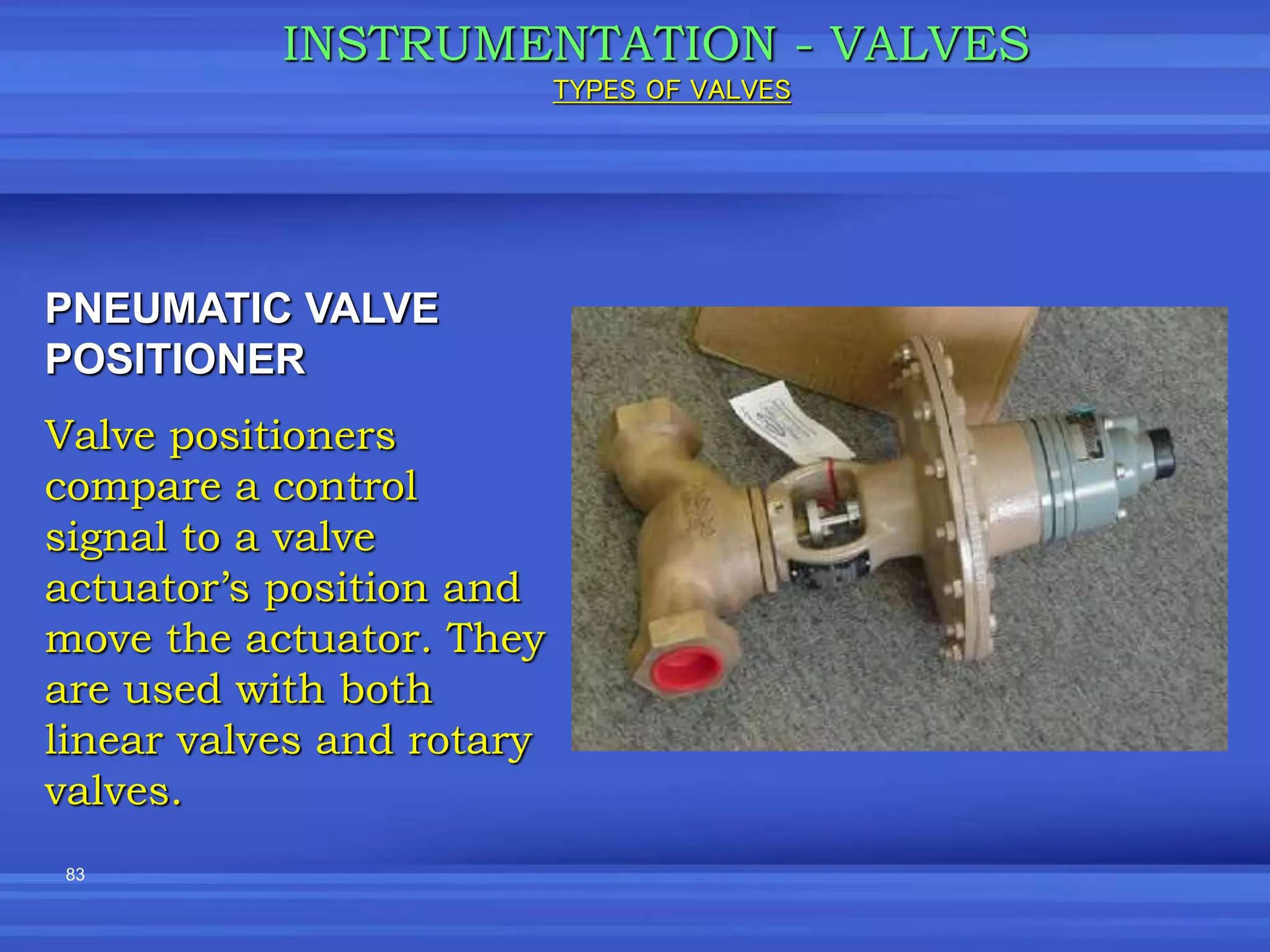
The document provides an overview of valves used in the petrochemical industry. It discusses the main types of valves including globe valves, butterfly valves, gate valves, plug valves, ball valves, diaphragm valves, needle valves, check valves, pressure relief valves, and pressure safety valves. It describes the purpose and characteristics of each valve type as well as considerations for valve selection such as diameter, pressure, temperature, and application. Actuators are also introduced as devices that supply force and motion to open and close valves.