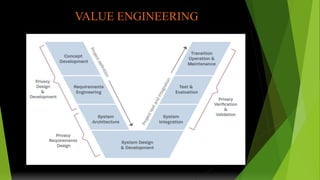
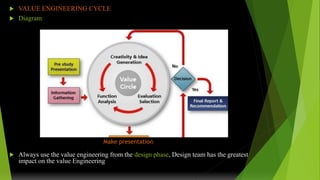
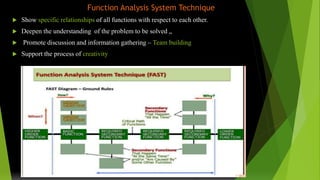
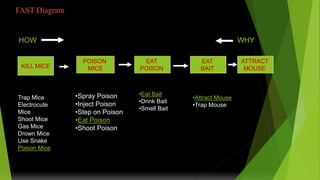
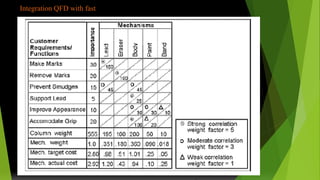
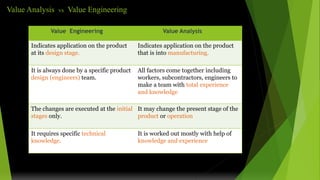
Value engineering began in 1947 as a technique to reduce costs. It focuses on the function of a product rather than its design or materials. The value engineering process involves understanding customer needs and functions, then generating and evaluating ideas to provide the necessary functions at the lowest cost without compromising quality. It uses tools like FAST (Function Analysis System Technique) diagrams to break down functions and identify opportunities. The goal is not just cost cutting but finding the most cost-effective solution to meet the desired functions. The value engineering cycle involves information gathering, creativity, evaluation, planning, reporting, and implementation phases.