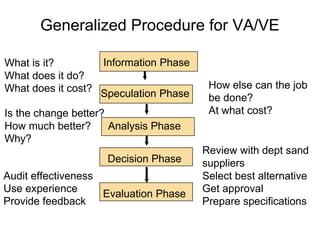
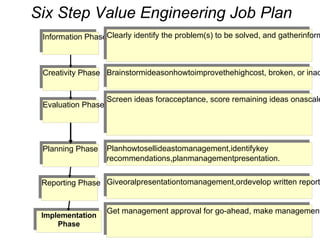
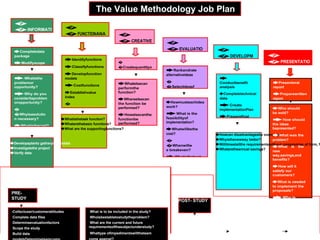
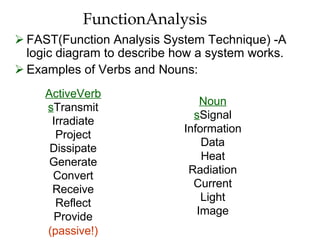
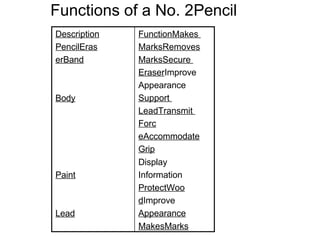
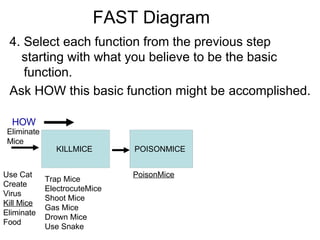
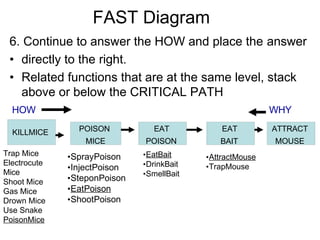
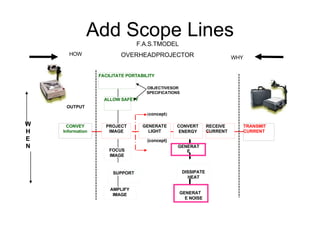
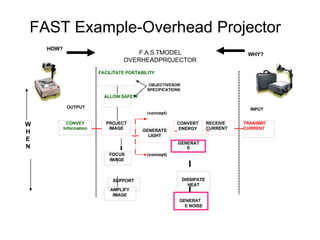
Definitions
🔜Value Engineering:-is a technique applied to identifying optimum value solutions during new product development.
🔜Value analysis:- is a technique applied to improving existing products, processesor services.
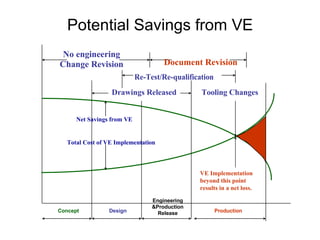
🔜The objective is usually to reduce cost, but may equally or simultaneously be to improve performance or quality.
-LDMiles
The Key Points of VA /VE
• Applying formal workplans.
• A team approach.
• Specific definition of functions.
• The simultaneous look at functions and costs.
• Control of the analysis process.
• Quantifiable results
What is VE?
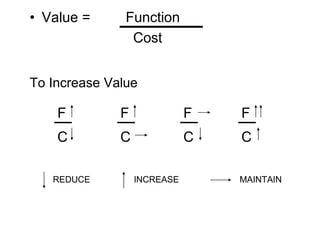
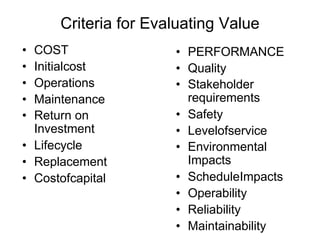
Value is the relationship between the defined function the customer requires and the costs incurred to provide that function.
– Cost Value
– Use Value
– Esteem Value
– Exchange Value
Value Engineering
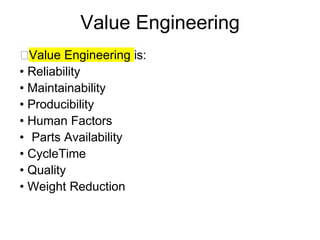
🔜Value Engineering is:
• Reliability
• Maintainability
• Producibility
• Human Factors
• Parts Availability
• CycleTime
• Quality
• Weight Reduction
Definitions
🔜Value Engineering:-is a technique applied to identifying optimum value solutions during new product development.
🔜Value analysis:- is a technique applied to improving existing products, processesor services.
🔜The objective is usually to reduce cost, but may equally or simultaneously be to improve performance or quality.
-LDMiles
The Key Points of VA /VE
• Applying formal workplans.
• A team approach.
• Specific definition of functions.
• The simultaneous look at functions and costs.
• Control of the analysis process.
• Quantifiable results
What is VE?
Value is the relationship between the defined function the customer requires and the costs incurred to provide that function.
– Cost Value
– Use Value
– Esteem Value
– Exchange Value
Value Engineering
🔜Value Engineering is:
• Reliability
• Maintainability
• Producibility
• Human Factors
• Parts Availability
• CycleTime
• Quality
• Weight Reduction
Definitions
🔜Value Engineering:-is a technique applied to identifying optimum value solutions during new product development.
🔜Value analysis:- is a technique applied to improving existing products, processesor services.
🔜The objective is usually to reduce cost, but may equally or simultaneously be to improve performance or quality.
-LDMiles
The Key Points of VA /VE
• Applying formal workplans.
• A team approach.
• Specific definition of functions.
• The simultaneous look at functions and costs.
• Control of the analysis process.
• Quantifiable results
What is VE?
Value is the relationship between the defined function the customer requires and the costs incurred to provide that function.
– Cost Value
– Use Value
– Esteem Value
– Exchange Value
Value Engineering
🔜Value Engineering is:
• Reliability
• Maintainability
• Producibility
• Human Factors
• Parts Availability
• CycleTime
• Quality
• Weight Reduction
Definitions
🔜Value Engineering:-is a technique applied to identifying optimum value solutions during new product development.
🔜Value analysis:- is a technique applied to improving existing products, pr