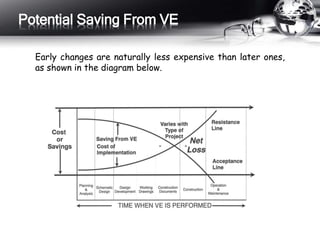
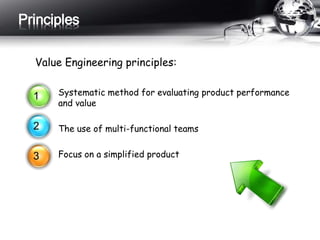
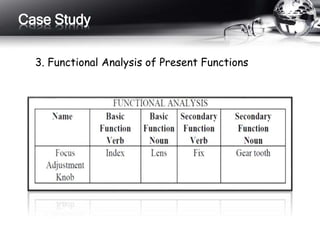
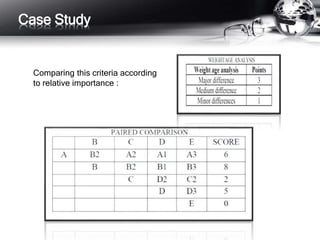
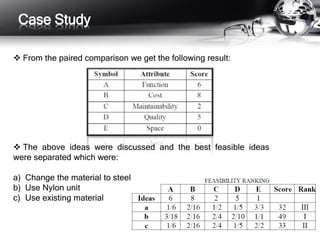
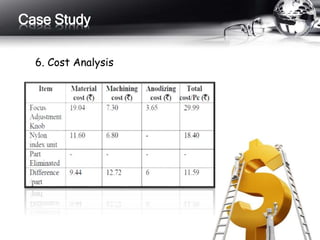
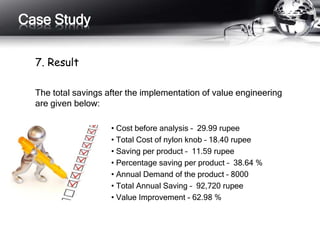
This document outlines the history and principles of value engineering. It discusses how value engineering seeks to balance cost, reliability, and performance. It describes the typical 8-step job plan process for conducting a value engineering study, including orientation, information gathering, functional analysis, creativity, evaluation, development, presentation, and implementation. Finally, it provides a case study example of applying value engineering to optimize the design of a focus adjustment knob for a slit lamp microscope. The redesign focused on changing the material and production process, resulting in a 38.64% cost savings.