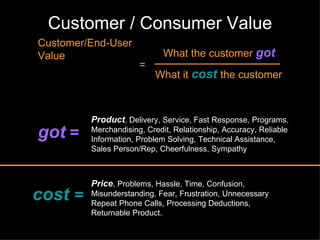
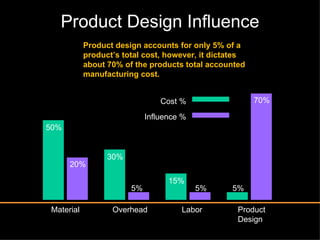
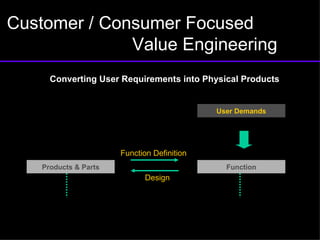
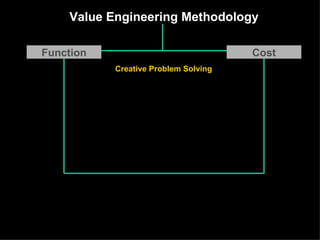
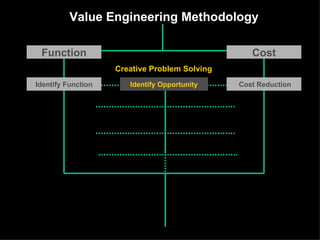
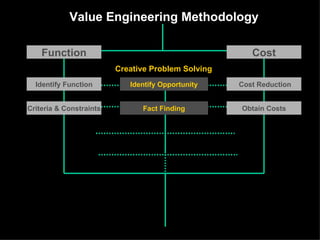
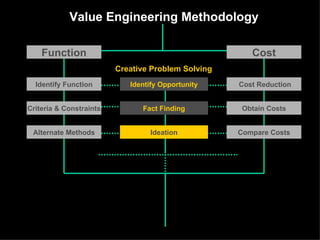
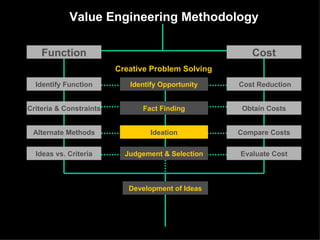
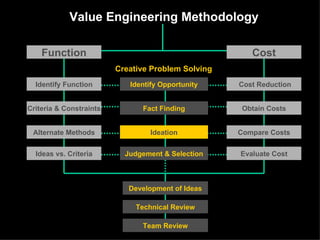
The document discusses improving product development through value engineering, emphasizing collaboration, exploration, and innovation focused on customer value. It highlights the significance of product design in influencing manufacturing costs, and presents a structured methodology for problem-solving and cost reduction. The approach aims to enhance performance and competitiveness while minimizing risks in product design and delivery.