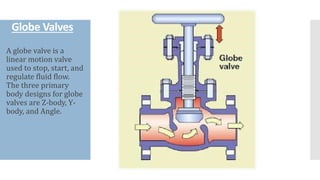
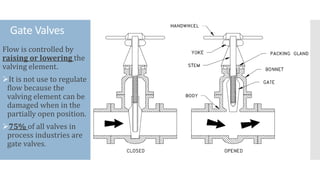
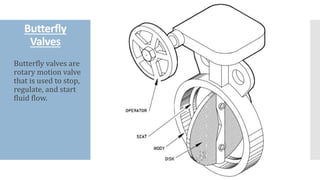
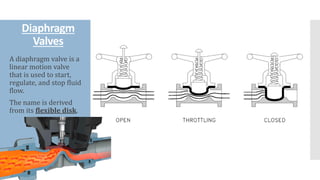
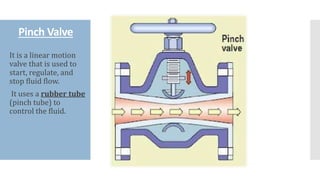
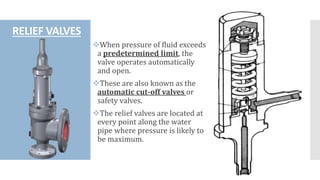
The document provides an overview of various types of valves used in fluid systems, detailing their functions, advantages, and disadvantages. Key categories include linear motion valves such as globe and diaphragm valves, and rotary motion valves such as ball and butterfly valves, each with distinct characteristics suitable for specific applications. Additionally, it discusses specialized valves like check, relief, and foot valves, emphasizing their roles in controlling fluid flow and pressure in industrial contexts.