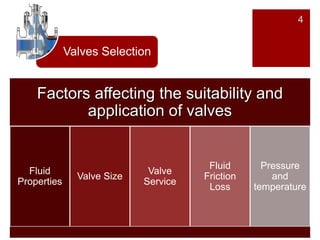
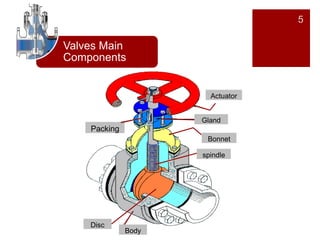
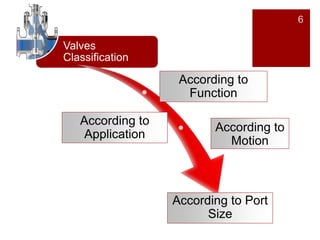
Valves are mechanical devices that control fluid flow through pipes. The document discusses the goals, definition, components, classifications, and materials of valves. Valves are classified according to motion, function, application, and port size. Common valve types include gate valves, globe valves, ball valves, plug valves, butterfly valves, and pinch valves. The document provides details on each type of valve including their definition, application, advantages, variations, and materials. It also provides tips on installation and maintenance of valves.