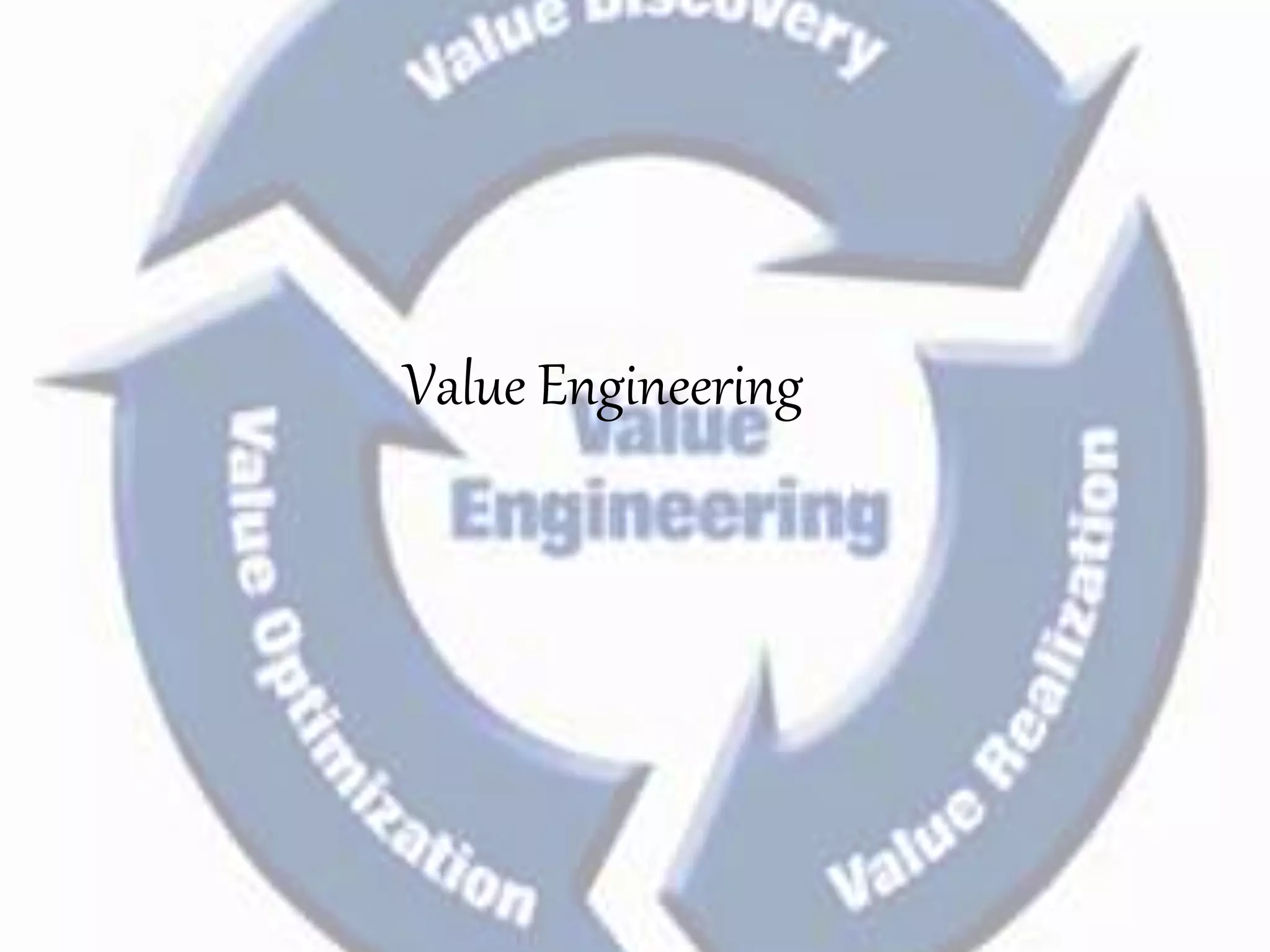
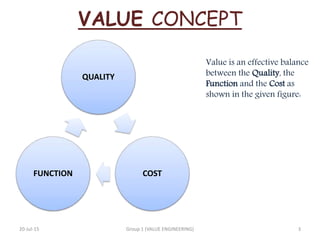
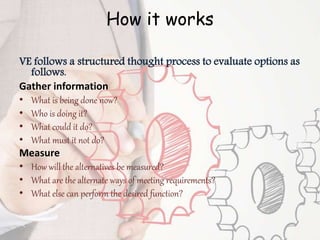
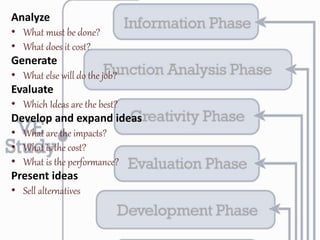
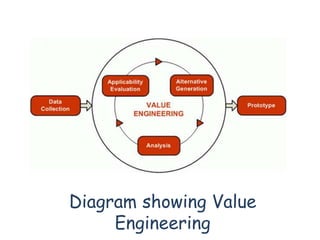
Value engineering is a systematic approach to reducing costs without compromising functionality. It focuses on identifying unnecessary costs and substituting cheaper alternatives. The value engineering process typically involves gathering information, generating alternatives, evaluating options, and presenting recommendations. Done effectively over several years, value engineering can significantly reduce construction costs for projects and homes, as demonstrated by a case study of a homebuilder that saved over $1 billion through value engineering methods.